Final ID: Su3100
The Strain of Pregnancy: Markers of Cardiac Strain and Inflammation in Pregnancies with and without Hypertension – a Case Control Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Pregnancy poses physiologic changes that can precipitate severe or fatal cardiovascular events among women with hypertension (HTN). Understanding mechanisms by which delivery might contribute to these events in women with HTN is critical for prevention.
Aims: To examine trends in markers of cardiac wall strain or inflammation measured via N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) in pregnancies with and without HTN.
Methods: In a prospective, 1:1 case-control design, we enrolled pregnant women with and without HTN between 24-32 weeks gestation (2019-2022). HTN was defined by a clinician diagnosis of chronic or gestational HTN or a baseline blood pressure (BP) ≥140/90 mm Hg. The control group (no HTN) had a systolic BP <120 mm Hg and no diagnosis of HTN. Serum was collected at baseline, pre-delivery (at the delivery admission), and postpartum day 1. We used mixed effects tobit models to compare log-transformed NTproBNP and hs-CRP, across HTN groups and over time, adjusted for age and BMI.
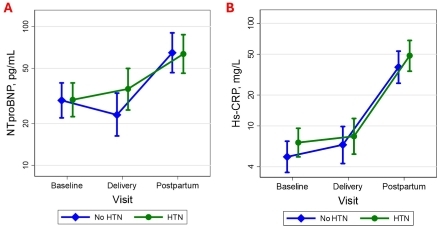
Results: The mean age of the HTN group (N=38) was 33.6 (SD 5.4) vs. 30.3 (5.8) years for the no HTN group (N=38). Mean (SD) baseline BP was 131.1 (14.7)/88.2 (13.5) for the HTN group and 110.1 (7.2)/70.9 (8.2) mm Hg for no HTN. At baseline, NTproBNP was 29.6 (4.2) in the HTN group and 29.5 (4.4) pg/mL in the no HTN group (Figure). Compared to baseline, there was a non-significant change in NTproBNP pre-delivery and an increase at postpartum for both groups (114% [49-208%] for HTN, 120% [51-219%] for no HTN). Baseline hs-CRP was 6.9 (1.1) in the HTN group and 5.1 (0.8) mg/L in the no HTN group. Compared to baseline, there was a non-significant change in hs-CRP pre-delivery and an increase at postpartum for both groups (550% [337-867%] for HTN, 662% [407-1050%] for no HTN). Across all time points, there were no significant differences in NTproBNP and hs-CRP between the two groups.
Conclusion: While HTN was not associated with greater cardiac wall strain or inflammation compared to no HTN, delivery alone led to an approximately 2-fold increase in cardiac wall strain and 7–fold increase in inflammation from mid-pregnancy to immediate postpartum.
Aims: To examine trends in markers of cardiac wall strain or inflammation measured via N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) in pregnancies with and without HTN.
Methods: In a prospective, 1:1 case-control design, we enrolled pregnant women with and without HTN between 24-32 weeks gestation (2019-2022). HTN was defined by a clinician diagnosis of chronic or gestational HTN or a baseline blood pressure (BP) ≥140/90 mm Hg. The control group (no HTN) had a systolic BP <120 mm Hg and no diagnosis of HTN. Serum was collected at baseline, pre-delivery (at the delivery admission), and postpartum day 1. We used mixed effects tobit models to compare log-transformed NTproBNP and hs-CRP, across HTN groups and over time, adjusted for age and BMI.
Results: The mean age of the HTN group (N=38) was 33.6 (SD 5.4) vs. 30.3 (5.8) years for the no HTN group (N=38). Mean (SD) baseline BP was 131.1 (14.7)/88.2 (13.5) for the HTN group and 110.1 (7.2)/70.9 (8.2) mm Hg for no HTN. At baseline, NTproBNP was 29.6 (4.2) in the HTN group and 29.5 (4.4) pg/mL in the no HTN group (Figure). Compared to baseline, there was a non-significant change in NTproBNP pre-delivery and an increase at postpartum for both groups (114% [49-208%] for HTN, 120% [51-219%] for no HTN). Baseline hs-CRP was 6.9 (1.1) in the HTN group and 5.1 (0.8) mg/L in the no HTN group. Compared to baseline, there was a non-significant change in hs-CRP pre-delivery and an increase at postpartum for both groups (550% [337-867%] for HTN, 662% [407-1050%] for no HTN). Across all time points, there were no significant differences in NTproBNP and hs-CRP between the two groups.
Conclusion: While HTN was not associated with greater cardiac wall strain or inflammation compared to no HTN, delivery alone led to an approximately 2-fold increase in cardiac wall strain and 7–fold increase in inflammation from mid-pregnancy to immediate postpartum.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparative Study Of Social Determinants, Hypertension, And Life Essential Factors In Alabama And Colorado From The 2021 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System
Chukwunyere Chibuike, Owuor Kevin
Advanced maternal age and association with major adverse cardiovascular events from NHANES from 1999 to 2018Mehta Adhya, Honigberg Michael, Kennedy Jamie, Spitz Jared, Sharma Garima, Agboola Olayinka, Satti Danish Iltaf, Harrington Colleen, Scott Nandita, Sarma Amy, Saad Antonio, Sullivan Scott, Epps Kelly