Final ID: P-120
Statewide burden of Atrial fibrillation and flutter attributable to High Systolic Blood Pressure in the United States from 1990-2021: A Comparative and Consistent Analysis
Abstract Body: Background: In the United States (US), the burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) and flutter, marked by substantial morbidity, mortality, and economic costs, is projected at approximately $6.65 billion annually, highlighting its growing concern. This study highlights the consistent and comparable statewide burden of AFib and Flutter attributable to high systolic blood pressure (HBP) over the last three decades, including during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, a period that posed significant healthcare management challenges for non-COVID-19 cases.
Method: Using Global Burden of Disease study 2021, we estimated AFib and flutter deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), Years lived with disability (YLDs), years of life lost (YLLs) by age, sex, year and location across the US from 1990-2021.
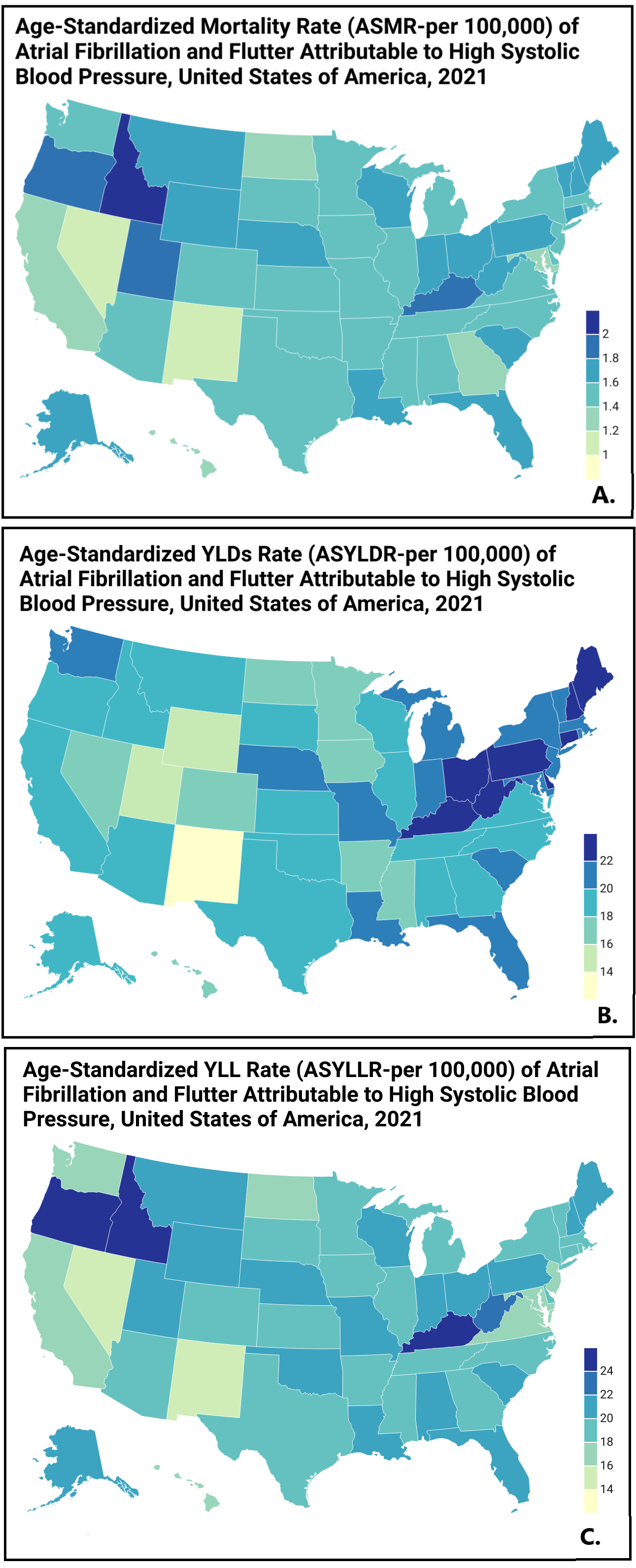
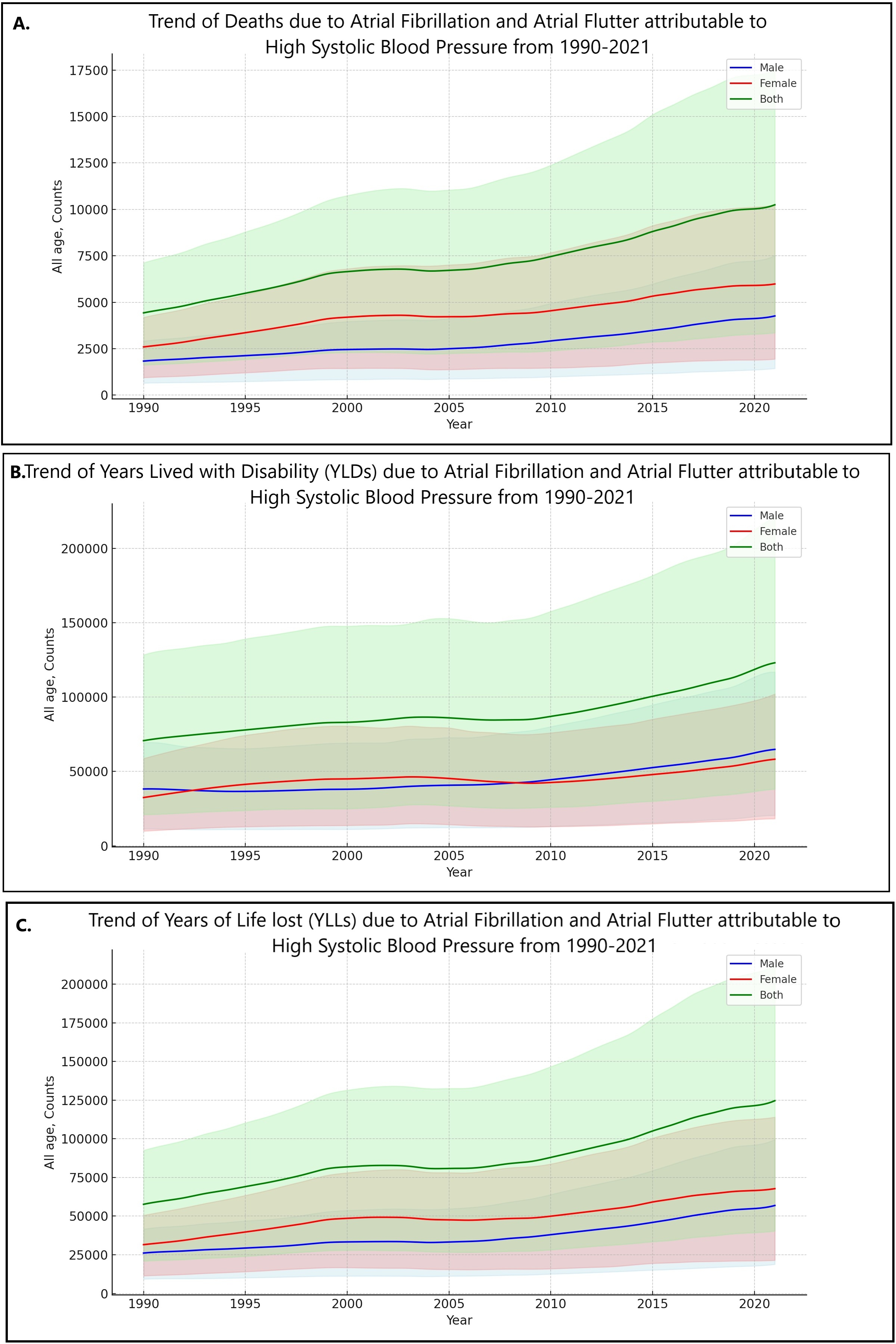
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in deaths due to AFib and flutter soared by 131% (95% uncertainty interval: 94%-161%), YLDs increased by 74% (33%-123%), and YLLs escalated by 116% (85%-139%). The age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) rose by 16% (3%-30%), with a 12% increase in the age-standardized YLD rate from 1990-2021. Notably, Idaho experienced the highest rise in ASMR at 58% (25%-90%), followed by Utah at 47% (16%-79%), while the most significant decreases occurred in the District of Columbia (12%) and Hawaii (1%). In 2021, the highest mortality was among those aged 90–94 years with 2,510 deaths, the most YLDs in the 80-84 age group at 22,164, and the greatest YLLs in the 85-89 age bracket at 21,902. Gender-wise, the death count increase was slightly higher in males (133%) compared to females (131%), with discrepancies also observed in DALYs (97% vs 89%) and YLDs (79% vs 70%).
Conclusions: Deaths due to Afin and flutter attributable to high blood pressure (HBP) constituted 29.04% of all related deaths in 2021. To mitigate this growing burden, it is crucial to implement comprehensive prevention measures. Campaigns aimed at controlling high blood pressure through lifestyle modifications, regular screening, and patient education can be effective. Engaging public stakeholders, policymakers, and clinicians in formulating and endorsing policies that promote heart health, enhance access to care, and improve treatment adherence is essential for reducing the incidence and impact of AFib and flutter.
Method: Using Global Burden of Disease study 2021, we estimated AFib and flutter deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), Years lived with disability (YLDs), years of life lost (YLLs) by age, sex, year and location across the US from 1990-2021.
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total percentage change (TPC) in deaths due to AFib and flutter soared by 131% (95% uncertainty interval: 94%-161%), YLDs increased by 74% (33%-123%), and YLLs escalated by 116% (85%-139%). The age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) rose by 16% (3%-30%), with a 12% increase in the age-standardized YLD rate from 1990-2021. Notably, Idaho experienced the highest rise in ASMR at 58% (25%-90%), followed by Utah at 47% (16%-79%), while the most significant decreases occurred in the District of Columbia (12%) and Hawaii (1%). In 2021, the highest mortality was among those aged 90–94 years with 2,510 deaths, the most YLDs in the 80-84 age group at 22,164, and the greatest YLLs in the 85-89 age bracket at 21,902. Gender-wise, the death count increase was slightly higher in males (133%) compared to females (131%), with discrepancies also observed in DALYs (97% vs 89%) and YLDs (79% vs 70%).
Conclusions: Deaths due to Afin and flutter attributable to high blood pressure (HBP) constituted 29.04% of all related deaths in 2021. To mitigate this growing burden, it is crucial to implement comprehensive prevention measures. Campaigns aimed at controlling high blood pressure through lifestyle modifications, regular screening, and patient education can be effective. Engaging public stakeholders, policymakers, and clinicians in formulating and endorsing policies that promote heart health, enhance access to care, and improve treatment adherence is essential for reducing the incidence and impact of AFib and flutter.
More abstracts on this topic:
A durable reduction in blood pressure by ultrasound renal denervation: A real-world, single center experience
King Jordan, Gharib Wissam
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertensionSchlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael