Final ID: P-164
Global Statistics of Hypertensive Heart Disease and its Trend from 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Global Analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract Body: Background: Hypertensive Heart Disease (HHD) ranks as the 11th leading cause of death worldwide. The management of metabolic diseases, including hypertension and diabetes, has been severely impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study represents the first comprehensive and comparative assessment of the global burden of HHD, spanning the last three decades and including the initial two years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method: Utilizing the Global Burden of Disease framework, we analyzed the prevalence, incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years lived with disability (YLDs) of HHD across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021. Our analysis was stratified by age, sex, and location.
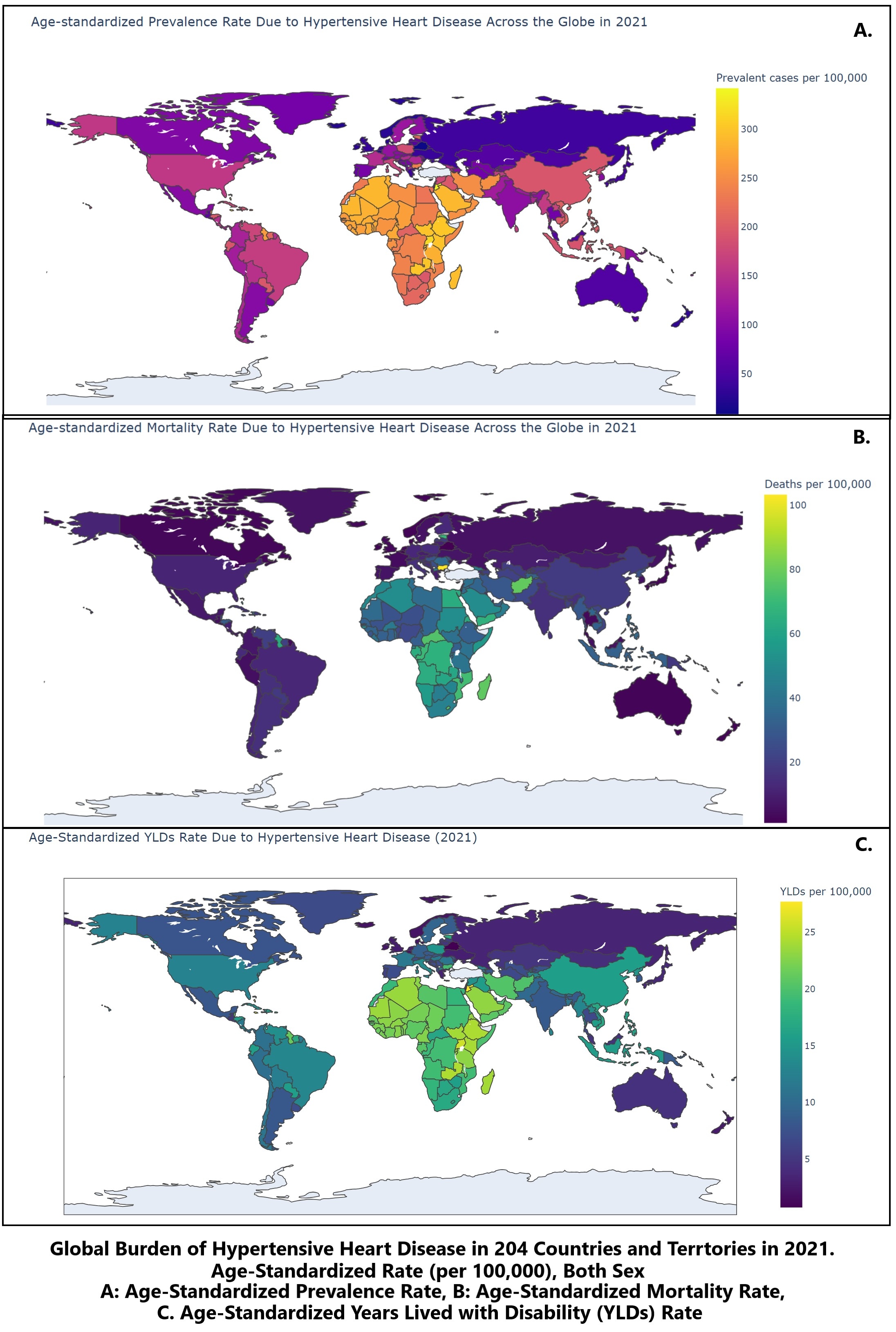
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the annual percentage change (APC) revealed a significant increase in HHD prevalence by 3.26%, deaths by 2.03%, and YLDs by 3.22%. Regionally, Australasia experienced the highest age-standardized total percentage change (TPC) in prevalence at 67% (95% UI: 43%-94%), while Eastern Europe saw a 65% (52%-80%) increase in death rates. High socio-demographic index countries recorded the largest TPC increase in YLDs at 46% (31%-60%). Notably, Latvia had the highest increase in TPC for death rates at 583% (489%-683%). In 2021, the highest prevalence was observed in the 70-74 age group with 2,192,028 cases, the highest death toll in the 80-84 age group with 216,409 deaths, and the highest YLDs in the 70-74 age group with 178,655 cases. Over the last three decades, females bore a higher burden than males, with TPC in prevalence (81% vs. 84%), deaths (27% vs. 25%), and YLDs (80% vs. 82%) from 1990 to 2021.
Conclusion: In 2021, HHD accounted for 6.86% of all cardiovascular disease-related deaths. To combat the growing burden of HHD, there is a pressing need for e-health and m-health interventions. Policymakers, public stakeholders, and clinicians must advocate for evidence-based strategies, including new media promotions involving influencers and celebrities. Emphasizing telemedicine, especially during pandemics, will be crucial in improving disease management and outcomes.
Method: Utilizing the Global Burden of Disease framework, we analyzed the prevalence, incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years lived with disability (YLDs) of HHD across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021. Our analysis was stratified by age, sex, and location.
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the annual percentage change (APC) revealed a significant increase in HHD prevalence by 3.26%, deaths by 2.03%, and YLDs by 3.22%. Regionally, Australasia experienced the highest age-standardized total percentage change (TPC) in prevalence at 67% (95% UI: 43%-94%), while Eastern Europe saw a 65% (52%-80%) increase in death rates. High socio-demographic index countries recorded the largest TPC increase in YLDs at 46% (31%-60%). Notably, Latvia had the highest increase in TPC for death rates at 583% (489%-683%). In 2021, the highest prevalence was observed in the 70-74 age group with 2,192,028 cases, the highest death toll in the 80-84 age group with 216,409 deaths, and the highest YLDs in the 70-74 age group with 178,655 cases. Over the last three decades, females bore a higher burden than males, with TPC in prevalence (81% vs. 84%), deaths (27% vs. 25%), and YLDs (80% vs. 82%) from 1990 to 2021.
Conclusion: In 2021, HHD accounted for 6.86% of all cardiovascular disease-related deaths. To combat the growing burden of HHD, there is a pressing need for e-health and m-health interventions. Policymakers, public stakeholders, and clinicians must advocate for evidence-based strategies, including new media promotions involving influencers and celebrities. Emphasizing telemedicine, especially during pandemics, will be crucial in improving disease management and outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
An Innovative, Non-invasive, Credit-Card Sized Device for Ambulatory 12 Lead ECG Recording: First-In-Human Experience Compared to Standard 12 Lead ECG
Deering Thomas, Vukajlovic Dejan, Babic Milos, Djurdjevic Branko, Atanasoski Vladimir, Miletic Marjan, Mittal Suneet, Sanders Prashanthan
Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stroke Outcomes Vary Substantially Across Private Equity FirmsBartlett Victoria, Johnson Daniel, Liu Michael, Zheng Zhaonian, Wadhera Rishi