Final ID: P-312
Comparing Activity Logs in 24-hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
Abstract Body: Background
Growing evidence suggests that activities during ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) may affect measurement. While activity logs are often used to characterize context of measurements, there is little evidence to inform strategies to optimize the collection of these data from patients.
Objective
To compare different log formats and their impact on data collection from activity logs of events occurring during ABPM.
Methods
We performed a quality improvement project in our Hypertension Center using three different types of 24-hour ABPM logs (unstructured, semi-structured, and structured). Each log asked patients to record their daily activities including sleep, meals, physical activity, pain or other symptoms, medications, stress, caffeine, and tobacco use. The structured logs requested patients document activities with check boxes, the unstructured logs requested documentation with free text, and the semi-structured log combined check boxes and free text. Over a 12-month period, patients received one of the three versions of the ABPM logs in an alternating non-randomized schedule. We used linear regression models with adjustments for age, sex, and Black race to determine the association between items reported and log structure.
Results
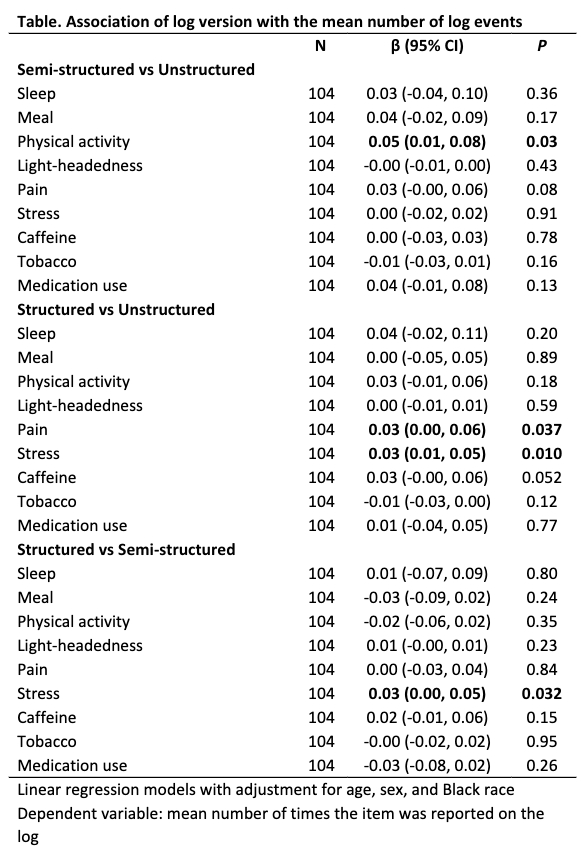
Between September 2022-2023, patients returned 47 unstructured, 26 semi-structured, and 31 structured logs (N=104). Patients were an average age of 58.9 years (SD, 17), 63% female and 23% Black. Compared with the unstructured log, the semi-structured log was associated with frequent reports of physical activity (0.05, P = 0.03), while the structured log was associated with more reports of pain (0.03, P =0.037) and stress (0.03, P =0.01). Compared to the semi-structured log, the structured log was associated with more reports of stress (0.03; P =0.032) .
Discussion
In this quality improvement project of patients undergoing ABPM, adding structure to the log increased reporting of clinically relevant information related to pain and stress. Whether these data are related to changes in blood pressure should be a focus of subsequent work.
Growing evidence suggests that activities during ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) may affect measurement. While activity logs are often used to characterize context of measurements, there is little evidence to inform strategies to optimize the collection of these data from patients.
Objective
To compare different log formats and their impact on data collection from activity logs of events occurring during ABPM.
Methods
We performed a quality improvement project in our Hypertension Center using three different types of 24-hour ABPM logs (unstructured, semi-structured, and structured). Each log asked patients to record their daily activities including sleep, meals, physical activity, pain or other symptoms, medications, stress, caffeine, and tobacco use. The structured logs requested patients document activities with check boxes, the unstructured logs requested documentation with free text, and the semi-structured log combined check boxes and free text. Over a 12-month period, patients received one of the three versions of the ABPM logs in an alternating non-randomized schedule. We used linear regression models with adjustments for age, sex, and Black race to determine the association between items reported and log structure.
Results
Between September 2022-2023, patients returned 47 unstructured, 26 semi-structured, and 31 structured logs (N=104). Patients were an average age of 58.9 years (SD, 17), 63% female and 23% Black. Compared with the unstructured log, the semi-structured log was associated with frequent reports of physical activity (0.05, P = 0.03), while the structured log was associated with more reports of pain (0.03, P =0.037) and stress (0.03, P =0.01). Compared to the semi-structured log, the structured log was associated with more reports of stress (0.03; P =0.032) .
Discussion
In this quality improvement project of patients undergoing ABPM, adding structure to the log increased reporting of clinically relevant information related to pain and stress. Whether these data are related to changes in blood pressure should be a focus of subsequent work.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertension
Weber Michael, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Schlaich Markus
An Innovative telemonitoring-wearable device with third heart sound detection for early detection of worsening heart failureMasuda Hirotada, Ekuni Shota, Misumi Yusuke, Akazawa Yasuhiro, Sakata Yasushi, Miyagawa Shigeru