Final ID: Sa4141
An Interpretable Model for Predicting Preoperative Cardiorespiratory Fitness Using Wearable Data in Free-Living Conditions.
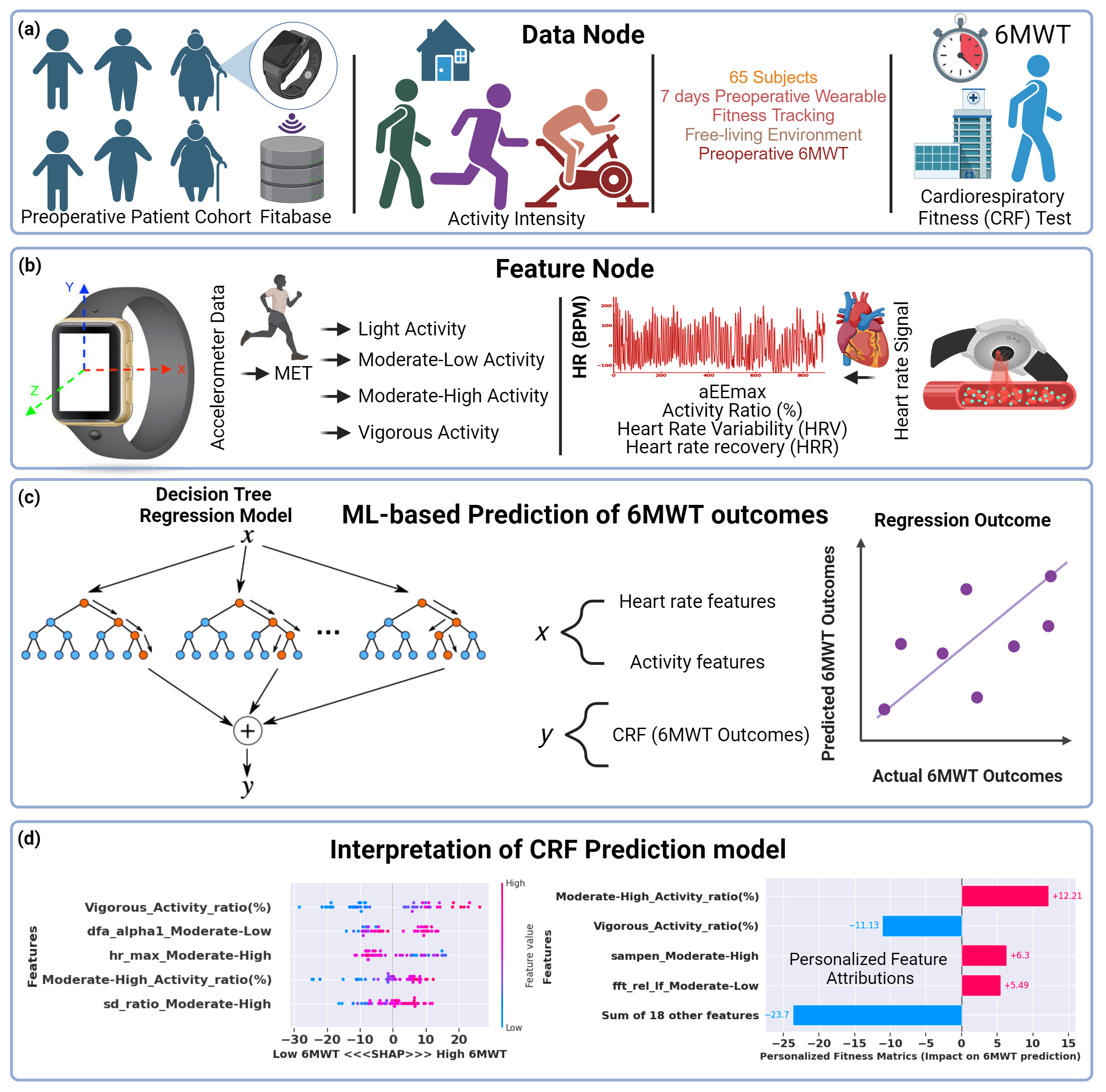
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Assessing preoperative cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is essential for determining surgical risk and outcomes. The advent of wrist-worn devices equipped with heart rate and activity monitoring presents new opportunities for CRF evaluation. Traditionally, CRF has been measured using submaximal exercise tests, such as the 6-minute walk test (6MWT). Monitoring CRF in everyday activities may offer valuable insights into patients' preoperative fitness levels. This study explores the potential of predicting 6MWT distances using a data-driven physiological CRF model derived from wearable devices in elderly patients in their free-living environments.
Hypothesis: Machine-learning algorithms can accurately estimate CRF using data from fitness trackers.
Methods: We examined heart rate and activity data from Fitbit devices worn by 65 older adult patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery. Data was collected over a week in free-living conditions. We aimed to utilize this wearable technology to forecast CRF in this group. A machine-learning ensemble regression model was employed to predict CRF, with 6MWT outcomes as the reference. The Shapley Feature Attribution method was applied to understand the contribution of specific features derived from wearable data to the model, aiding in personalized fitness predictions.
Results: Higher CRF was associated with increased levels of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), maximal activity energy expenditure (aEEmax), 4-minute heart rate recovery (HRR), and non-linear heart rate variability (HRV) features. These measures positively correlated with improved 6MWT outcomes. Our regression models, including random forest and linear regression, showed strong predictive capabilities, with coefficients of determination (R^2) of 0.91 and 0.81, respectively. Shapley Feature Attribution analysis revealed that higher levels of MVPA, aEEmax, HRR240, and non-linear HRV dynamics are reliable indicators of better CRF test performance.
Conclusions: Integrating wearable activity and heart rate data offers a robust framework for preoperative CRF assessment, enhancing surgical risk evaluation and patient outcomes in everyday conditions.
Hypothesis: Machine-learning algorithms can accurately estimate CRF using data from fitness trackers.
Methods: We examined heart rate and activity data from Fitbit devices worn by 65 older adult patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery. Data was collected over a week in free-living conditions. We aimed to utilize this wearable technology to forecast CRF in this group. A machine-learning ensemble regression model was employed to predict CRF, with 6MWT outcomes as the reference. The Shapley Feature Attribution method was applied to understand the contribution of specific features derived from wearable data to the model, aiding in personalized fitness predictions.
Results: Higher CRF was associated with increased levels of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), maximal activity energy expenditure (aEEmax), 4-minute heart rate recovery (HRR), and non-linear heart rate variability (HRV) features. These measures positively correlated with improved 6MWT outcomes. Our regression models, including random forest and linear regression, showed strong predictive capabilities, with coefficients of determination (R^2) of 0.91 and 0.81, respectively. Shapley Feature Attribution analysis revealed that higher levels of MVPA, aEEmax, HRR240, and non-linear HRV dynamics are reliable indicators of better CRF test performance.
Conclusions: Integrating wearable activity and heart rate data offers a robust framework for preoperative CRF assessment, enhancing surgical risk evaluation and patient outcomes in everyday conditions.
More abstracts on this topic:
High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Moderate Continuous Training in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Patients with Chronotropic Incompetence: A 2025 Systematic Review
Asif Sami, Mushtaq Ayesha
Clinical Characteristics of Idiopathic Cardiomyopathy After Optimal Medical Therapy in Working-Age Patients in a Regional Community HospitalArai Haruka, Urakubo Hirokazu, Shibayama Junichi, Okabe Yoshitaka, Mitamura Yasuhito