Final ID: 56
High Blood Pressure Is Associated with Lower Brain Volume and Cortical Thickness in Healthy Young Adults
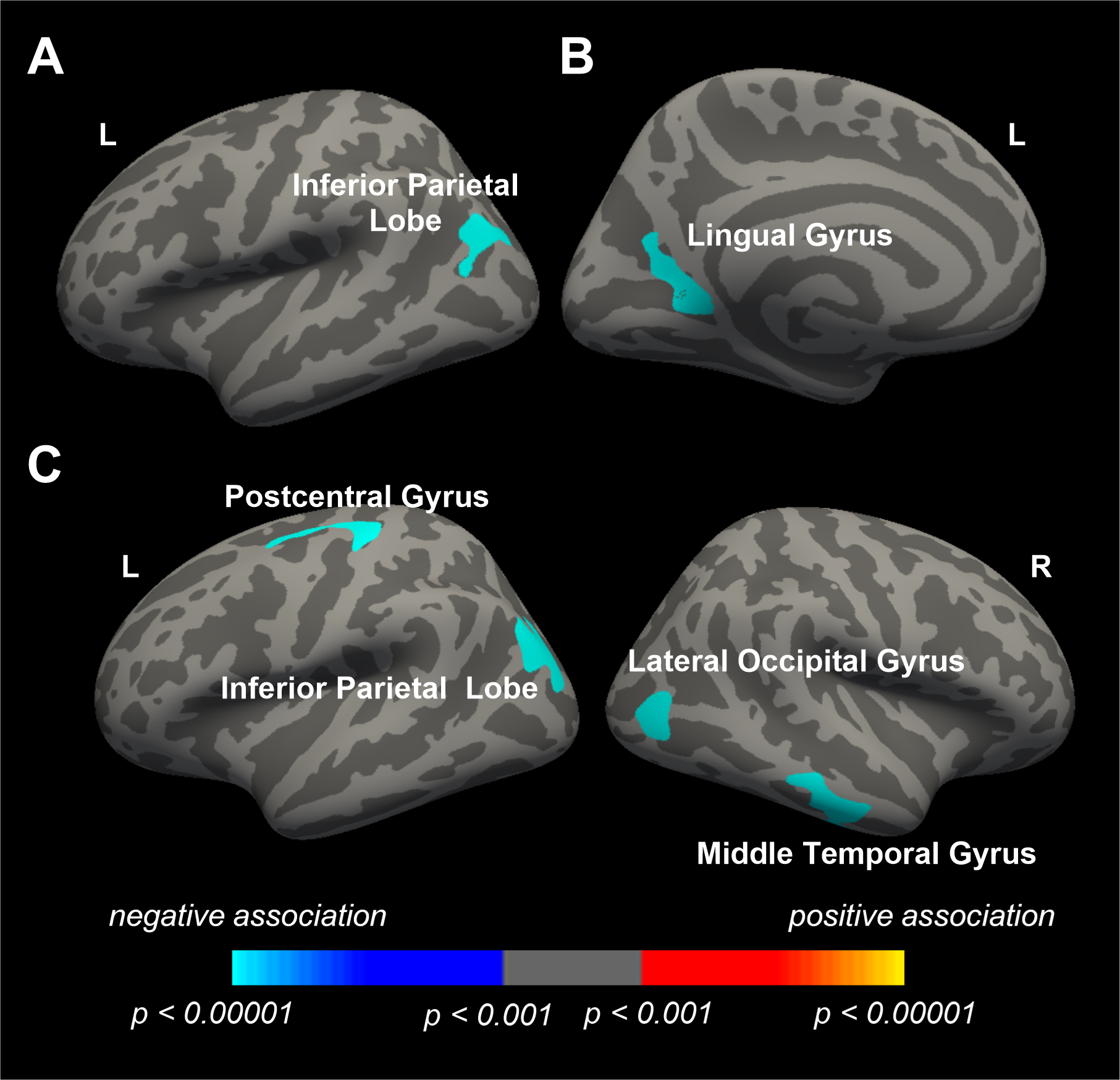
Abstract Body: Background: High blood pressure (BP) in middle-aged and older adults is associated with lower brain volume and cortical thickness assessed with structural MRI. However, little evidence is available in young adults. Objective: We investigated the associations of high BP with brain volumes and cortical thickness in healthy young adults. We hypothesized that high BP is associated with lower brain volume and cortical thickness in young adults. Methods: This cross-sectional study included 1095 young adults (54% women, 22-37 years) from the Human Connectome Project (HCP) who self-reported not having a history of hypertension or taking antihypertensive medications. Brachial systolic (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP) were measured with semi-automatic or manual sphygmomanometer during study visits. Structural MRI was used to measure gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM) volume and mean cortical thickness. Associations of BP and hypertension stage with total and regional brain volumes and cortical thickness were analyzed using linear regression and analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) after adjusting for age, sex, education years, body mass index (BMI), smoking, alcohol consumption history, zygosity, and total intracranial volume. Results: SBP and DBP were (mean ± SD) 123.6 ± 14.2 and 76.5 ± 10.6 mmHg, respectively (n = 1095). High DBP was associated with lower total GM (p = 0.012), cortical GM (p = 0.004), subcortical GM (p = 0.012), and total WM volumes (p = 0.031). There were no associations of SBP and hypertension stage with total brain volume and cortical thickness. High SBP and DBP were associated with lower regional cortical thickness in the parietal lobe and lingual gyrus, and lower regional cortical volume in the postcentral gyrus, inferior parietal lobe, lateral occipital gyrus, and middle temporal gyrus. Conclusion: Associations of high BP, particularly DBP, with lower total and regional brain volume and cortical thickness were observed in healthy young adults. These findings suggest the importance of prevention or control of high BP early in life for brain health.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community Outreach Program Focused on Hypertension Awareness Reaches 600+ People in Rural Georgia and Works to Build the Next Generation of Biomedical Scientists
Dent Elena, Ilatovskaya Daria, Pinkerton Brittany, Crider Emily, Ryan Michael, Sullivan Jennifer
A pilot study of an intervention for self-management of blood pressure among refugees fleeing war and resettled in the United StatesBehnam Rawnaq, Godino Job, Celis Deisy, Anderson Cheryl, Al-rousan Tala