Final ID: P3048
Relationships of Body Roundness Index and Triglyceride–glucose Index with 5-year All-cause Mortality in Patients with Diabetes and Comorbid Hypertension: Evidence from Two Prospective Cohort Studies
Abstract Body: Aims: We aimed to characterise the complex relationships of body roundness index (BRI) and triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) with 5-year all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes and comorbid hypertension.
Methods: 5,728 patients from the 1999–2014 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) cycles and 3,456 from the 2005–2010 China Kailuan cycles were included. BRI was calculated as 364.2−365.5×√(1−(waist circumference in centimeters/2π)2÷(0.5×height in centimeters)2). TyG was calculated as the logarithmic product of the fasting triglyceride and glucose concentrations. The cut-off values of BRI and TyG were based on median values.
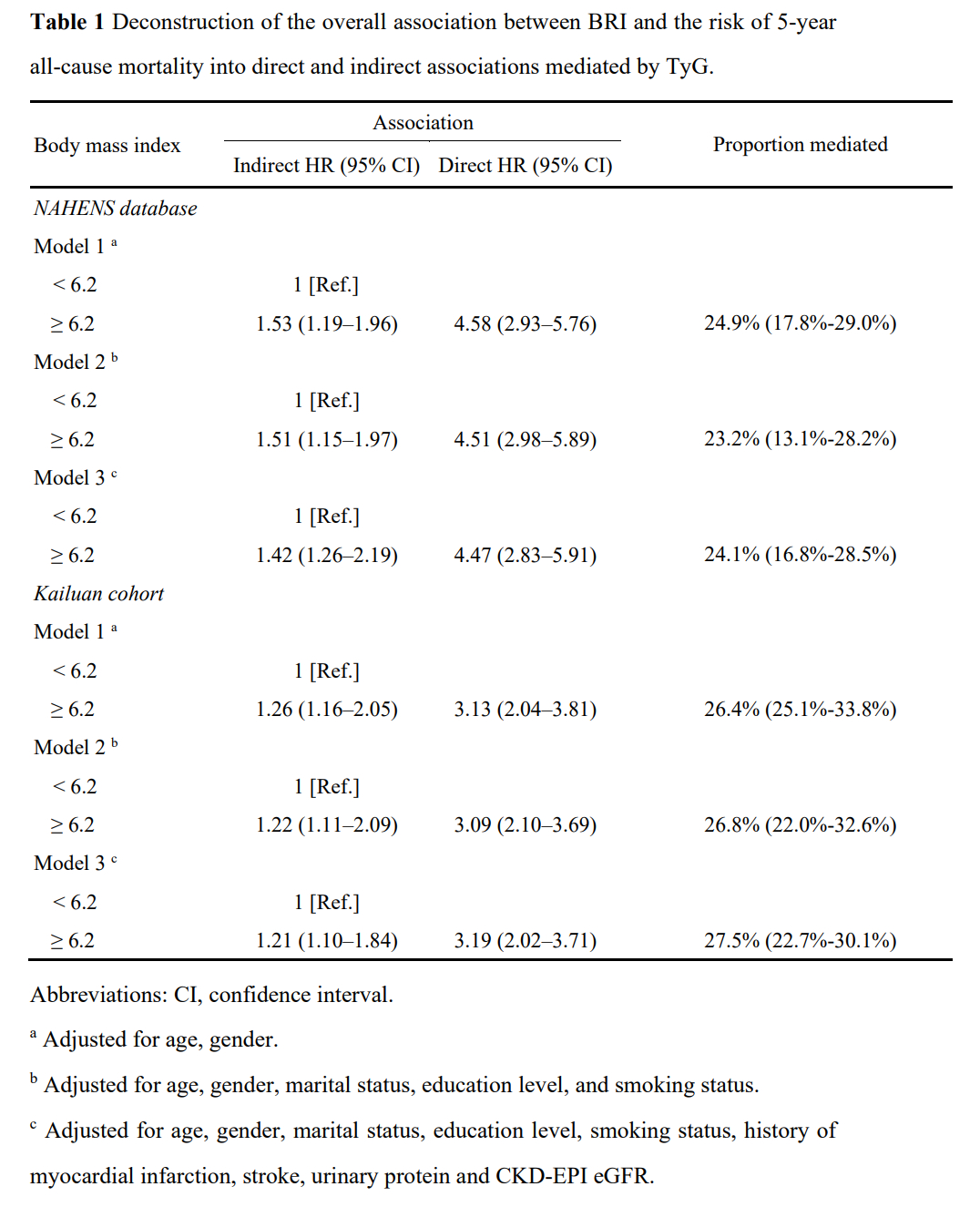
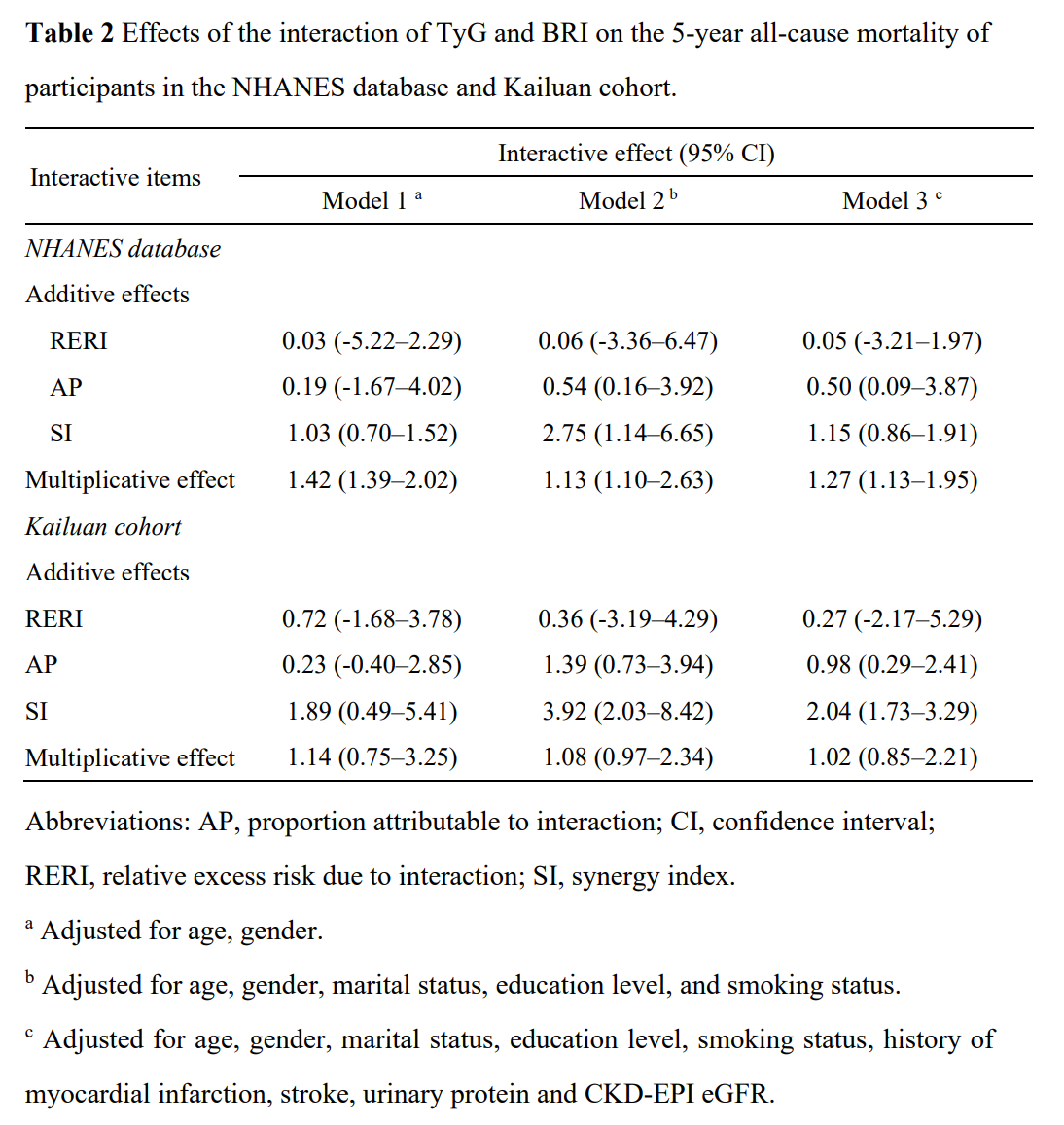
Results: The prevalence of 5-year all-cause mortality was 8.4% in the NHANES database and 9.2% in the Kailuan cohort. Multivariable Cox regression demonstrated that a BRI of >6.2 (HR: 2.53, 95% CI: 1.71–2.96) and TyG of >9.5 (HR: 1.64, 95% CI: 1.39–2.72) were independent predictors of 5-year all-cause mortality in diabetic patients with hypertension after adjusting forage, gender, marital status, education level, smoking status, history of myocardial infarction, stroke, urinary protein and CKD-EPI eGFR. These results were reconfirmed in the Kailuan cohort for BRI (HR: 2.91, 95% CI: 1.93–3.57) and TyG (HR: 2.13, 95% CI: 1.86–3.02). TyG was found to mediate the association between BRI and all-cause mortality, being responsible for 24.1% (16.8%-28.5%) in the NHANES database and 27.5% (22.7%-30.1%) in the Kailuan cohort. No significant additive interactions were found between BRI and TyG on 5-year all-cause mortality. Significant multiplicative effects were identified between TyG and BRI in the NHANES database alone (Additive: RERI = 0.05, 95% CI – 3.21–1.97; Multiplicative, HR = 1.27, 95% CI 1.13–1.95 in the NHANES database; Additive: RERI = 0.27, 95% CI – 2.17–5.29; Multiplicative, HR = 1.02, 95% CI 0.85–2.21 in the Kailuan cohort).
Conclusions: BRI and TyG were independent risk factors for 5-year all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes and comorbid hypertension. TyG was found to mediate a considerable proportion of the effect of BRI on all-cause mortality in cohorts from both the United States and China. Interventions aimed at improving obesity and abnormal fat distribution might reduce the all-cause mortality risk associated with insulin resistance.
Methods: 5,728 patients from the 1999–2014 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) cycles and 3,456 from the 2005–2010 China Kailuan cycles were included. BRI was calculated as 364.2−365.5×√(1−(waist circumference in centimeters/2π)2÷(0.5×height in centimeters)2). TyG was calculated as the logarithmic product of the fasting triglyceride and glucose concentrations. The cut-off values of BRI and TyG were based on median values.
Results: The prevalence of 5-year all-cause mortality was 8.4% in the NHANES database and 9.2% in the Kailuan cohort. Multivariable Cox regression demonstrated that a BRI of >6.2 (HR: 2.53, 95% CI: 1.71–2.96) and TyG of >9.5 (HR: 1.64, 95% CI: 1.39–2.72) were independent predictors of 5-year all-cause mortality in diabetic patients with hypertension after adjusting forage, gender, marital status, education level, smoking status, history of myocardial infarction, stroke, urinary protein and CKD-EPI eGFR. These results were reconfirmed in the Kailuan cohort for BRI (HR: 2.91, 95% CI: 1.93–3.57) and TyG (HR: 2.13, 95% CI: 1.86–3.02). TyG was found to mediate the association between BRI and all-cause mortality, being responsible for 24.1% (16.8%-28.5%) in the NHANES database and 27.5% (22.7%-30.1%) in the Kailuan cohort. No significant additive interactions were found between BRI and TyG on 5-year all-cause mortality. Significant multiplicative effects were identified between TyG and BRI in the NHANES database alone (Additive: RERI = 0.05, 95% CI – 3.21–1.97; Multiplicative, HR = 1.27, 95% CI 1.13–1.95 in the NHANES database; Additive: RERI = 0.27, 95% CI – 2.17–5.29; Multiplicative, HR = 1.02, 95% CI 0.85–2.21 in the Kailuan cohort).
Conclusions: BRI and TyG were independent risk factors for 5-year all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes and comorbid hypertension. TyG was found to mediate a considerable proportion of the effect of BRI on all-cause mortality in cohorts from both the United States and China. Interventions aimed at improving obesity and abnormal fat distribution might reduce the all-cause mortality risk associated with insulin resistance.
More abstracts on this topic:
2-Methoxyestradiol By Inhibiting Central Action of 12S-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Protects Ovariectomized Mice From Hypertension
Dutta Shubha, Singh Purnima, Song Chi Young, Shin Ji Soo, Malik Kafait
Association of METS-IR and Subclinical Myocardial Injury with Cardiovascular Mortality in U.S. AdultsCheon Patrick, Ononye Chuka, O'connor Shannon, Kazibwe Richard