Final ID: 050
Diet quality, pathway-specific polygenic risk scores, and risk of type 2 diabetes among US men and women
Abstract Body: Background
Healthy diets are associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk, but it is unclear if individuals with different genetic risks benefit from specific dietary strategies.
Hypothesis
The associations between healthy dietary patterns and lower T2D risk may be modified by global and pathway-specific polygenic risk scores (PRS).
Methods
We conducted prospective analyses in 40,609 participants from the Nurses’ Health Studies and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, who were free of baseline diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, with up to 36 years of follow-up. Diet was assessed every 4 years via a food frequency questionnaire. We examined 6 recommendation-based and 2 mechanistic-based dietary patterns. A global PRS and 12 pathway-specific PRS denoting distinct T2D mechanisms were calculated. Cox regression was used to examine diet, PRS, and their interactions with T2D risk.
Results
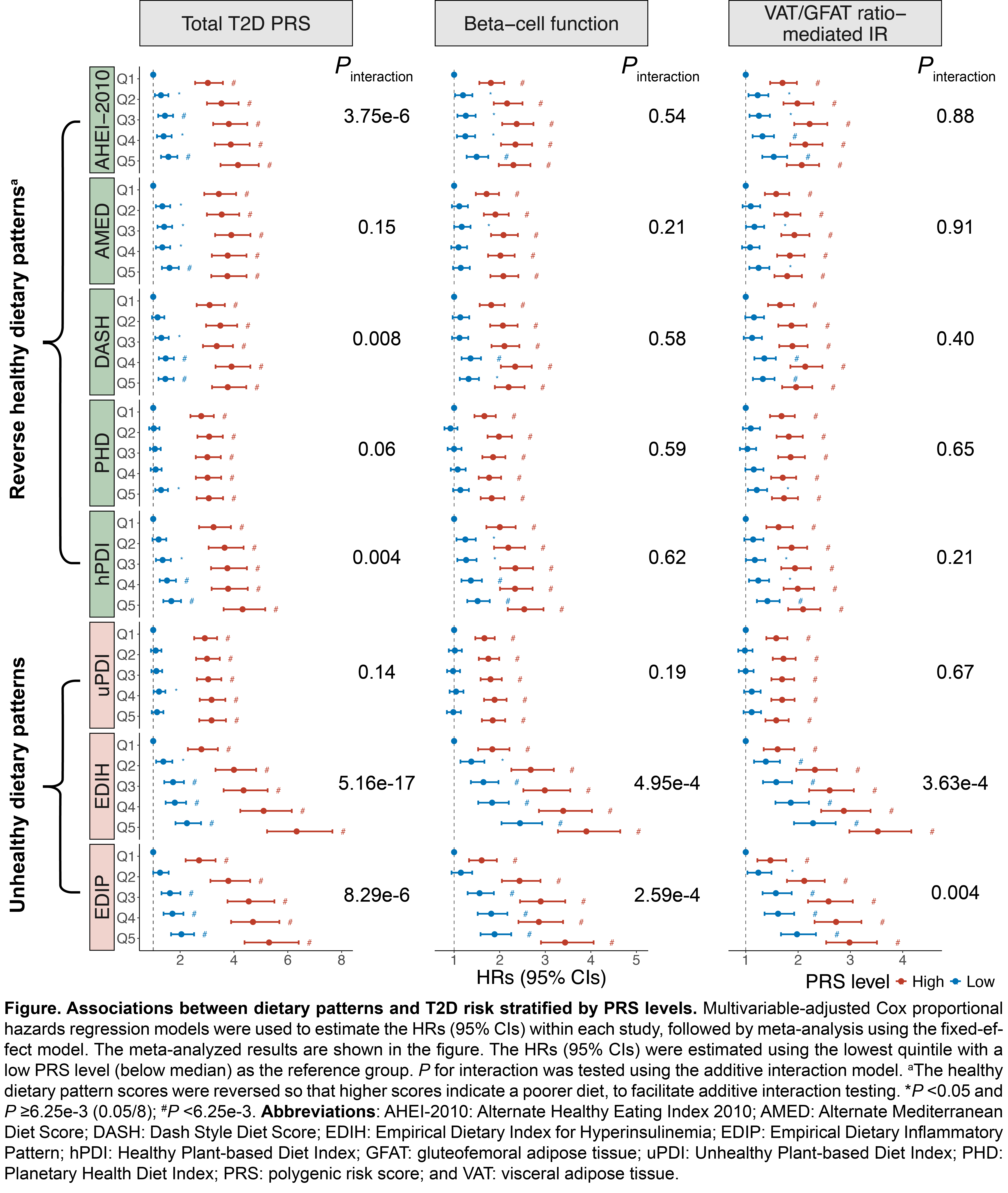
We identified a total of 4,760 T2D cases during the follow-up. Higher global PRS and 11 pathway-specific PRS, except the one related to bilirubin metabolism, significantly predicted higher T2D risk. In multivariable-adjusted analyses, all dietary indices indicating a lower dietary quality were associated with higher T2D risk (hazard ratios comparing extreme quintiles 1.06-2.21, P-trend <0.05/8). We found additive interactions between the Global PRS and the alternate Healthy Eating Index, healthy plant-based diet index, and proinflammatory and hyper-insulinemic diets, in relation to T2D risk (relative excess risk due to interaction 0.09 to 0.32, P-interaction ≤0.004; Figure). PRS for beta-cell dysfunction and fat deposition-mediated insulin resistance also showed interactions with proinflammatory and hyper-insulinemic diets (P-interaction ≤0.004; Figure).
Conclusions
Healthy dietary patterns are associated with lower T2D risk across a wide genetic risk spectrum. Diets targeting inflammation and insulinemia may be particularly beneficial for those genetically predisposed to beta-cell dysfunction and fat deposition-mediated insulin resistance.
Healthy diets are associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk, but it is unclear if individuals with different genetic risks benefit from specific dietary strategies.
Hypothesis
The associations between healthy dietary patterns and lower T2D risk may be modified by global and pathway-specific polygenic risk scores (PRS).
Methods
We conducted prospective analyses in 40,609 participants from the Nurses’ Health Studies and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, who were free of baseline diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, with up to 36 years of follow-up. Diet was assessed every 4 years via a food frequency questionnaire. We examined 6 recommendation-based and 2 mechanistic-based dietary patterns. A global PRS and 12 pathway-specific PRS denoting distinct T2D mechanisms were calculated. Cox regression was used to examine diet, PRS, and their interactions with T2D risk.
Results
We identified a total of 4,760 T2D cases during the follow-up. Higher global PRS and 11 pathway-specific PRS, except the one related to bilirubin metabolism, significantly predicted higher T2D risk. In multivariable-adjusted analyses, all dietary indices indicating a lower dietary quality were associated with higher T2D risk (hazard ratios comparing extreme quintiles 1.06-2.21, P-trend <0.05/8). We found additive interactions between the Global PRS and the alternate Healthy Eating Index, healthy plant-based diet index, and proinflammatory and hyper-insulinemic diets, in relation to T2D risk (relative excess risk due to interaction 0.09 to 0.32, P-interaction ≤0.004; Figure). PRS for beta-cell dysfunction and fat deposition-mediated insulin resistance also showed interactions with proinflammatory and hyper-insulinemic diets (P-interaction ≤0.004; Figure).
Conclusions
Healthy dietary patterns are associated with lower T2D risk across a wide genetic risk spectrum. Diets targeting inflammation and insulinemia may be particularly beneficial for those genetically predisposed to beta-cell dysfunction and fat deposition-mediated insulin resistance.
More abstracts on this topic:
Atrial Fibrillation in Valvular Heart Disease: Assessing the Impact of Genetics in the UK Biobank
Cristin Luca, Tang Janet, Tastet Lionel, Marcus Gregory, Delling Francesca
Association of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio with blood pressure is influenced by the polygenic risk score for hypertension: Analysis of UK Biobank dataFujii Wataru, Yamazaki Osamu, Kaseda Ken, Hirohama Daigoro, Kochi Yuta, Shibata Shigeru