Final ID: 032
Genetic Drivers of Comorbid Heterogeneity in Obesity: Genome-Wide Association Analysis in Three Cohorts with 40 Years of Follow-up
Abstract Body: Background
Obesity, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), is a complex trait with substantial heterogeneity in its etiology, comorbidity risk, and prevention strategies.
Hypothesis
Individuals with early-onset obesity-related comorbidities (vs. late-onset) carry different genetic risk loci for obesity with varied biological consequences.
Methods
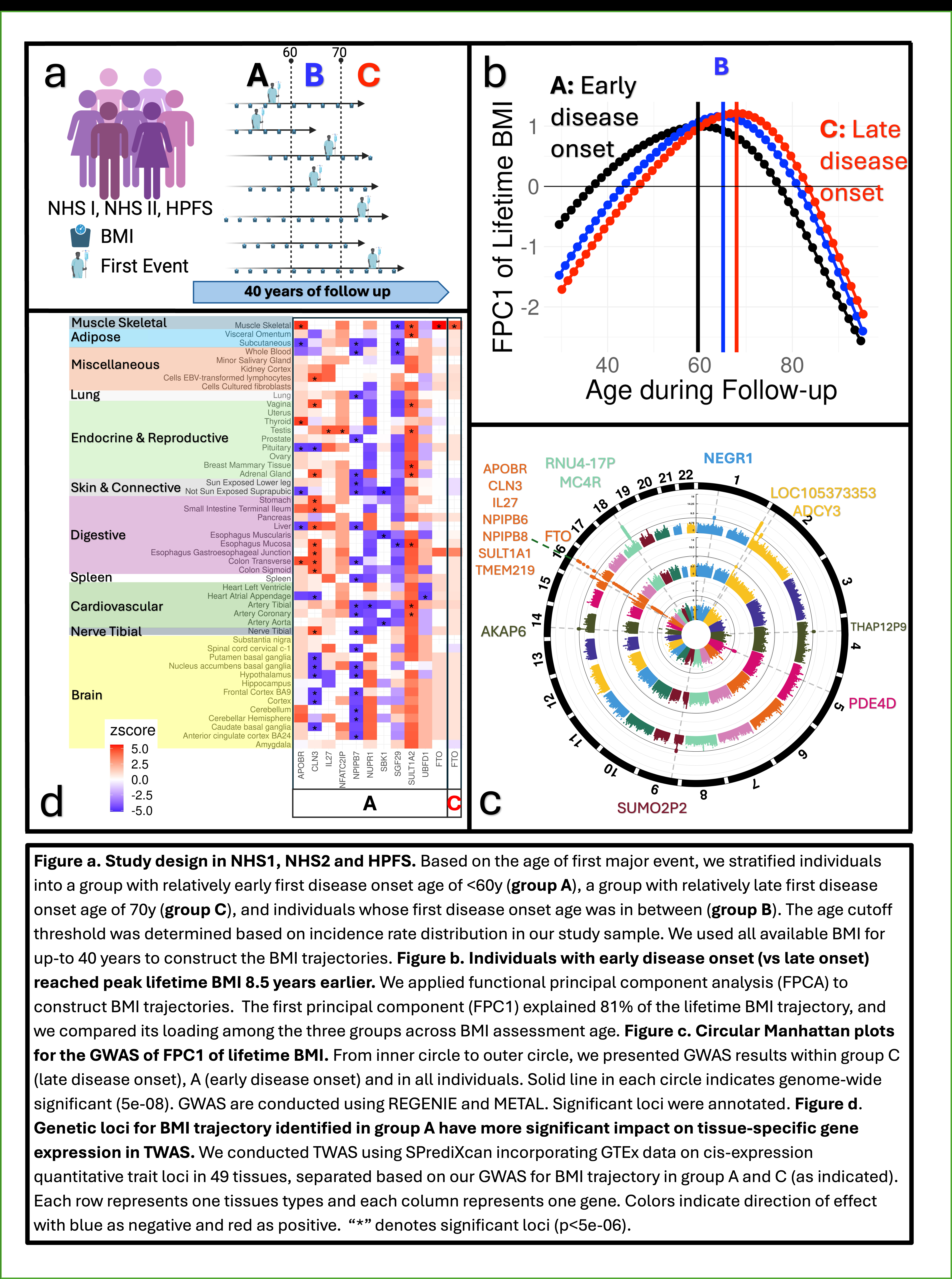
We examined longitudinal data from 43,567 participants in the Nurses’ Health Studies and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, including biennial measurements of body mass index (BMI) and diagnosis of 14 obesity-related diseases such as CVD, during up to 40 years of follow-up. We estimated long-term BMI trajectory using functional principal component analysis. Genome-wide association studies were conducted for BMI trajectory in individuals with early-onset (first event <60y old) and late-onset (first event >70y old) obesity-related diseases (Fig. a), followed by transcriptome-wide studies (TWAS) and Mendelian Randomization (MR) analyses to explore genetic variants impact on gene expressions in 49 tissue types integrating GTEx data.
Results
Individuals with early-onset obesity-related diseases reached their lifetime peak BMI, on average 8.5 years earlier than those with late disease onset (Fig. b). We identified 10 genetic loci for BMI trajectory (P < 5e-8) in all participants. FTO was the only locus consistently identified for BMI trajectory regardless of the timing of first comorbidity, with a significant impact on its gene expression in skeletal muscle (Fig. c). Among individuals with early-onset comorbidities, TWAS further identified 10 loci for BMI trajectory, and MR confirmed their impact on tissue-specific expressions, including SULT1A1 in visceral adipose tissue, NPIPB7 in coronary artery and metabolic organs, and APOBR in subcutaneous adipose tissue and liver (Fig. d). However, no other gene was identified for BMI trajectory in TWAS in individuals with late-onset comorbidities.
Conclusions
Individuals with early-onset obesity-related comorbidities appear to carry obesity risk loci that have more significant impact on tissue-specific gene expressions. Understanding genetic heterogeneity in obesity may aid personalized prevention.
Obesity, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), is a complex trait with substantial heterogeneity in its etiology, comorbidity risk, and prevention strategies.
Hypothesis
Individuals with early-onset obesity-related comorbidities (vs. late-onset) carry different genetic risk loci for obesity with varied biological consequences.
Methods
We examined longitudinal data from 43,567 participants in the Nurses’ Health Studies and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, including biennial measurements of body mass index (BMI) and diagnosis of 14 obesity-related diseases such as CVD, during up to 40 years of follow-up. We estimated long-term BMI trajectory using functional principal component analysis. Genome-wide association studies were conducted for BMI trajectory in individuals with early-onset (first event <60y old) and late-onset (first event >70y old) obesity-related diseases (Fig. a), followed by transcriptome-wide studies (TWAS) and Mendelian Randomization (MR) analyses to explore genetic variants impact on gene expressions in 49 tissue types integrating GTEx data.
Results
Individuals with early-onset obesity-related diseases reached their lifetime peak BMI, on average 8.5 years earlier than those with late disease onset (Fig. b). We identified 10 genetic loci for BMI trajectory (P < 5e-8) in all participants. FTO was the only locus consistently identified for BMI trajectory regardless of the timing of first comorbidity, with a significant impact on its gene expression in skeletal muscle (Fig. c). Among individuals with early-onset comorbidities, TWAS further identified 10 loci for BMI trajectory, and MR confirmed their impact on tissue-specific expressions, including SULT1A1 in visceral adipose tissue, NPIPB7 in coronary artery and metabolic organs, and APOBR in subcutaneous adipose tissue and liver (Fig. d). However, no other gene was identified for BMI trajectory in TWAS in individuals with late-onset comorbidities.
Conclusions
Individuals with early-onset obesity-related comorbidities appear to carry obesity risk loci that have more significant impact on tissue-specific gene expressions. Understanding genetic heterogeneity in obesity may aid personalized prevention.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Clinical Trial of Healthy Food Subsidies and Behavioral Interventions to Increase Fruit and Vegetable Purchasing in an Online Store
Hua Sophia, Klaiman Tamar, Dixon Erica, Volpp Kevin, Putt Mary, Coratti Samantha, White Jenna, Hossain Mohammad, Posner Hannah, Wang Erkuan, Zhu Jingsan, John Aileen
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat DietGomes Viviane, Watts Stephanie, Fink Gregory, Kim Lauren, Lopez Krystal, Gilbert Bryce, Bailey Victoria, Marques Bruno, Garver Hannah, Mckenzie Mckenzie, Lauver Adam