Final ID: 061
Joint Associations of Objectively Measured Physical Activity and Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome with All-Cause Mortality in US Adults
Abstract Body: Introduction: Physical activity is recommended for slowing the progression of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome. Guidelines suggest lifestyle modification may be most beneficial for those with advanced CKM (stages 3-4), but few studies have compared the impact of physical activity across the CKM spectrum.
Objective: We examined associations between physical activity (PA) patterns and risk of all-cause mortality across CKM stages.
Methods: We conducted a weighted, prospective cohort analysis of the 2003-2006 National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (NHANES), with follow-up until December 31, 2019. We restricted analyses to those adults who were ≥ 20 years old, not pregnant, and able to walk. We classified participants according to CKM stage. We calculated average daily moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) using up to 7 days of actigraphy data and the standard cut-point of 2000 activity counts per minute. We visualized the MVPA distributions by CKM stage and calculated the proportion of adults meeting the recommended MVPA target of ≥ 150 minutes a week (≥ 21.4 minutes per day). We fit Cox regression models to estimate relative and absolute mortality risk using a polynomial B-spline of log-MVPA with a single knot at the midpoint. We stratified all analyses by CKM stage and adjusted models for demographics.
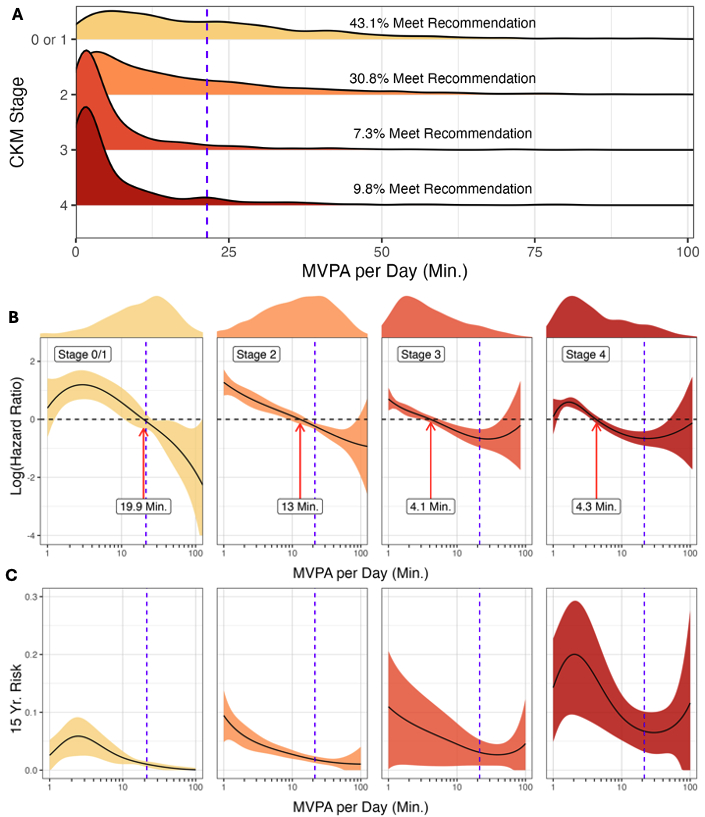
Results: We included 7,246 adults (weighted mean age 47.6 yrs, 51.5% female). Over a median follow up of 14.4 years, there were 1676 deaths. The percentage of US adults achieving the AHA-recommended MVPA target ranged from 7.3% (CKM stage 3) to 43.1% (CKM stage 0 to 1) (Fig. 1A). Greater MVPA was associated with lower hazard of mortality across CKM stages. Hazard ratios of reaching the AHA recommendation, as opposed to being sedentary, ranged from 0.93 (CKM stage 0/1) to 0.52 (CKM stage 4). The minimum MVPA associated with lower mortality ranged from 4.1 minutes per day (CKM stage 3) to 19.9 minutes/day (CKM stage 0/1) (Fig. 1B). The associations between greater MVPA and lower absolute mortality risk were more pronounced in later stage CKM (Fig. 1C).
Conclusion: MVPA is associated with lower mortality along the full spectrum of CKM syndrome. The benefits of MVPA appeared largest in advanced CKM (stages 3-4), where even modest activity potentially confers cardioprotection.
Objective: We examined associations between physical activity (PA) patterns and risk of all-cause mortality across CKM stages.
Methods: We conducted a weighted, prospective cohort analysis of the 2003-2006 National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (NHANES), with follow-up until December 31, 2019. We restricted analyses to those adults who were ≥ 20 years old, not pregnant, and able to walk. We classified participants according to CKM stage. We calculated average daily moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) using up to 7 days of actigraphy data and the standard cut-point of 2000 activity counts per minute. We visualized the MVPA distributions by CKM stage and calculated the proportion of adults meeting the recommended MVPA target of ≥ 150 minutes a week (≥ 21.4 minutes per day). We fit Cox regression models to estimate relative and absolute mortality risk using a polynomial B-spline of log-MVPA with a single knot at the midpoint. We stratified all analyses by CKM stage and adjusted models for demographics.
Results: We included 7,246 adults (weighted mean age 47.6 yrs, 51.5% female). Over a median follow up of 14.4 years, there were 1676 deaths. The percentage of US adults achieving the AHA-recommended MVPA target ranged from 7.3% (CKM stage 3) to 43.1% (CKM stage 0 to 1) (Fig. 1A). Greater MVPA was associated with lower hazard of mortality across CKM stages. Hazard ratios of reaching the AHA recommendation, as opposed to being sedentary, ranged from 0.93 (CKM stage 0/1) to 0.52 (CKM stage 4). The minimum MVPA associated with lower mortality ranged from 4.1 minutes per day (CKM stage 3) to 19.9 minutes/day (CKM stage 0/1) (Fig. 1B). The associations between greater MVPA and lower absolute mortality risk were more pronounced in later stage CKM (Fig. 1C).
Conclusion: MVPA is associated with lower mortality along the full spectrum of CKM syndrome. The benefits of MVPA appeared largest in advanced CKM (stages 3-4), where even modest activity potentially confers cardioprotection.
More abstracts on this topic:
Arrhythmias as Early Predictors of CKD: Real-World Evidence from a National Cardio-Kidney-Metabolic Cohort
Russo Pierantonio, Nathan Ramaa, Poh Jason, Singh Harjeet, Boyle Ken, Wright Brent, Hendrickson Erik
An ADPKD-Associated Pathway in Cardiac Homeostasis, Heart Failure, and Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolicLiu Chia-feng, Leon Steven, Wessely Oliver, Tang Wai Hong