Final ID: P1163
Reproductive Risk Factors and Burden of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome among Young Women
Abstract Body: Objective
Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome describes the intersection between cardiovascular disease (CVD), kidney disease, and metabolic disorders. Little is known about reproductive risk factors, known to be associated with long-term CVD, and CKM syndrome. Our objective was to quantify the associations of reproductive risk factors with CKM syndrome prevalence and severity.
Methods
We conducted a weighted cross-sectional analysis of non-pregnant women from ages 20-49 years in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013 to 2020). We calculated the prevalence of CKM syndrome stage overall and by the following self-reported reproductive risk factors: early menstruation, infertility, large for gestational age neonate, parity > 5, and history of gestational diabetes. We used logistic regression to estimate age-adjusted associations between the reproductive risk factors and CKM syndrome stages > 2 vs. stages 1 or 0.
Results
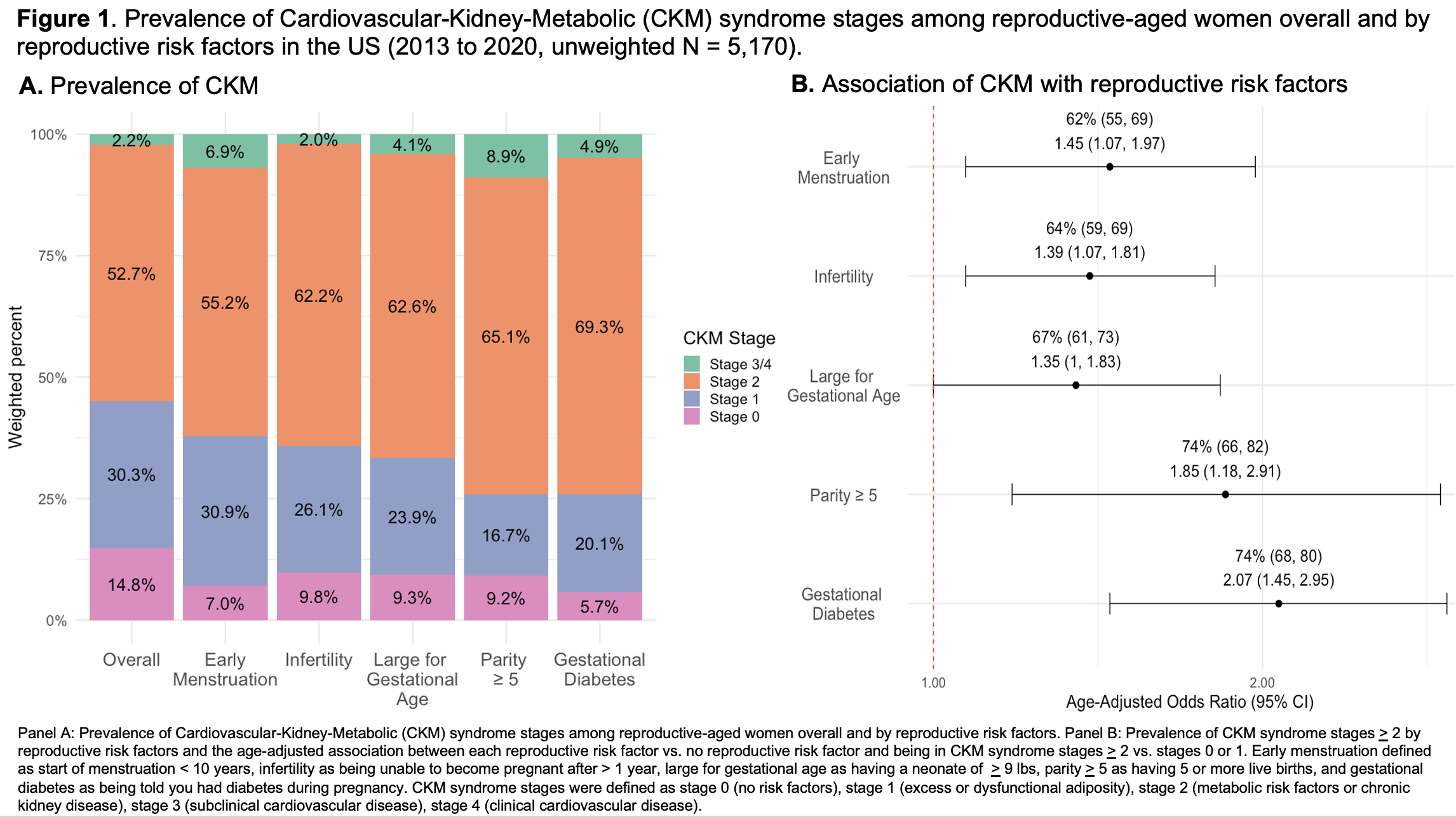
Reproductive risk factors were common with 40% (95% CI: 37%, 42%) of women reporting the presence of at least one factor. Overall, 55% (95% CI: 53%, 57%) of reproductive-aged women were in stage > 2, and women with a history of adverse reproductive risk factors were more likely to be in higher CKM stages (Figure 1A). The presence of each reproductive risk factor was associated with a higher prevalence of CKM stage > 2 vs. stage 1 or 0, with the strongest associations observed for parity > 5 and history of gestational diabetes (Figure 1B).
Conclusion
Reproductive risk factors were strongly associated with prevalent CKM syndrome among young women. Incorporating reproductive risk factors into clinical prediction equations may ultimately improve risk stratification for CVD among young women.
Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome describes the intersection between cardiovascular disease (CVD), kidney disease, and metabolic disorders. Little is known about reproductive risk factors, known to be associated with long-term CVD, and CKM syndrome. Our objective was to quantify the associations of reproductive risk factors with CKM syndrome prevalence and severity.
Methods
We conducted a weighted cross-sectional analysis of non-pregnant women from ages 20-49 years in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013 to 2020). We calculated the prevalence of CKM syndrome stage overall and by the following self-reported reproductive risk factors: early menstruation, infertility, large for gestational age neonate, parity > 5, and history of gestational diabetes. We used logistic regression to estimate age-adjusted associations between the reproductive risk factors and CKM syndrome stages > 2 vs. stages 1 or 0.
Results
Reproductive risk factors were common with 40% (95% CI: 37%, 42%) of women reporting the presence of at least one factor. Overall, 55% (95% CI: 53%, 57%) of reproductive-aged women were in stage > 2, and women with a history of adverse reproductive risk factors were more likely to be in higher CKM stages (Figure 1A). The presence of each reproductive risk factor was associated with a higher prevalence of CKM stage > 2 vs. stage 1 or 0, with the strongest associations observed for parity > 5 and history of gestational diabetes (Figure 1B).
Conclusion
Reproductive risk factors were strongly associated with prevalent CKM syndrome among young women. Incorporating reproductive risk factors into clinical prediction equations may ultimately improve risk stratification for CVD among young women.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute Bilateral Breast Swelling as a Rare Manifestation of Heart Failure Exacerbation: A Case Report
Mohyeldin Moiud, Anto Anandu, Hossain Muhammad
Cardiovascular Health Modifies Genetic Risk for the Hypertensive Disorders of PregnancyMathew Vineetha, Patel Aniruddh, Cho So Mi, Jowell Amanda, Pabon Maria, Silver Robert, Levine Lisa, Grobman William, Catov Janet, Haas David, Honigberg Michael, Khan Raiyan, Mcneil Rebecca, Yan Qi, Pe Er Itsik, Truong Buu, Natarajan Pradeep, Yee Lynn, Sharma Garima