Final ID: P1087
Impact of Allostatic Load on Prevalent and Incident Pre-Heart Failure in the Echocardiographic Study of Latinos (ECHO-SOL)
Abstract Body: Introduction
Allostatic load (AL) is multi-system index that physiologically quantifies the effects of chronic stress. The relationship of AL to pre-heart failure (HF), a precursor of clinical HF, has not been defined.
Methods
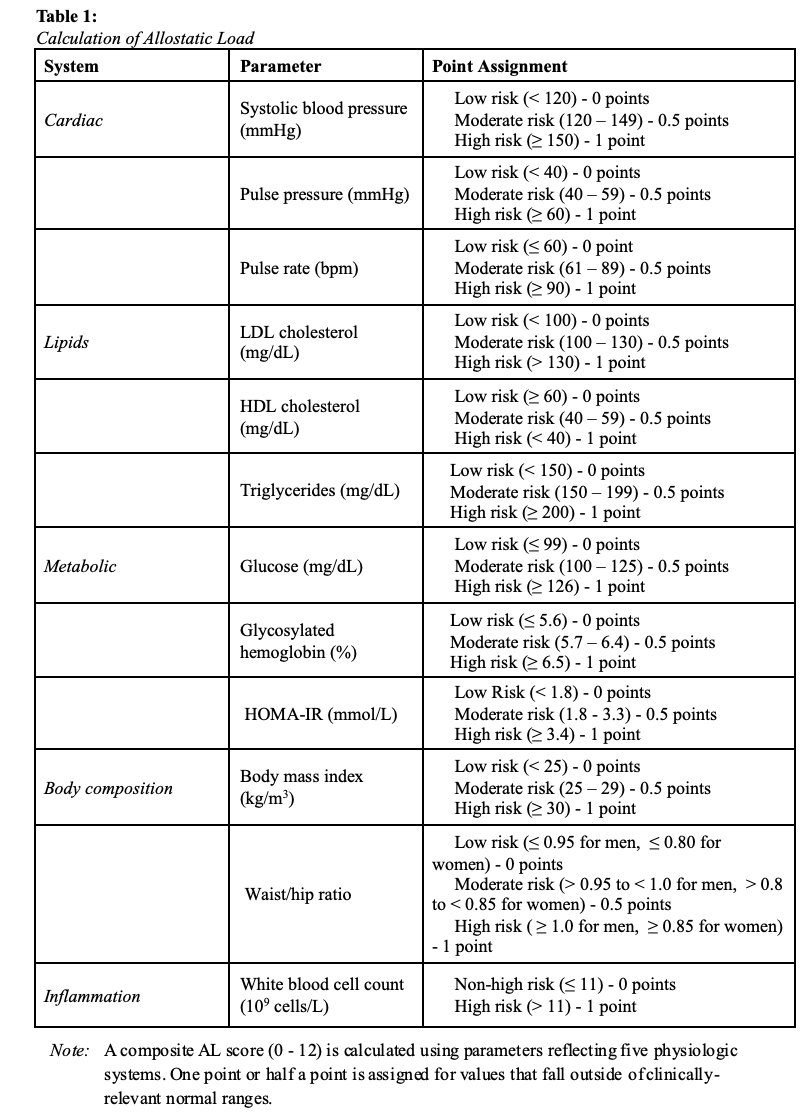
We studied 1,643 Hispanic/Latino adults who were free of clinical HF. An AL score was calculated using multiple physiologic parameters: (1) body mass index and waist hip ratio; (2) white blood cell count; (3) triglycerides, high-density lipoproteins, and low-density lipoproteins; (4) systolic blood pressure, pulse pressure and heart rate; and (5) serum glucose, insulin resistance, and glycosylated hemoglobin. For each parameter, points were assigned for values that fell outside normal ranges (Table 1). Echocardiographic measures of pre-HF were obtained across three domains: 1. systolic function (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF], global longitudinal strain [GLS]); 2. diastolic function (mitral inflow velocity [E], mitral annular early diastolic velocity [e’], E/e’); and 3. cardiac remodeling (left ventricular mass index [LVMI], relative wall thickness [RWT], and left atrial volume index [LAVI]). Measurements were obtained at baseline and at follow-up after an average of 4.3 years. Incident pre-HF was defined among those without pre-HF at baseline. Survey-weighted linear and logistic regression analyses were employed.
Results
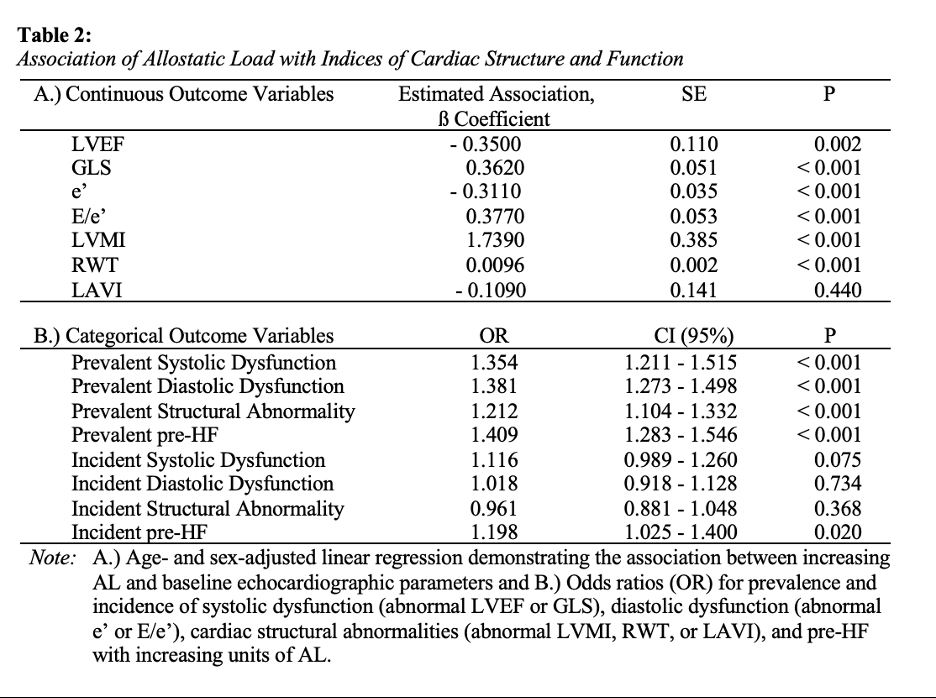
The mean age of the study population was 56.4 years (SE = 0.395) and 58.5% were female. AL scores ranged from 0.5 - 10 with a mean of 5.15 (SE = 0.062). Greater AL burden was associated with worsened cardiac parameters (lower baseline LVEF, GLS, and e’; higher baseline LVMI, RWT, and E/e’), more prevalent systolic/diastolic dysfunction and structural remodeling, and increased odds of prevalent pre-HF after age and sex adjustment. Incident pre-HF risk also increased with a higher baseline AL burden (Table 2).
Conclusion
Increasing AL was associated with prevalent cardiac abnormalities, prevalent pre-HF, and incident pre-HF. The use of AL as a predictive tool for pre-HF warrants further study.
Allostatic load (AL) is multi-system index that physiologically quantifies the effects of chronic stress. The relationship of AL to pre-heart failure (HF), a precursor of clinical HF, has not been defined.
Methods
We studied 1,643 Hispanic/Latino adults who were free of clinical HF. An AL score was calculated using multiple physiologic parameters: (1) body mass index and waist hip ratio; (2) white blood cell count; (3) triglycerides, high-density lipoproteins, and low-density lipoproteins; (4) systolic blood pressure, pulse pressure and heart rate; and (5) serum glucose, insulin resistance, and glycosylated hemoglobin. For each parameter, points were assigned for values that fell outside normal ranges (Table 1). Echocardiographic measures of pre-HF were obtained across three domains: 1. systolic function (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF], global longitudinal strain [GLS]); 2. diastolic function (mitral inflow velocity [E], mitral annular early diastolic velocity [e’], E/e’); and 3. cardiac remodeling (left ventricular mass index [LVMI], relative wall thickness [RWT], and left atrial volume index [LAVI]). Measurements were obtained at baseline and at follow-up after an average of 4.3 years. Incident pre-HF was defined among those without pre-HF at baseline. Survey-weighted linear and logistic regression analyses were employed.
Results
The mean age of the study population was 56.4 years (SE = 0.395) and 58.5% were female. AL scores ranged from 0.5 - 10 with a mean of 5.15 (SE = 0.062). Greater AL burden was associated with worsened cardiac parameters (lower baseline LVEF, GLS, and e’; higher baseline LVMI, RWT, and E/e’), more prevalent systolic/diastolic dysfunction and structural remodeling, and increased odds of prevalent pre-HF after age and sex adjustment. Incident pre-HF risk also increased with a higher baseline AL burden (Table 2).
Conclusion
Increasing AL was associated with prevalent cardiac abnormalities, prevalent pre-HF, and incident pre-HF. The use of AL as a predictive tool for pre-HF warrants further study.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal Alters Alternative Polyadenylation to Regulate mRNA Isoform Diversity in the Transition from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts to Myofibroblasts
Natarajan Kartiga, Neupane Rahul, Yalamanchili Hari Krishna, Palaniyandi Suresh, Wagner Eric, Guha Ashrith, Amirthalingam Thandavarayan Rajarajan
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong