Final ID: MP08
The Association of Urinary Sodium with Incident Apparent Treatment Resistant Hypertension among African Americans: Findings from The Jackson Heart Study
Abstract Body: BACKGROUND:
Hypertension is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease and disproportionately affects African American (AA) adults, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality in this population. Apparent Treatment Resistant hypertension (aTRH), where blood pressure (BP) remains uncontrolled despite the use of multiple antihypertensive medications, is particularly prevalent among AA adults. Sodium intake is associated with BP levels, yet the relationship between urinary sodium (a measure of dietary sodium intake) and aTRH in AA adults remains unclear. This study examined the association between 24-hour urinary sodium excretion and incident aTRH among AA adults with hypertension, using data from the Jackson Heart Study (JHS).
METHODS:
The JHS included 5,306 self-identified AA adults from Jackson, Mississippi, with data collected at three visits (2000-2013). For this analysis, we focused on 452 participants with hypertension at baseline with non-missing urinary excretion and medication data. Urinary sodium excretion was categorized into quartiles, and aTRH was defined as uncontrolled BP while taking ≥3 classes of antihypertensive medication. We used a semi-parametric proportional hazards regression model to determine the association between 24-hour urinary sodium excretion and incident aTRH, adjusting for potential confounders.
RESULTS:
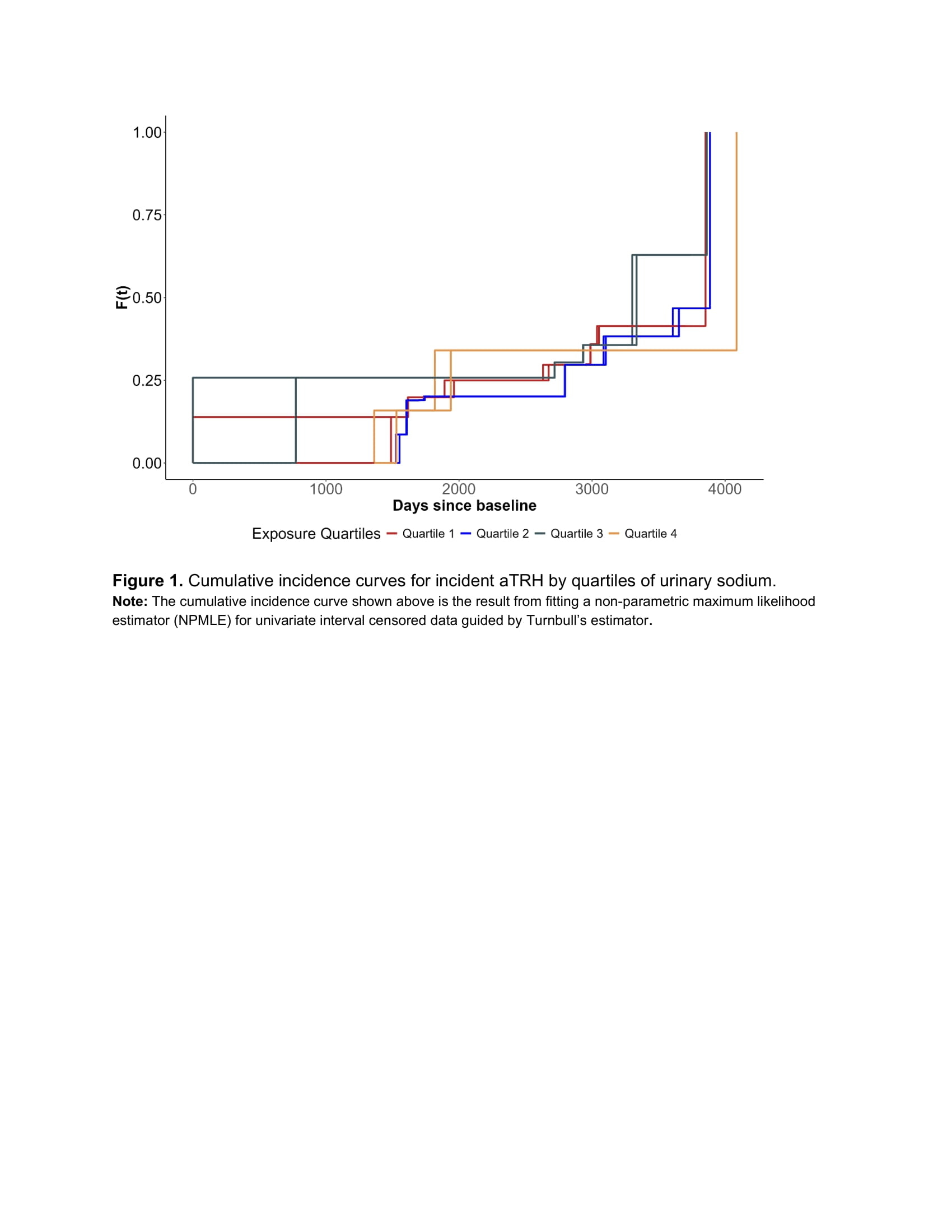
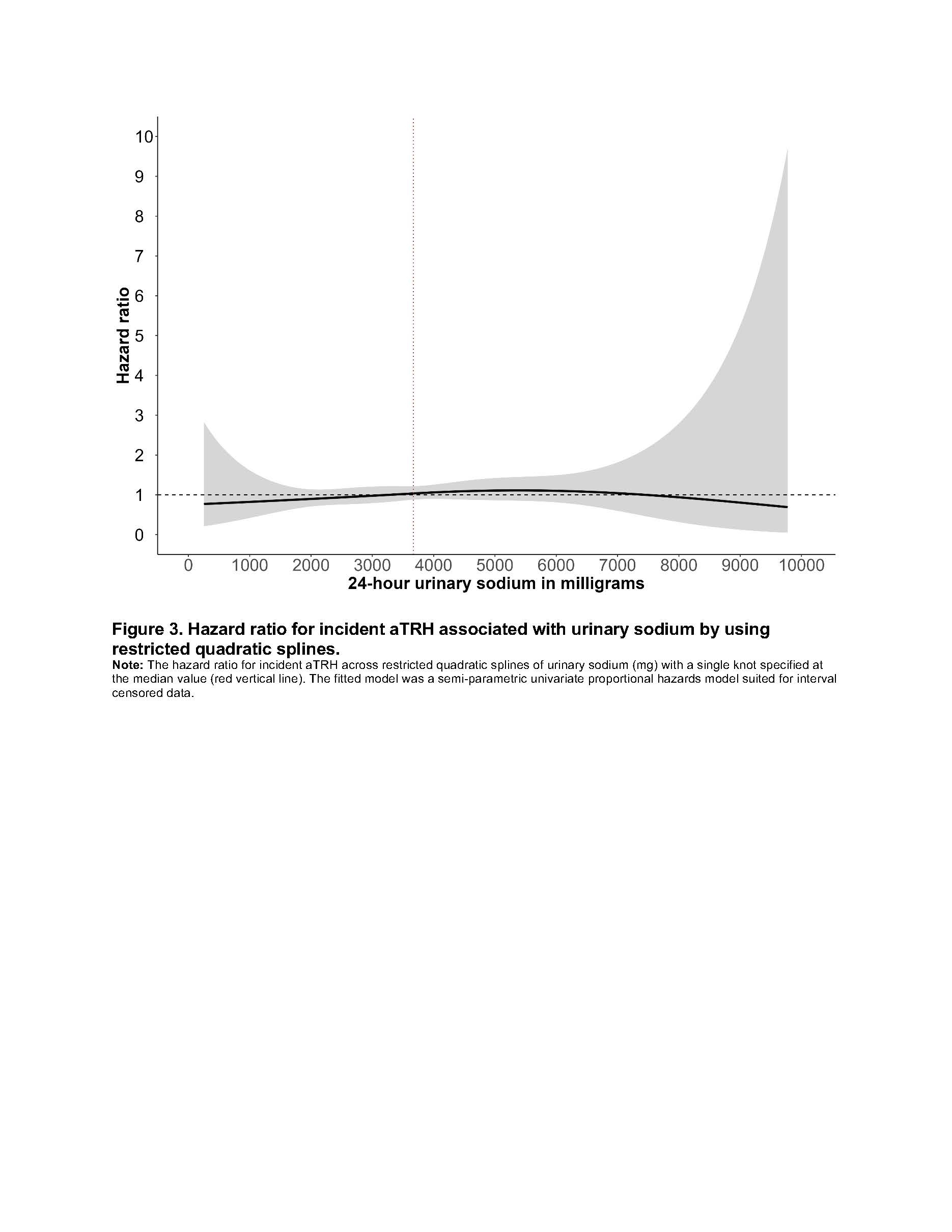
Participants were 63 years old on average and 27.7% men. Higher sodium excretion was associated with younger age, higher income, alcohol consumption, and greater antihypertensive medication use, whereas those with history of stroke or chronic kidney disease had lower sodium excretion. Over a median follow-up of 7.5 years, 123 participants (27.2%) developed aTRH. Participants in quartiles 3 and 4 of urinary sodium excretion showed higher incidence rates of aTRH, though fully adjusted hazard ratios were not statistically significant [HRs (95% confidence intervals [CIs]): [Q2=0.71 (0.34, 1.46), Q3=1.02 (0.50, 2.06), Q4=0.95 (0.46, 2.00); P=0.166).
CONCLUSIONS:
There was no statistically significant association between urinary sodium and incident aTRH among AA adults with hypertension. However, the findings highlight the need for targeted public health interventions to reduce sodium consumption in this population. Larger, longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings and explore the complex associations between sodium intake and hypertension management.
Hypertension is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease and disproportionately affects African American (AA) adults, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality in this population. Apparent Treatment Resistant hypertension (aTRH), where blood pressure (BP) remains uncontrolled despite the use of multiple antihypertensive medications, is particularly prevalent among AA adults. Sodium intake is associated with BP levels, yet the relationship between urinary sodium (a measure of dietary sodium intake) and aTRH in AA adults remains unclear. This study examined the association between 24-hour urinary sodium excretion and incident aTRH among AA adults with hypertension, using data from the Jackson Heart Study (JHS).
METHODS:
The JHS included 5,306 self-identified AA adults from Jackson, Mississippi, with data collected at three visits (2000-2013). For this analysis, we focused on 452 participants with hypertension at baseline with non-missing urinary excretion and medication data. Urinary sodium excretion was categorized into quartiles, and aTRH was defined as uncontrolled BP while taking ≥3 classes of antihypertensive medication. We used a semi-parametric proportional hazards regression model to determine the association between 24-hour urinary sodium excretion and incident aTRH, adjusting for potential confounders.
RESULTS:
Participants were 63 years old on average and 27.7% men. Higher sodium excretion was associated with younger age, higher income, alcohol consumption, and greater antihypertensive medication use, whereas those with history of stroke or chronic kidney disease had lower sodium excretion. Over a median follow-up of 7.5 years, 123 participants (27.2%) developed aTRH. Participants in quartiles 3 and 4 of urinary sodium excretion showed higher incidence rates of aTRH, though fully adjusted hazard ratios were not statistically significant [HRs (95% confidence intervals [CIs]): [Q2=0.71 (0.34, 1.46), Q3=1.02 (0.50, 2.06), Q4=0.95 (0.46, 2.00); P=0.166).
CONCLUSIONS:
There was no statistically significant association between urinary sodium and incident aTRH among AA adults with hypertension. However, the findings highlight the need for targeted public health interventions to reduce sodium consumption in this population. Larger, longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings and explore the complex associations between sodium intake and hypertension management.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertension
Schlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic ReviewChaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna