Final ID: P3100
Associations of maternal salt intake with low birth weight and small for gestational age in a large cohort
Abstract Body: Background: Excessive salt intake has been strongly associated with multiple health conditions, while evidence linking salt consumption during pregnancy and birth outcomes remains limited.
Methods: We included 4,267 mother-child pairs from a prospective cohort study which has been followed since 2017 in Shanghai, China. Salt consumption was estimated based on cooking salt and soy sauce from household condiment weighing measurements over a week, and then categorized into <5.0 (reference), 5.0-10.0, and ≥10.0 g/day. Salt density was calculated as the amount of salt divided by total energy intake from food frequency questionnaires. Outcomes related to birth weight were defined according to standard clinical cutoffs, including low birth weight (LBW), macrosomia, small for gestational age (SGA), and large for gestational age (LGA).
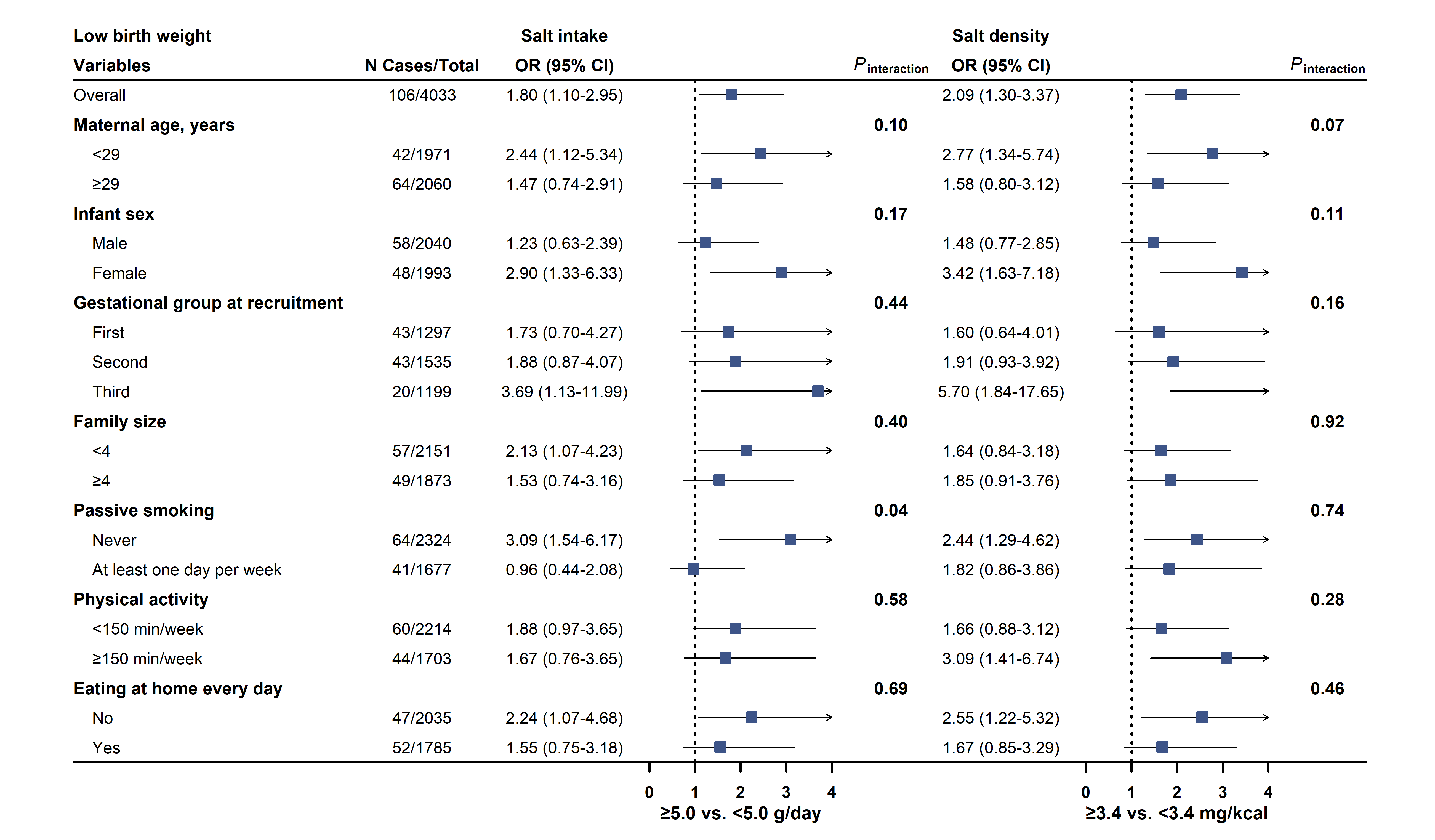
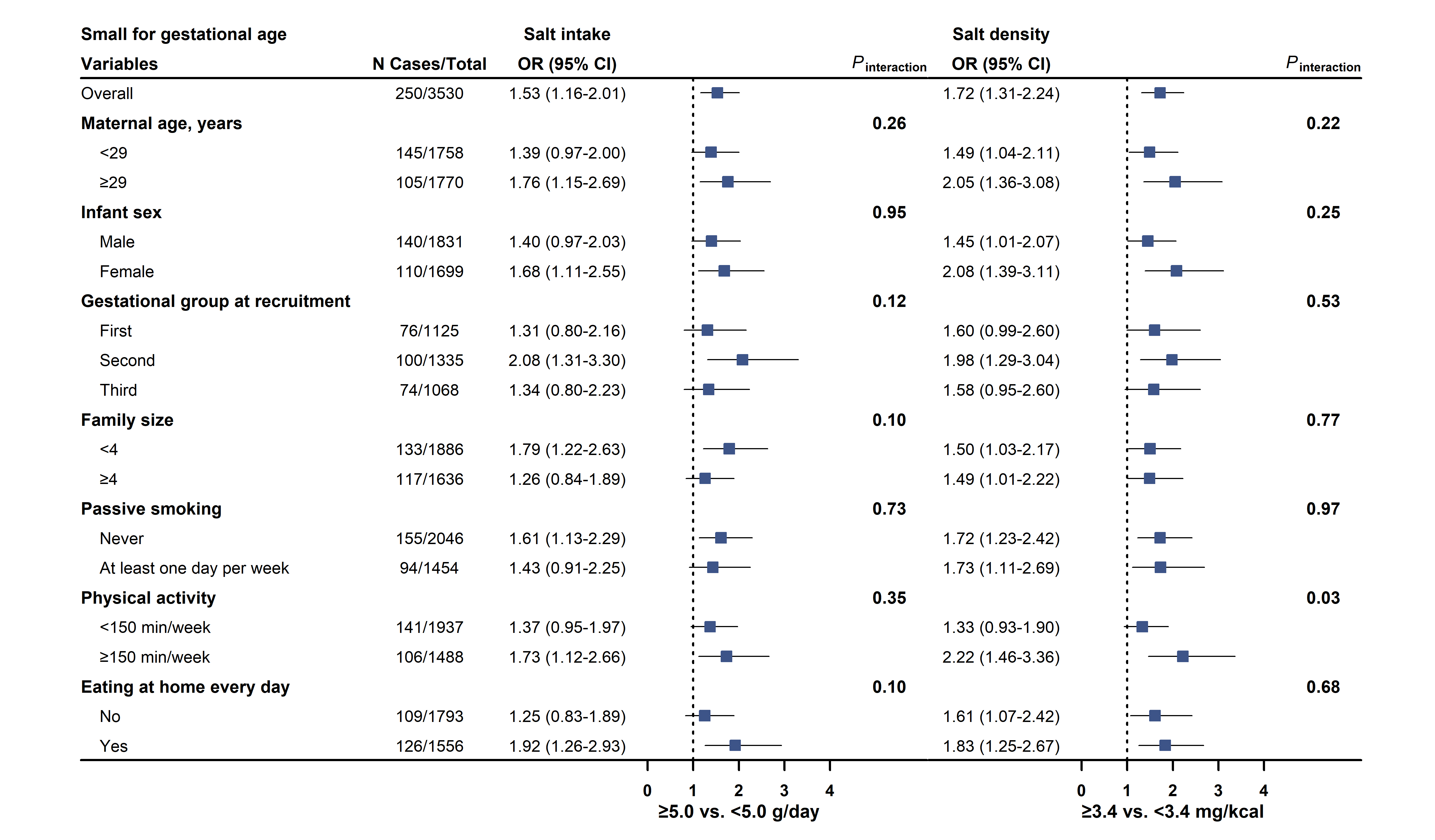
Results: Multivariable-adjusted odds ratios (ORs) of LBW were 1.72 (95% CI 1.01-2.91) for 5.0-10.0 g/day salt intake, and 2.06 (95% CI 1.02-4.13) for ≥10.0 g/day, compared to those of <5.0 g/day (P-trend=0.04). For SGA, ORs were 1.46 (95% CI 1.09-1.97) for 5.0-10.0 g/day and 1.69 (95% CI 1.16-2.47; P-trend=0.006) for ≥10.0 g/day. Similarly, OR comparing extreme tertile (high vs. low) of salt density was (1.91; 95% CI 1.08-3.36; P-trend=0.01) for LBW and (1.63; 95% CI 1.18-2.25; P-trend<0.001) for SGA. No significant associations were observed for salt intake in relation to macrosomia or LGA. These findings remain stable in all sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
Conclusions: In this study, habitual salt intake above 5 g/day was associated with increased risks of LBW and SGA, which warrants confirmation by interventional studies.
Methods: We included 4,267 mother-child pairs from a prospective cohort study which has been followed since 2017 in Shanghai, China. Salt consumption was estimated based on cooking salt and soy sauce from household condiment weighing measurements over a week, and then categorized into <5.0 (reference), 5.0-10.0, and ≥10.0 g/day. Salt density was calculated as the amount of salt divided by total energy intake from food frequency questionnaires. Outcomes related to birth weight were defined according to standard clinical cutoffs, including low birth weight (LBW), macrosomia, small for gestational age (SGA), and large for gestational age (LGA).
Results: Multivariable-adjusted odds ratios (ORs) of LBW were 1.72 (95% CI 1.01-2.91) for 5.0-10.0 g/day salt intake, and 2.06 (95% CI 1.02-4.13) for ≥10.0 g/day, compared to those of <5.0 g/day (P-trend=0.04). For SGA, ORs were 1.46 (95% CI 1.09-1.97) for 5.0-10.0 g/day and 1.69 (95% CI 1.16-2.47; P-trend=0.006) for ≥10.0 g/day. Similarly, OR comparing extreme tertile (high vs. low) of salt density was (1.91; 95% CI 1.08-3.36; P-trend=0.01) for LBW and (1.63; 95% CI 1.18-2.25; P-trend<0.001) for SGA. No significant associations were observed for salt intake in relation to macrosomia or LGA. These findings remain stable in all sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
Conclusions: In this study, habitual salt intake above 5 g/day was associated with increased risks of LBW and SGA, which warrants confirmation by interventional studies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abnormal Calcium Regulation Leads to Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy During Pregnancy in the GSNOR-Deficient Mouse Model of Preeclampsia
Dulce Raul, Balkan Wayne, Hare Joshua, Kulandavelu Shathiyah
Advanced Lipid Status Parameters in Women With PreeclampsiaGojkovic Tamara, Saric Matutinovic Marija, Ivanisevic Jasmina, Vladimirov Sandra, Spasojevic Kalimanovska Vesna, Mikovic Zeljko, Stefanovic Aleksandra, Ardalic Daniela, Antonic Tamara, Banjac Gorica, Zeljkovic Aleksandra, Vekic Jelena, Miljkovic Trailovic Milica, Munjas Jelena, Jovicic Snezana