Final ID: 055
Gestational Diabetes and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Exploring the Role of Gut microbiome and Blood Metabolome in the Hispanic Community Health Study / Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL)
Abstract Body: Introduction: Women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the underlying mechanisms, particularly the roles of gut microbiota and blood metabolites, remain unclear.
Hypothesis: Women with history of GDM have an altered gut microbiota and blood metabolites, which may lead to a higher T2D risk.
Methods: Among parous women from HCHS/SOL, gut microbiome was assessed by shotgun sequencing (visit 2, 2014-17). We identified microbial species associated with presence vs. absence of history of GDM (visit 2, n=1525), and serum metabolites associated with both history of GDM (baseline, 2008-11, n=2968) and GDM-related microbiota (visit 2, n=391). We also examined prospective associations of the GDM-related microbiome (visit 2, n=798) with incident T2D over 6 years follow-up, and of microbial-related metabolites (baseline, n=2341) with incident T2D over 12 years.
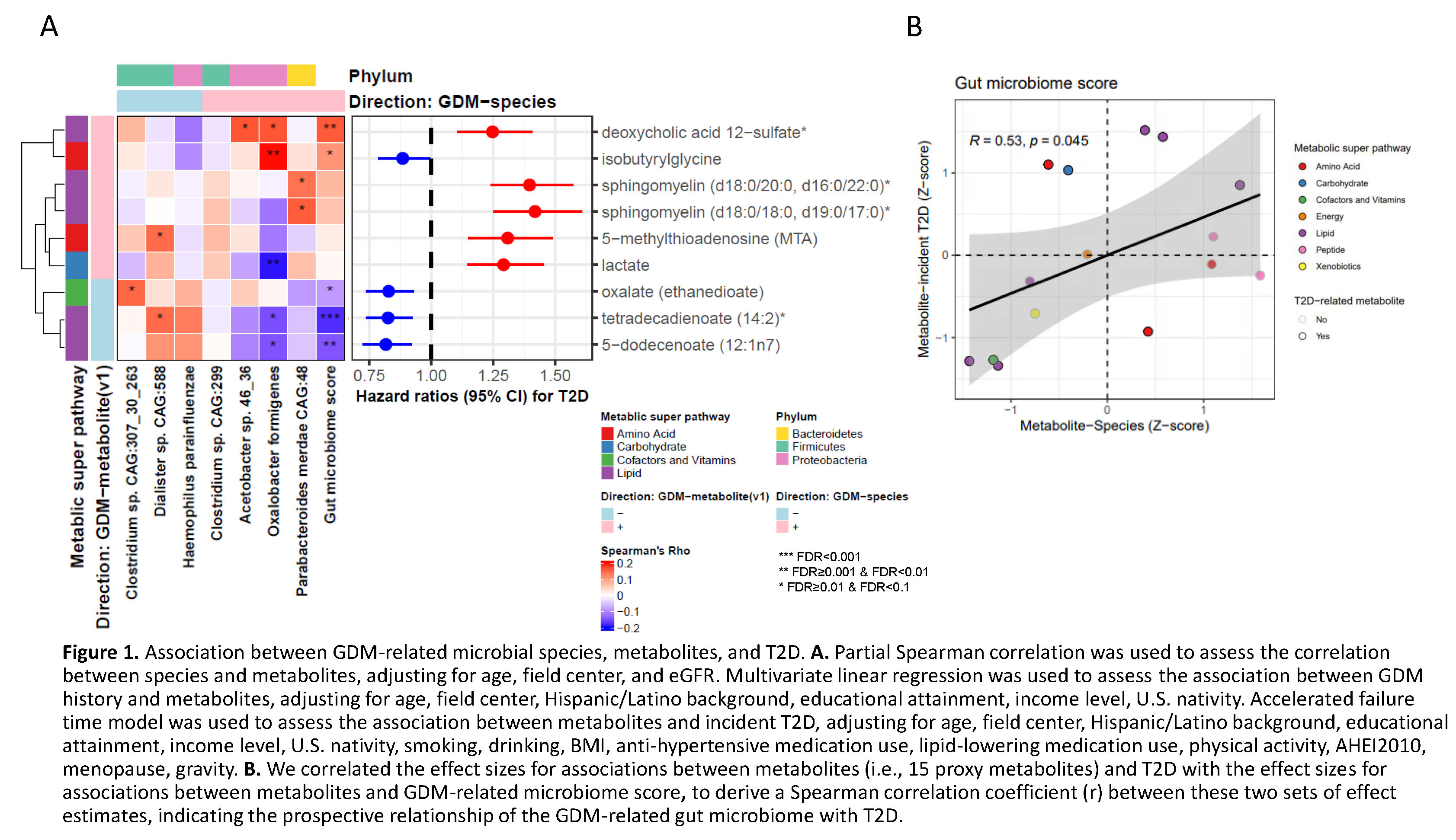
Results: Seven species showed differential abundance between women with and without history of GDM, including higher abundance of 4 species (e.g., Parabacteroides merdae CAG:48), and lower abundance of 3 species (e.g., Dialister sp. CAG:588). A GDM-related microbiome score, generated via linear combination of 7 species, was associated with higher T2D risk (RR=1.08 [95% CI: 1.00, 1.18] per SD). Fifteen metabolites (e.g., saturated sphingomyelins) were associated with both history of GDM and the microbiome score in consistent direction, 9 of which were prospectively associated with incident T2D (Fig. 1A). Proxy association analysis based on these metabolites suggested a positive relationship between the GDM-related microbiome and T2D (Fig. 1B). A metabolite score derived from the 9 microbial-related metabolites partially mediated the relationship between GDM and T2D risk (21.8%, 95% CI: 8.1%, 54%).
Conclusion: Among U.S. Hispanic/Latino women, history of GDM is associated with an unfavorable gut microbiota and related metabolites, suggesting a potential role of gut microbiota in GDM-T2D relationship.
Hypothesis: Women with history of GDM have an altered gut microbiota and blood metabolites, which may lead to a higher T2D risk.
Methods: Among parous women from HCHS/SOL, gut microbiome was assessed by shotgun sequencing (visit 2, 2014-17). We identified microbial species associated with presence vs. absence of history of GDM (visit 2, n=1525), and serum metabolites associated with both history of GDM (baseline, 2008-11, n=2968) and GDM-related microbiota (visit 2, n=391). We also examined prospective associations of the GDM-related microbiome (visit 2, n=798) with incident T2D over 6 years follow-up, and of microbial-related metabolites (baseline, n=2341) with incident T2D over 12 years.
Results: Seven species showed differential abundance between women with and without history of GDM, including higher abundance of 4 species (e.g., Parabacteroides merdae CAG:48), and lower abundance of 3 species (e.g., Dialister sp. CAG:588). A GDM-related microbiome score, generated via linear combination of 7 species, was associated with higher T2D risk (RR=1.08 [95% CI: 1.00, 1.18] per SD). Fifteen metabolites (e.g., saturated sphingomyelins) were associated with both history of GDM and the microbiome score in consistent direction, 9 of which were prospectively associated with incident T2D (Fig. 1A). Proxy association analysis based on these metabolites suggested a positive relationship between the GDM-related microbiome and T2D (Fig. 1B). A metabolite score derived from the 9 microbial-related metabolites partially mediated the relationship between GDM and T2D risk (21.8%, 95% CI: 8.1%, 54%).
Conclusion: Among U.S. Hispanic/Latino women, history of GDM is associated with an unfavorable gut microbiota and related metabolites, suggesting a potential role of gut microbiota in GDM-T2D relationship.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age at Menarche Associated with Longitudinal Increases in Blood Pressure in Postmenopausal Indian Women: Data from the Centre for Cardiometabolic Risk Reduction in South-Asia (CARRS) study
Quarpong Wilhemina, Chandrasekaran Suchitra, Mehta Puja, Narayan K, Tandon Nikhil, Ramakrishnan Usha, Patel Shivani
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat DietGomes Viviane, Watts Stephanie, Fink Gregory, Kim Lauren, Lopez Krystal, Gilbert Bryce, Bailey Victoria, Marques Bruno, Garver Hannah, Mckenzie Mckenzie, Lauver Adam