Final ID: P3026
Prevalence of Cardiac Arrhythmias by Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stage: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
Abstract Body: Background: Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome is a systemic disorder resulting from the complex relationships between obesity, diabetes, kidney disease, and the cardiovascular system. CKM syndrome is associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, sudden cardiac death, and atrial fibrillation (AF), but the prevalence and burden of other major arrythmias have not been characterized in CKM.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study who attended Visit 6 (2016 – 2017) and wore a non-invasive single-lead electrocardiogram patch (Zio XT) for up to 2 weeks. We evaluated the age-adjusted prevalence of 4 major arrhythmias (AF, long pause lasting >3 seconds, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia, and Mobitz type 2 or third-degree atrioventricular block) by CKM stages. CKM stage is defined as: Stage 0/1 – no risk factors or excess/dysfunctional adiposity; Stage 2: metabolic risk factors or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease; Stage 3: subclinical CVD, high predicted CVD risk, or very high-risk chronic kidney disease; and Stage 4: clinical CVD.
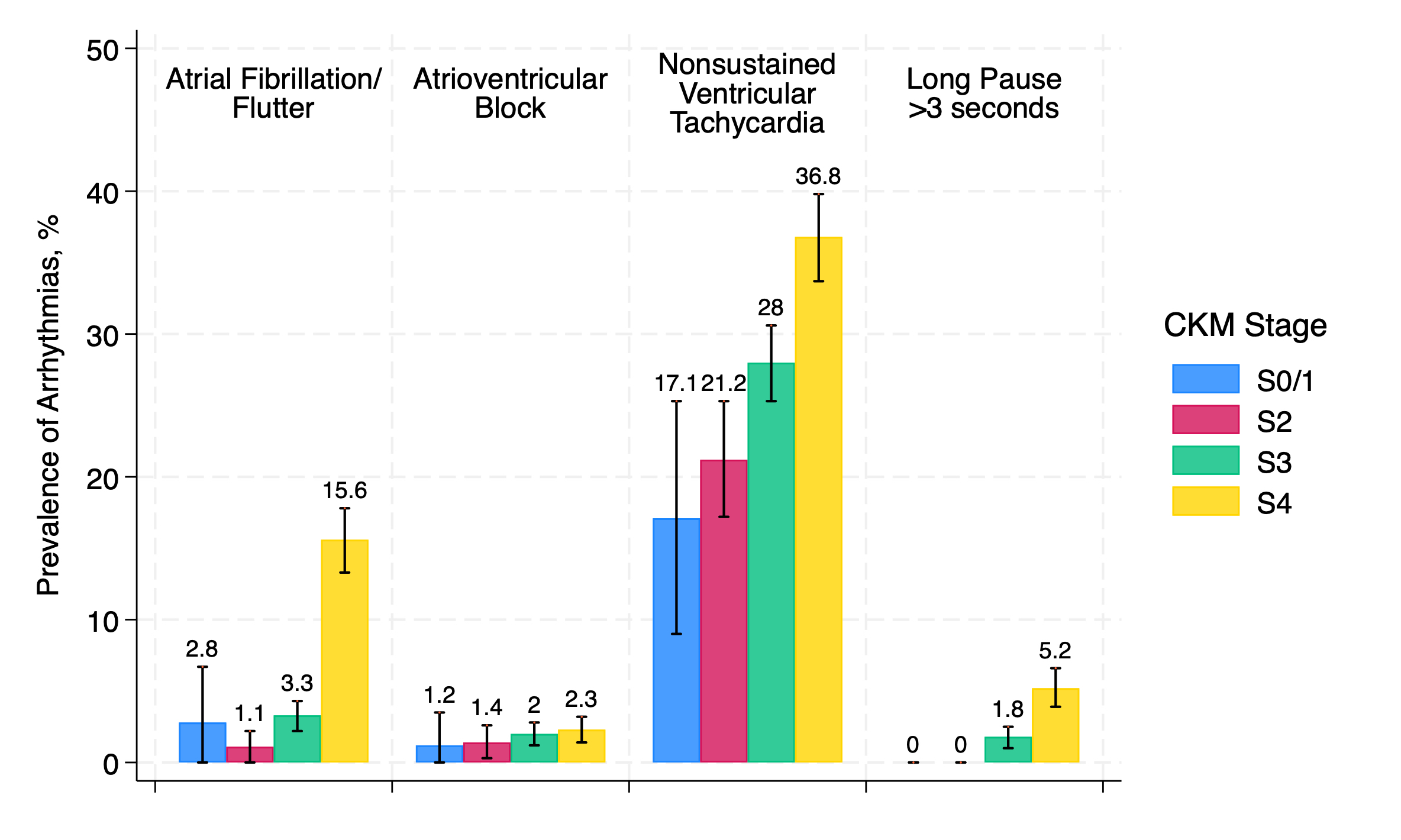
Results: Our study included 2,616 ARIC participants (mean age 79.2 years; 58% female; 26% Black). Overall, prevalence of advanced CKM syndrome was high (Stage 4: 37.8%, Stage 3: 42.2%, Stage 2: 16.4%, Stage 0/1: 3.3%). Compared to participants with Stage 0/1 CKM, participants with Stage 4 CKM were more likely to be older (mean age 80.2 vs. 76.1 years), male (48% vs. 31%), Black (29% vs. 7%), haveFigure).
Conclusions: The age-adjusted prevalence of clinically significant arrhythmias is high among older community-dwelling adults with advanced CKM syndrome. Efforts to achieve and maintain more optimal CKM health may help to reduce the odds of developing major arrhythmias.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study who attended Visit 6 (2016 – 2017) and wore a non-invasive single-lead electrocardiogram patch (Zio XT) for up to 2 weeks. We evaluated the age-adjusted prevalence of 4 major arrhythmias (AF, long pause lasting >3 seconds, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia, and Mobitz type 2 or third-degree atrioventricular block) by CKM stages. CKM stage is defined as: Stage 0/1 – no risk factors or excess/dysfunctional adiposity; Stage 2: metabolic risk factors or moderate- to high-risk chronic kidney disease; Stage 3: subclinical CVD, high predicted CVD risk, or very high-risk chronic kidney disease; and Stage 4: clinical CVD.
Results: Our study included 2,616 ARIC participants (mean age 79.2 years; 58% female; 26% Black). Overall, prevalence of advanced CKM syndrome was high (Stage 4: 37.8%, Stage 3: 42.2%, Stage 2: 16.4%, Stage 0/1: 3.3%). Compared to participants with Stage 0/1 CKM, participants with Stage 4 CKM were more likely to be older (mean age 80.2 vs. 76.1 years), male (48% vs. 31%), Black (29% vs. 7%), have
Conclusions: The age-adjusted prevalence of clinically significant arrhythmias is high among older community-dwelling adults with advanced CKM syndrome. Efforts to achieve and maintain more optimal CKM health may help to reduce the odds of developing major arrhythmias.
More abstracts on this topic:
An Innovative telemonitoring-wearable device with third heart sound detection for early detection of worsening heart failure
Masuda Hirotada, Ekuni Shota, Misumi Yusuke, Akazawa Yasuhiro, Sakata Yasushi, Miyagawa Shigeru
A novel Urocortin-2 analog COR-1167 corrects cardiac and renal dysfunction on top of Empagliflozin in a rat model of acute decompensated heart failureStephan Yohan, Corruble Clement, Charrier Lucie, Nicol Lionel, Kowala Mark, Ozoux Marie-laure, Lawson Francesca, Janiak Philip, Mulder Paul