Final ID: P1155
Different Heart Failure Risk Factors Have Distinct Patterns of Preclinical Cardiac Dysfunction: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract Body: Introduction
In individuals at risk for heart failure (HF), pre-clinical cardiac dysfunction is a target for preventive interventions. We hypothesized that different HF risk factors are associated with distinct patterns of cardiac dysfunction, with implications for underlying pathophysiology and approaches to screening and prevention.
Methods
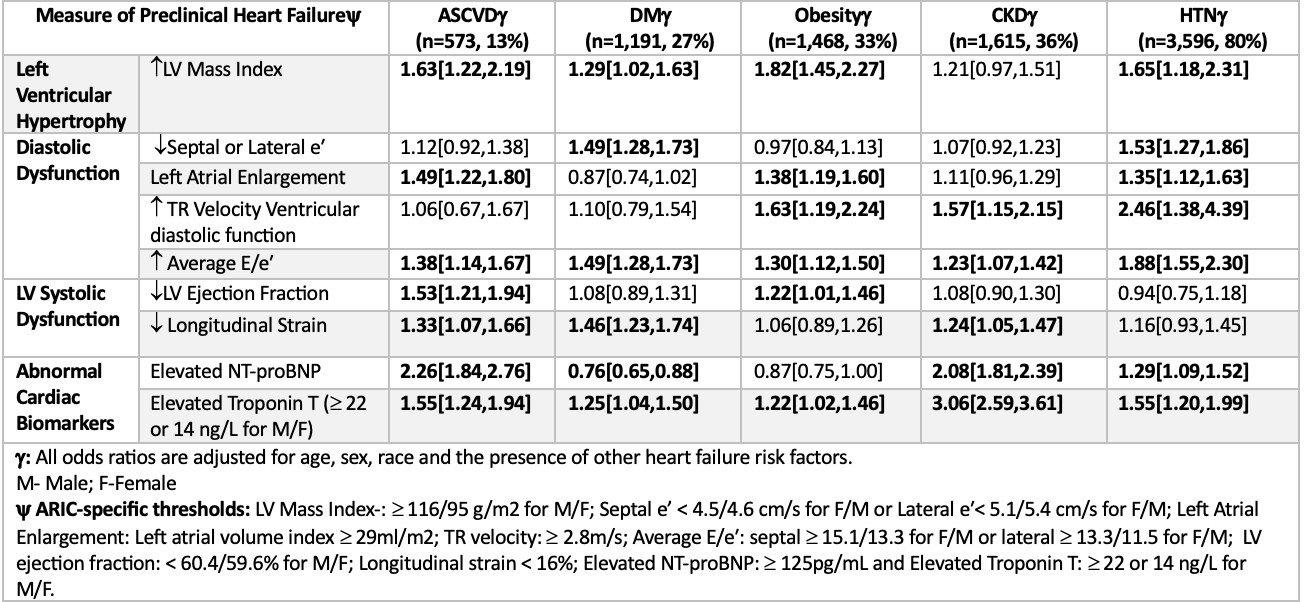
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 4,470 participants without prevalent HF from Visit 5 (2011-13) of the ARIC study with echocardiographic data, cardiac biomarker measurements (the N terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide [NT-proBNP] and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T [hs-cTnT]) and data on HF risk factors (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], obesity, diabetes [DM], hypertension and chronic kidney disease [CKD]). Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess the associations of HF risk factors with different echocardiographic abnormalities and elevated cardiac biomarker levels, adjusted for age, sex, race, and other HF risk factors (Table).
Results
The mean age was 76 years, with 58% women and 20% Black individuals. A total of 2,424 (54.2%) participants had abnormal echocardiographic measures, and 2,169 (48.5%) participants had elevated NT-proBNP or hs-TnT. Among HF risk factors, only ASCVD was independently associated with left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction (Table). In contrast, hypertension was associated with 4/4 indices of LV diastolic dysfunction, obesity 3/4 diastolic indices and CKD, ASCVD and DM with 2/4 diastolic indices. All risk factors were associated with increased LV filling pressures (average E/e'). Obesity was most strongly associated with LV hypertrophy among risk factors. All risk factors were associated with elevated hs-cTnT, but nominally inverse associations with NT-proBNP were seen for both diabetes and obesity.
Conclusion
Different HF risk factors are associated with distinct patterns of preclinical cardiac dysfunction. Tailored approaches to screening and prevention may be needed to most effectively avert the onset of clinical HF for individuals with different risk factor profiles.
In individuals at risk for heart failure (HF), pre-clinical cardiac dysfunction is a target for preventive interventions. We hypothesized that different HF risk factors are associated with distinct patterns of cardiac dysfunction, with implications for underlying pathophysiology and approaches to screening and prevention.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 4,470 participants without prevalent HF from Visit 5 (2011-13) of the ARIC study with echocardiographic data, cardiac biomarker measurements (the N terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide [NT-proBNP] and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T [hs-cTnT]) and data on HF risk factors (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], obesity, diabetes [DM], hypertension and chronic kidney disease [CKD]). Multivariable logistic regression was used to assess the associations of HF risk factors with different echocardiographic abnormalities and elevated cardiac biomarker levels, adjusted for age, sex, race, and other HF risk factors (Table).
Results
The mean age was 76 years, with 58% women and 20% Black individuals. A total of 2,424 (54.2%) participants had abnormal echocardiographic measures, and 2,169 (48.5%) participants had elevated NT-proBNP or hs-TnT. Among HF risk factors, only ASCVD was independently associated with left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction (Table). In contrast, hypertension was associated with 4/4 indices of LV diastolic dysfunction, obesity 3/4 diastolic indices and CKD, ASCVD and DM with 2/4 diastolic indices. All risk factors were associated with increased LV filling pressures (average E/e'). Obesity was most strongly associated with LV hypertrophy among risk factors. All risk factors were associated with elevated hs-cTnT, but nominally inverse associations with NT-proBNP were seen for both diabetes and obesity.
Conclusion
Different HF risk factors are associated with distinct patterns of preclinical cardiac dysfunction. Tailored approaches to screening and prevention may be needed to most effectively avert the onset of clinical HF for individuals with different risk factor profiles.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Dabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic ReviewChaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna