Final ID: MP42
Metabolomic signatures of carbohydrate quantity and quality in association with risk of type 2 diabetes
Abstract Body: Objective
Metabolomic indices that summarize metabolomic responses to diet may be instrumental for the examination and establishment of associations between diet and diseases. We aim to identify metabolomic signatures of the amounts and types of carbohydrate intake and examine their association with type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk.
Research design and methods
The discovery phase utilized data from the Lifestyle Validation Studies, which included 1,196 participants with plasma metabolomics and primary food sources assessed using 7-day dietary records, which included intakes of carbohydrate, added sugar, whole grain, refined grain, vegetable, fruit, potato, and legume. Elastic net regression within a cross-validation framework was used to calculate metabolite profiles correlated with carbohydrate intake. The association of these profiles with incident T2D was investigated using multivariable Cox regression in 11,454 participants from the Nurses' Health Study (NHS), NHS II, and Health Professionals Follow-up Study.
Results
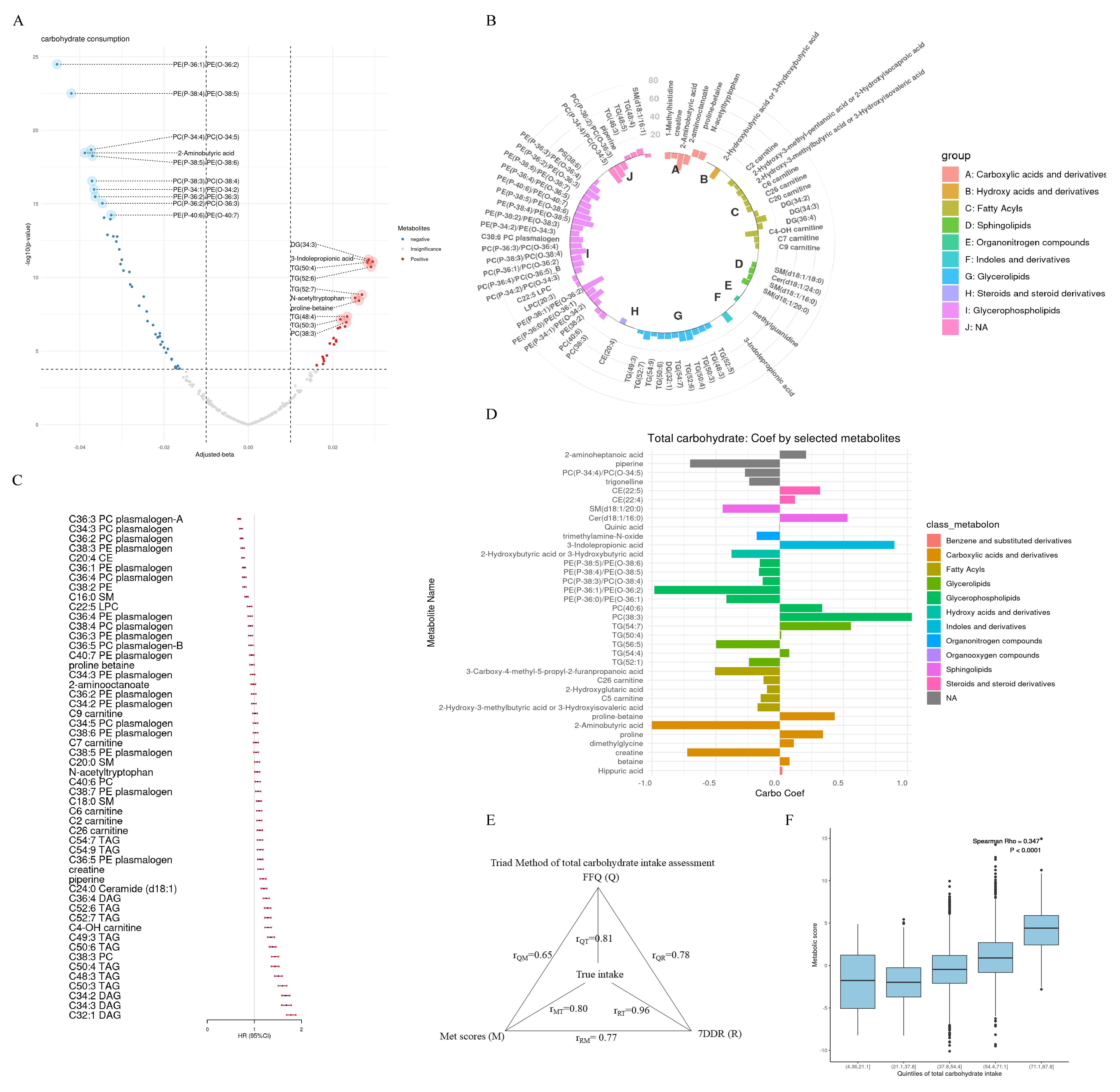
Metabolites positively associated with total carbohydrate and added sugar intake mainly included glycerolipids, while glycerophospholipids were negatively associated with these variables. Whole grain consumption was positively associated with betaine, 3-indolepropionic acid (IPA), and hippuric acid. For vegetables and legumes, IPA, N-acetylornithine, and pipecolic acid were among the top positive metabolites. Fruit was positively associated with proline-betaine and IPA. Identified metabolomic signatures showed significant correlations with carbohydrate intake (Pearson r ranging 0.56-0.80 with true intake assessed using the triad method). Signatures for total carbohydrate, added sugar, refined grain, and potato were positively associated with T2D incidence [HR per SD: 1.07 (1.06-1.12), 1.07 (1.02-1.12), 1.12 (1.07-1.18), and 1.36 (1.29-1.44), respectively]. Conversely, signatures for whole grain, vegetable, fruit, and legume were inversely associated with T2D [HR per SD: 0.73 (0.70-0.77), 0.95 (0.90-0.99), 0.88 (0.83-0.92), and 0.93 (0.88-0.97), respectively].
Conclusions
This study identified a panel of plasma metabolites related to the total and specific types of carbohydrate consumption. The metabolomic signatures of carbohydrate intake from different dietary sources were differentially associated with the risk of T2D. These findings corroborated the observations of carbohydrate intake assessed using questionnaires or other recall-based instruments.
Metabolomic indices that summarize metabolomic responses to diet may be instrumental for the examination and establishment of associations between diet and diseases. We aim to identify metabolomic signatures of the amounts and types of carbohydrate intake and examine their association with type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk.
Research design and methods
The discovery phase utilized data from the Lifestyle Validation Studies, which included 1,196 participants with plasma metabolomics and primary food sources assessed using 7-day dietary records, which included intakes of carbohydrate, added sugar, whole grain, refined grain, vegetable, fruit, potato, and legume. Elastic net regression within a cross-validation framework was used to calculate metabolite profiles correlated with carbohydrate intake. The association of these profiles with incident T2D was investigated using multivariable Cox regression in 11,454 participants from the Nurses' Health Study (NHS), NHS II, and Health Professionals Follow-up Study.
Results
Metabolites positively associated with total carbohydrate and added sugar intake mainly included glycerolipids, while glycerophospholipids were negatively associated with these variables. Whole grain consumption was positively associated with betaine, 3-indolepropionic acid (IPA), and hippuric acid. For vegetables and legumes, IPA, N-acetylornithine, and pipecolic acid were among the top positive metabolites. Fruit was positively associated with proline-betaine and IPA. Identified metabolomic signatures showed significant correlations with carbohydrate intake (Pearson r ranging 0.56-0.80 with true intake assessed using the triad method). Signatures for total carbohydrate, added sugar, refined grain, and potato were positively associated with T2D incidence [HR per SD: 1.07 (1.06-1.12), 1.07 (1.02-1.12), 1.12 (1.07-1.18), and 1.36 (1.29-1.44), respectively]. Conversely, signatures for whole grain, vegetable, fruit, and legume were inversely associated with T2D [HR per SD: 0.73 (0.70-0.77), 0.95 (0.90-0.99), 0.88 (0.83-0.92), and 0.93 (0.88-0.97), respectively].
Conclusions
This study identified a panel of plasma metabolites related to the total and specific types of carbohydrate consumption. The metabolomic signatures of carbohydrate intake from different dietary sources were differentially associated with the risk of T2D. These findings corroborated the observations of carbohydrate intake assessed using questionnaires or other recall-based instruments.
More abstracts on this topic:
Amino acid and organic acid signature in urine of prepubescents with higher cardiometabolic risk evaluated by waist-to-height ratio
Oliveira Lilian Caroline, Azinheira Nobrega Cruz Nayara, Passadore Mariana, Bocato Mariana, Mill Jose Geraldo, Barbosa Jr Fernando, Casarini Dulce Elena
Association of Eicosanoid Metabolites with Body Mass IndexChitsazan Mandana, Ho Jennifer, Parekh Juhi, Lau Emily, Alotaibi Mona, Yu Bing, Allen Norrina, Allison Matthew, Jain Mohit, Cheng Susan