Final ID: 072
Plasma Metabolome Predicts Long-term Body Weight Gain and Type 2 Diabetes in Non-Obese Individuals
Abstract Body: Introduction: Body weight is known to modulate the human blood metabolome, although whether certain plasma metabolomic profiles predict long-term weight change remains unknown.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that there are inter-relationships between plasma metabolome, current weight, weight change, and incident type 2 diabetes (T2D).
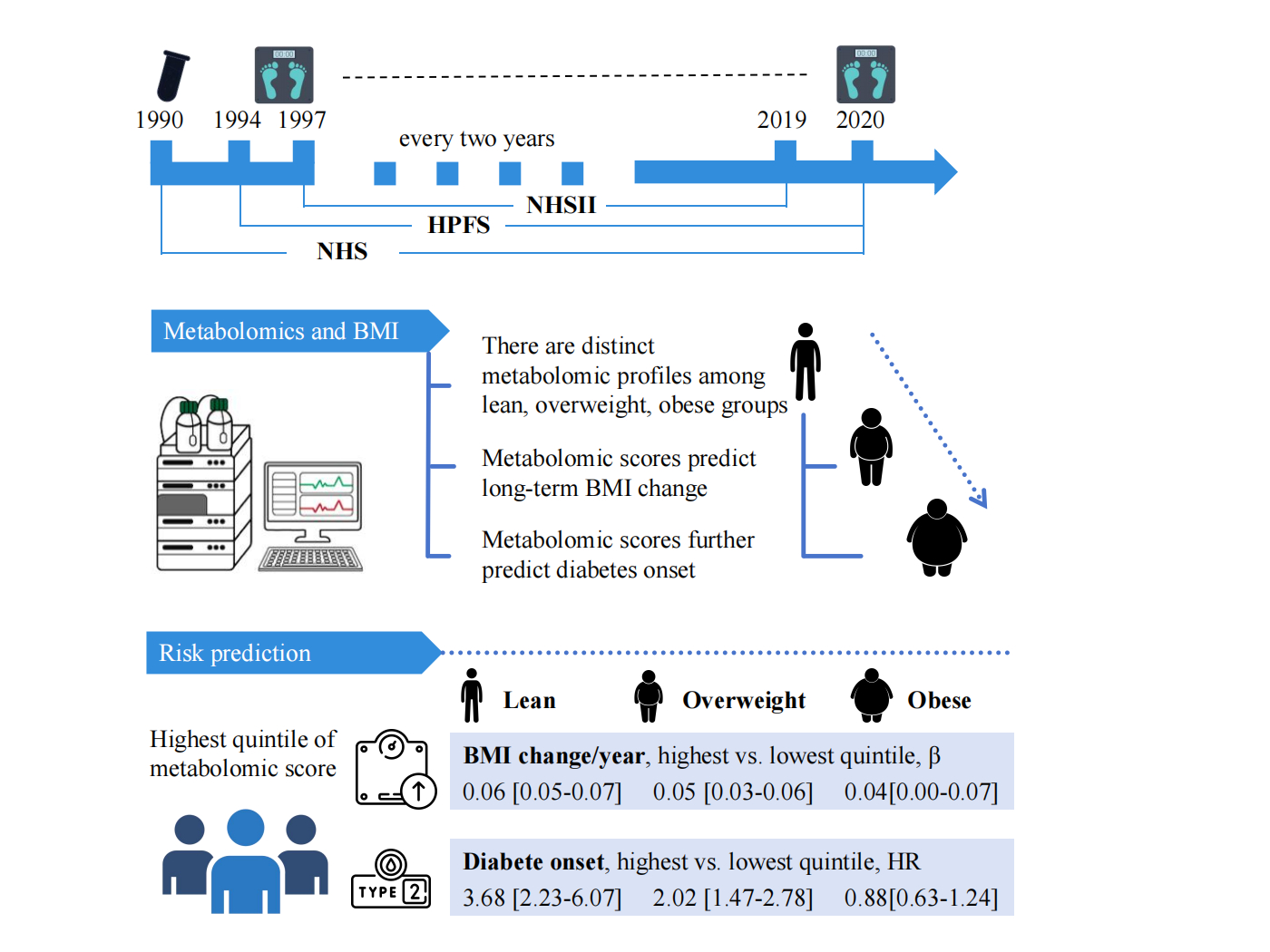
Methods: We measured 260 annotated metabolites among 7, 499 participants in Nurses’ Health Study, Nurses’ Health Study II, and Health Professionals Follow-up Study using nontargeted LC-MS. We assessed the associations of these metabolites and BMI trajectory since blood draw during 26.0 years of follow-up using a mixed-effect model, also by BMI groups at blood draw (lean: 18.5-24.9 kg/m2, overweight: 25.0-29.9 kg/m2, and obese: ≥30 kg/m2). A metabolomic score reflecting BMI change slope was identified using elastic net regression with a training/testing approach. Associations between the metabolomic scores and T2D were evaluated using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results: Cross-sectionally, metabolites associated with current BMI level among lean, overweight, and obese individuals minimally overlapped (of 260 metabolites, 2 overlapping among the three groups). Distinct metabolomic profiles associated with BMI trajectories were also identified among the three groups. While 46 metabolites significantly predicted BMI change slope in the lean group, only 20 and 13 metabolites predicted the slope among overweight and obese groups, respectively, with no metabolites overlapping among the three groups. Among lean individuals, the elastic net regression identified 82 metabolites, predominantly lipids and organic acids, to construct a score that reflected faster BMI gain. The score was significantly associated with the BMI slope in lean group (training: Spearman r = 0.33; testing: Spearman r = 0.20), but the correlation was weaker among overweight, and obese groups (Spearman r = 0.15, and 0.08, respectively). The metabolomic score was significantly associated with a higher risk of T2D in the lean group (aHR per 1SD: 1.41 [95% CI 1.25-1.59]) and overweight group (aHR per 1SD: 1.29 [95% CI 1.17-1.42]) groups, but not in the obese group.
Conclusions: Metabolomic profiles associated with current BMI and BMI trajectory differ significantly among lean, overweight, and obese individuals. A metabolomic score that predicts BMI change is associated with higher T2D risk in lean and overweight individuals, but not among obese individuals.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that there are inter-relationships between plasma metabolome, current weight, weight change, and incident type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods: We measured 260 annotated metabolites among 7, 499 participants in Nurses’ Health Study, Nurses’ Health Study II, and Health Professionals Follow-up Study using nontargeted LC-MS. We assessed the associations of these metabolites and BMI trajectory since blood draw during 26.0 years of follow-up using a mixed-effect model, also by BMI groups at blood draw (lean: 18.5-24.9 kg/m2, overweight: 25.0-29.9 kg/m2, and obese: ≥30 kg/m2). A metabolomic score reflecting BMI change slope was identified using elastic net regression with a training/testing approach. Associations between the metabolomic scores and T2D were evaluated using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results: Cross-sectionally, metabolites associated with current BMI level among lean, overweight, and obese individuals minimally overlapped (of 260 metabolites, 2 overlapping among the three groups). Distinct metabolomic profiles associated with BMI trajectories were also identified among the three groups. While 46 metabolites significantly predicted BMI change slope in the lean group, only 20 and 13 metabolites predicted the slope among overweight and obese groups, respectively, with no metabolites overlapping among the three groups. Among lean individuals, the elastic net regression identified 82 metabolites, predominantly lipids and organic acids, to construct a score that reflected faster BMI gain. The score was significantly associated with the BMI slope in lean group (training: Spearman r = 0.33; testing: Spearman r = 0.20), but the correlation was weaker among overweight, and obese groups (Spearman r = 0.15, and 0.08, respectively). The metabolomic score was significantly associated with a higher risk of T2D in the lean group (aHR per 1SD: 1.41 [95% CI 1.25-1.59]) and overweight group (aHR per 1SD: 1.29 [95% CI 1.17-1.42]) groups, but not in the obese group.
Conclusions: Metabolomic profiles associated with current BMI and BMI trajectory differ significantly among lean, overweight, and obese individuals. A metabolomic score that predicts BMI change is associated with higher T2D risk in lean and overweight individuals, but not among obese individuals.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acetylation of Electron Transfer Flavoprotein Alpha Is a Possible Regulatory Mechanism of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Diabetic Hearts
Tatekoshi Yuki, Yano Masaki, Hosoda Ryusuke, Saga Yukika, Kuno Atsushi
Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Novel Systemic Mediator of Obesity-Related Endothelial DysfunctionBerry Auburn, Desouza Christopher, Ruzzene Samuel, Izaias Joao E., Holzer Joshua, Orozco-fersiva Nathalie, Stone Madeleine, Greiner Jared, Garcia Vinicius, Stauffer Brian