Final ID: Tu108
Improved Skeletal Muscle Metabolism and Exercise Capacity Following Hydrogen Sulfide Therapy in Cardiometabolic HFpEF
Abstract Body: Introduction: Exercise intolerance is the cardinal feature of cardiometabolic HFpEF that is largely driven by impairments in skeletal muscle metabolism and function. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an essential regulator of mitochondrial function and metabolic homeostasis. We have previously demonstrated reductions in skeletal muscle enzymatic H2S production and H2S bioavailability in rodent models of HFpEF. The potential for H2S donor therapy to restore skeletal muscle metabolism and improve exercise capacity in HFpEF has not been explored.
Hypothesis: We tested the hypothesis that oral H2S donor (SG-1002) therapy would restore critical aspects of skeletal muscle metabolism and exercise performance in cardiometabolic HFpEF.
Methods: Five weeks after the onset of HFpEF (high-fat diet + L-NAME) male C57BL6/J mice (n=12 per group) were administered dietary SG-1002 (95 mg/kg/day) for 5 weeks and compared to HFD + L-NAME alone mice (i.e., control). Exercise performance was assessed using forced treadmill and voluntary wheel running (VWR) with continuous monitoring of indirect calorimetry. Skeletal muscle (soleus and gastroc) mitochondrial function was assessed by high-resolution respirometry. Palmitate (fatty acid oxidation, FAO) and leucine (BCAA) oxidation were determined by radiolabeled isotope (14C) assays. A force grid meter was used to determine muscle grip force production. GC-chemiluminescence was used to measure H2S bioavailability.
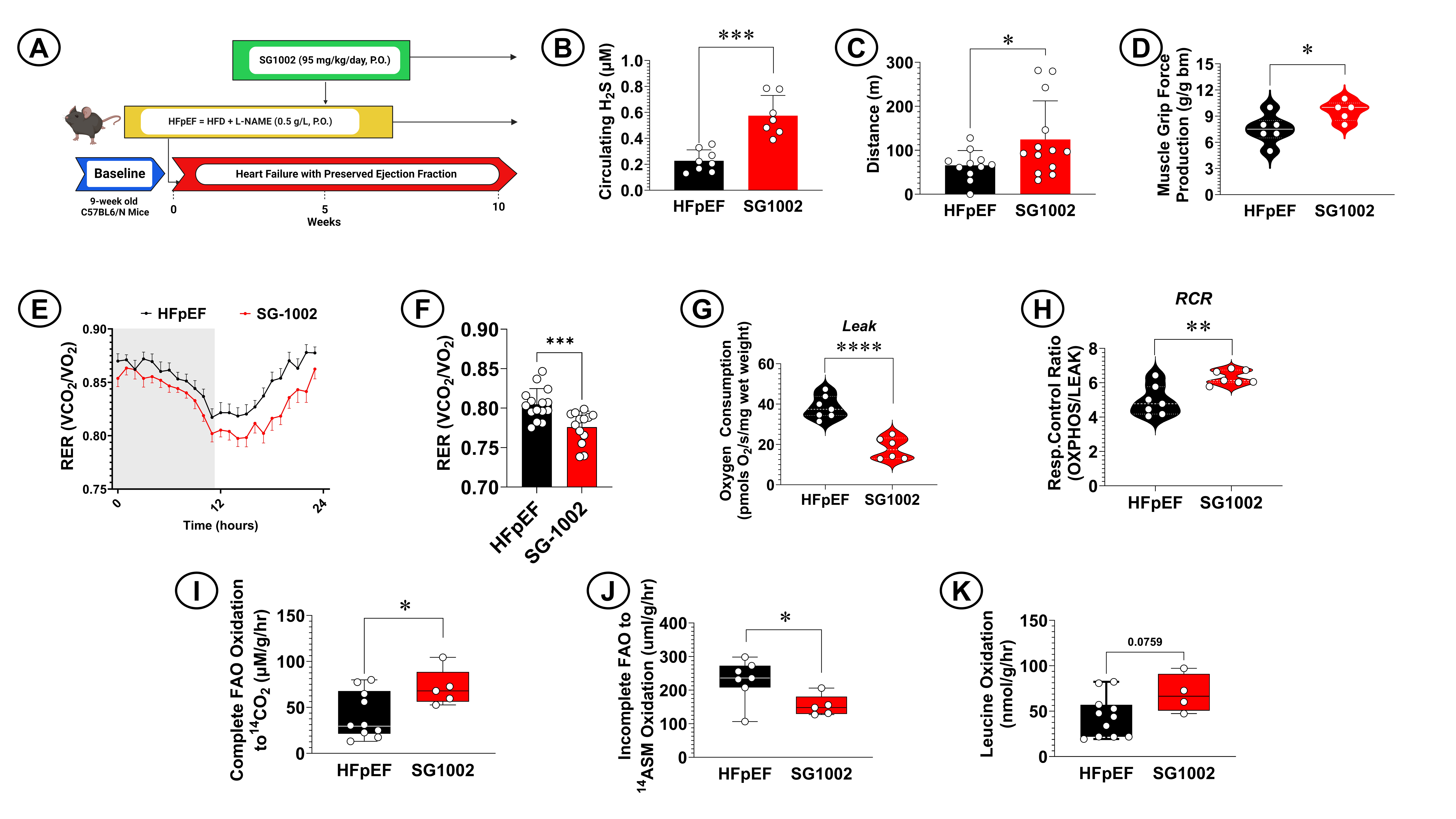
Results: SG-1002 therapy significantly (p < 0.001) increased circulating H2S bioavailability (0.57 ± 0.15 vs. 0.22 ± 0.08 µM) when compared to HFpEF control mice. Forced treadmill running (125 ± 87 vs 64 ± 33 meters), grip force production (9.6± 1.1 vs. 7.5 ± 1.3 g/g lean mass) were increased (p < 0.05 vs. control for both) following SG-1002 treatment. During VWR, whole-body fat oxidation was increased (p=0.0008, 0.3 ± .01 lower RER) in SG-1002-treated mice. At the skeletal muscle level, SG-1002 treatment reduced LEAK state respiration by 52% (p < 0.0001 vs. control) and increased complete FAO by 30% (p < 0.05) while reducing incomplete FAO by 33% (p < 0.05 between groups).
Conclusion: We demonstrate that H2S donor therapy significantly improves exercise capacity and underlying skeletal muscle dysfunction in a mouse “two-hit” model of cardiometabolic HFpEF.
Hypothesis: We tested the hypothesis that oral H2S donor (SG-1002) therapy would restore critical aspects of skeletal muscle metabolism and exercise performance in cardiometabolic HFpEF.
Methods: Five weeks after the onset of HFpEF (high-fat diet + L-NAME) male C57BL6/J mice (n=12 per group) were administered dietary SG-1002 (95 mg/kg/day) for 5 weeks and compared to HFD + L-NAME alone mice (i.e., control). Exercise performance was assessed using forced treadmill and voluntary wheel running (VWR) with continuous monitoring of indirect calorimetry. Skeletal muscle (soleus and gastroc) mitochondrial function was assessed by high-resolution respirometry. Palmitate (fatty acid oxidation, FAO) and leucine (BCAA) oxidation were determined by radiolabeled isotope (14C) assays. A force grid meter was used to determine muscle grip force production. GC-chemiluminescence was used to measure H2S bioavailability.
Results: SG-1002 therapy significantly (p < 0.001) increased circulating H2S bioavailability (0.57 ± 0.15 vs. 0.22 ± 0.08 µM) when compared to HFpEF control mice. Forced treadmill running (125 ± 87 vs 64 ± 33 meters), grip force production (9.6± 1.1 vs. 7.5 ± 1.3 g/g lean mass) were increased (p < 0.05 vs. control for both) following SG-1002 treatment. During VWR, whole-body fat oxidation was increased (p=0.0008, 0.3 ± .01 lower RER) in SG-1002-treated mice. At the skeletal muscle level, SG-1002 treatment reduced LEAK state respiration by 52% (p < 0.0001 vs. control) and increased complete FAO by 30% (p < 0.05) while reducing incomplete FAO by 33% (p < 0.05 between groups).
Conclusion: We demonstrate that H2S donor therapy significantly improves exercise capacity and underlying skeletal muscle dysfunction in a mouse “two-hit” model of cardiometabolic HFpEF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abrupt cardiac rupture of the patient with ATTR amyloidosis
Tagata Kento, Yutaro Nomoto, Tao Koji, Kataoka Tetsuro, Ohishi Mitsuru
A mechanism whereby SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin reverses cardiac diastolic dysfunction in a model of HFpEFLiu Man, Liu Hong, Kang Gyeoung-jin, Kim Eunji, Neumann Mitchell, Johnson Madeline, Murikinati Ruthvika, Dudley Samuel