Final ID:
ECG deep learning model accurately predicts ischemic stroke risk
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Stroke continues to present a significant burden of morbidity and disability worldwide. Effective risk stratification could enable targeted prevention by identifying patients at high risk who may benefit from intensive monitoring. Although clinical risk scores such as the Framingham Stroke Risk Profile (FSRP) exist, their complexity and difficulty in clinical application limit widespread use.
Methods:
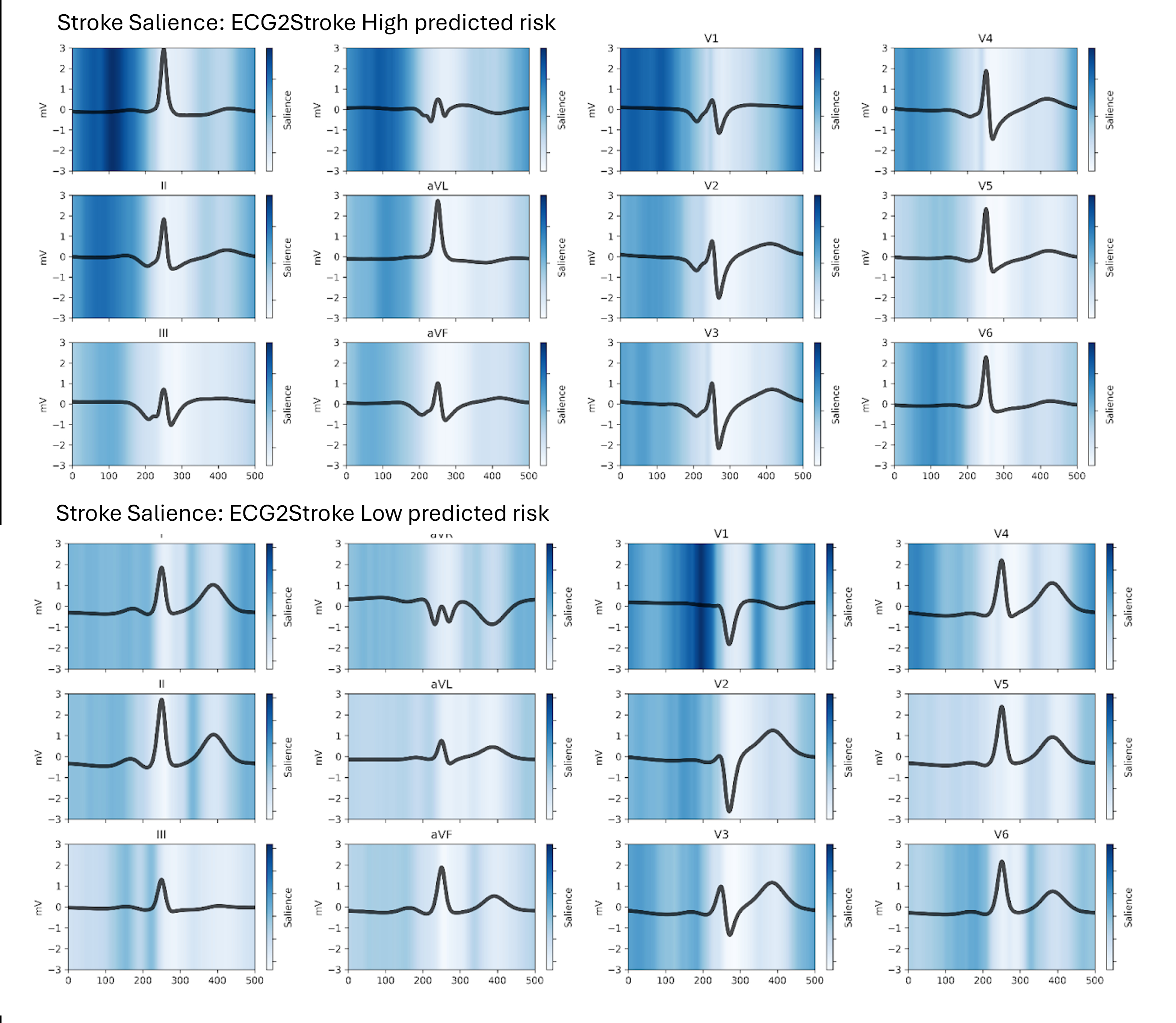
Leveraging electronic health record (EHR) and electrocardiographic (ECG) data from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BI), we developed ECG2Stroke, a deep learning model using baseline ECG data to predict 10-year ischemic stroke risk in patients without prior stroke. ECG2Stroke performance was compared to FSRP and CHADS2VASC using univariate Cox proportional hazards models. Saliency maps highlighted ECG segments differentiating predicted high- and low-risk patients.
Results:
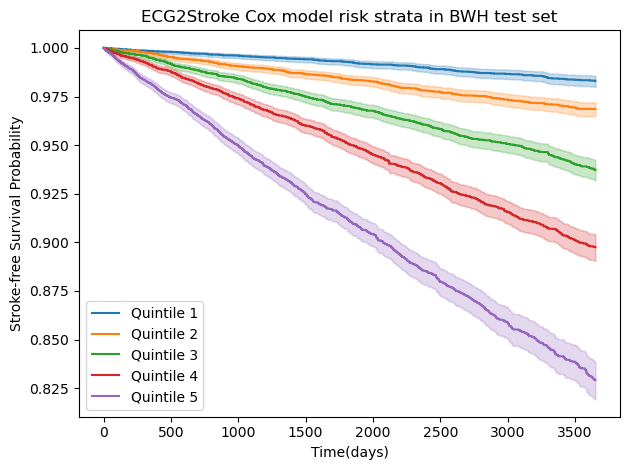
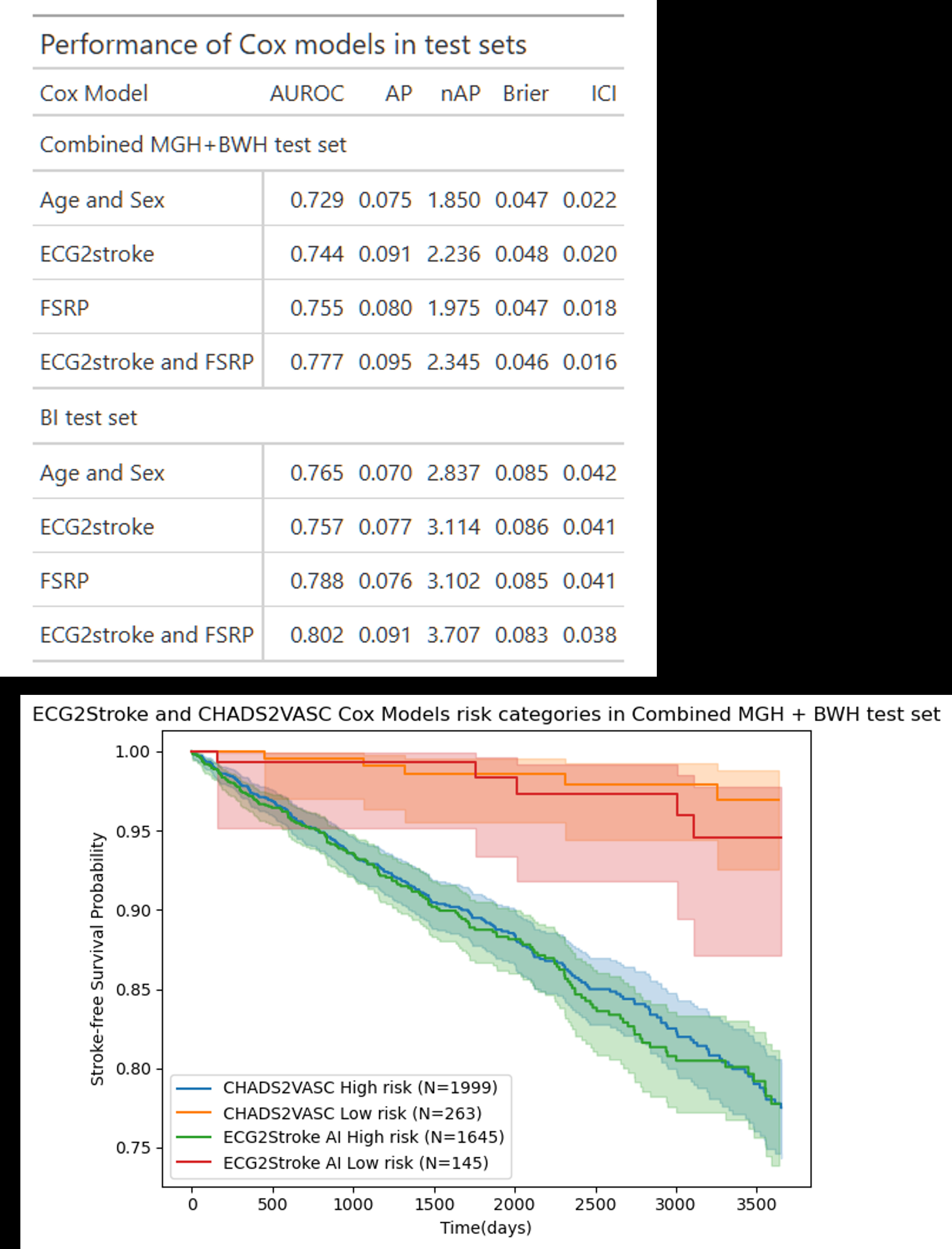
The training set included 101,496 MGH patients, with test sets from MGH (n=4,771), BWH (n=68,884), and BI (n=28,586). ECG2Stroke demonstrated strong predictive performance across test sets (AUROC: MGH=0.766, BWH=0.755, BI=0.811; AP: MGH=0.202, BWH=0.127, BI=0.237) and excellent calibration (Integrated Calibration Index: MGH=0.029, BWH=0.008, BI=0.018). Performance was comparable to FSRP. In atrial fibrillation patients not on anticoagulation, no significant differences in stroke-free survival were observed between low (<0.05) and high (>0.20) risk strata defined by ECG2stroke vs CHADS2VASC.
Conclusions:
The ECG2Stroke deep learning model, utilizing baseline ECG alone, demonstrates comparable accuracy to established clinical risk scores, offering a practical tool for ischemic stroke risk prediction in diverse patient populations.
Stroke continues to present a significant burden of morbidity and disability worldwide. Effective risk stratification could enable targeted prevention by identifying patients at high risk who may benefit from intensive monitoring. Although clinical risk scores such as the Framingham Stroke Risk Profile (FSRP) exist, their complexity and difficulty in clinical application limit widespread use.
Methods:
Leveraging electronic health record (EHR) and electrocardiographic (ECG) data from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BI), we developed ECG2Stroke, a deep learning model using baseline ECG data to predict 10-year ischemic stroke risk in patients without prior stroke. ECG2Stroke performance was compared to FSRP and CHADS2VASC using univariate Cox proportional hazards models. Saliency maps highlighted ECG segments differentiating predicted high- and low-risk patients.
Results:
The training set included 101,496 MGH patients, with test sets from MGH (n=4,771), BWH (n=68,884), and BI (n=28,586). ECG2Stroke demonstrated strong predictive performance across test sets (AUROC: MGH=0.766, BWH=0.755, BI=0.811; AP: MGH=0.202, BWH=0.127, BI=0.237) and excellent calibration (Integrated Calibration Index: MGH=0.029, BWH=0.008, BI=0.018). Performance was comparable to FSRP. In atrial fibrillation patients not on anticoagulation, no significant differences in stroke-free survival were observed between low (<0.05) and high (>0.20) risk strata defined by ECG2stroke vs CHADS2VASC.
Conclusions:
The ECG2Stroke deep learning model, utilizing baseline ECG alone, demonstrates comparable accuracy to established clinical risk scores, offering a practical tool for ischemic stroke risk prediction in diverse patient populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Personal Risk Assessment Device in Patients with Chest Pain
Shvilkin Alexei, Zlatic Natasa, Atanasoski Vladimir, Grujovic Zdolsek Sanja, Popovic Maneski Lana, Miletic Marjan, Vukcevic Vladan
A Machine Learning-Derived Socio-Environmental Risk Score More Accurately Predicts Cardiovascular Events and Better Addresses Health Inequities than Social Deprivation IndexChen Zhuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Rajagopalan Sanjay, Ponnana Sai Rahul, Dazard Jean-eudes, Zhang Tong, Dong Weichuan, Okyere Robert, Sirasapalli Santosh, Deo Salil, Khraishah Haitham