Final ID: Su2129
Efficacy and Safety of Obicetrapib in Dyslipidemia or Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Obicetrapib is a next-generation cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor. It has emerged as a promising agent for improving lipid parameters and potentially reducing risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Methods: A systematic search of databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Clinical Trials, and Cochrane Library, was conducted to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Outcomes included the assessment of LDL-C reduction, changes in ApoB, non-HDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, Lp(a), MACE, as well as the safety and tolerability profile of Obicetrapib in patients with dyslipidemia or ASCVD. Standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were pooled using random-effects.
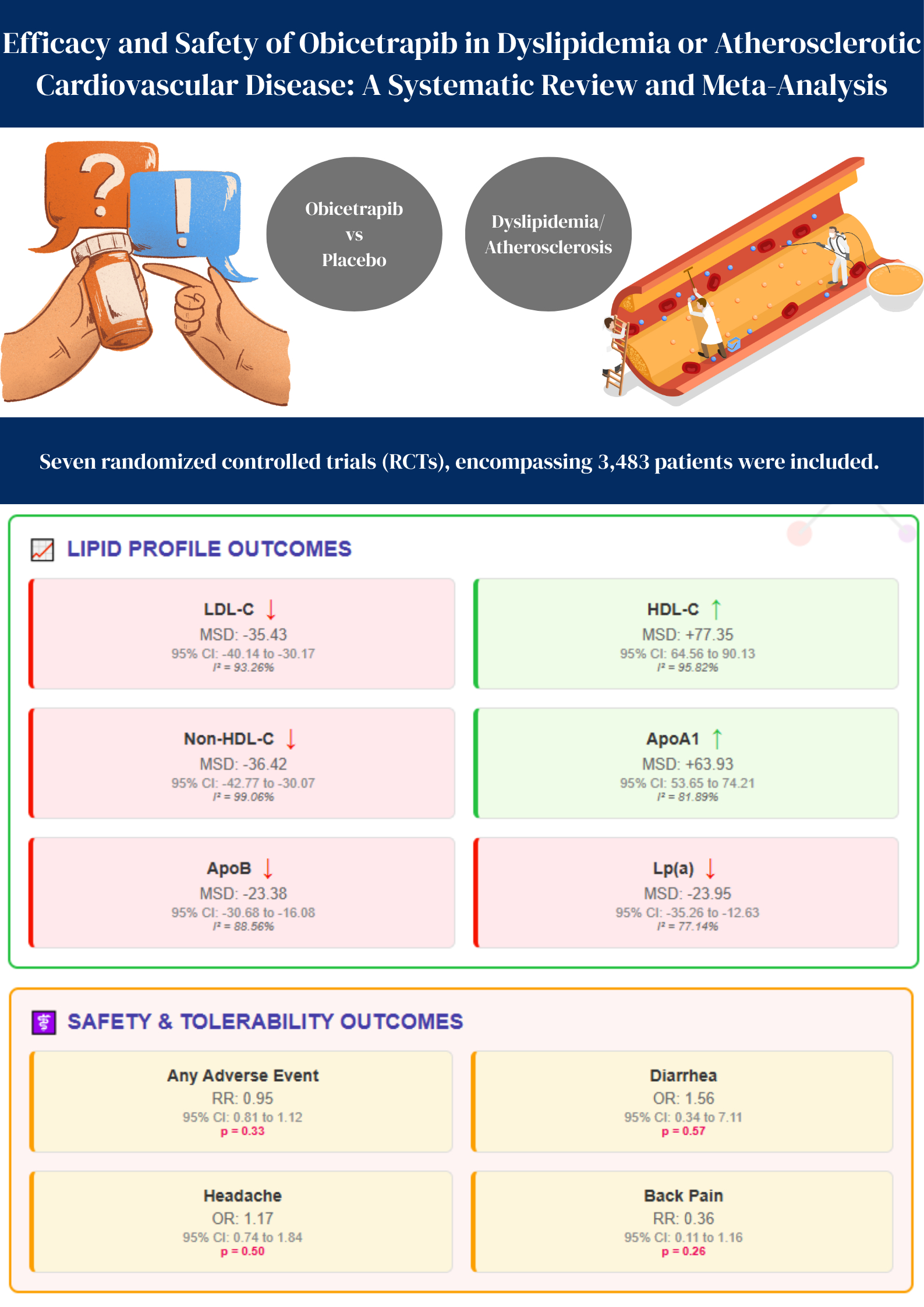
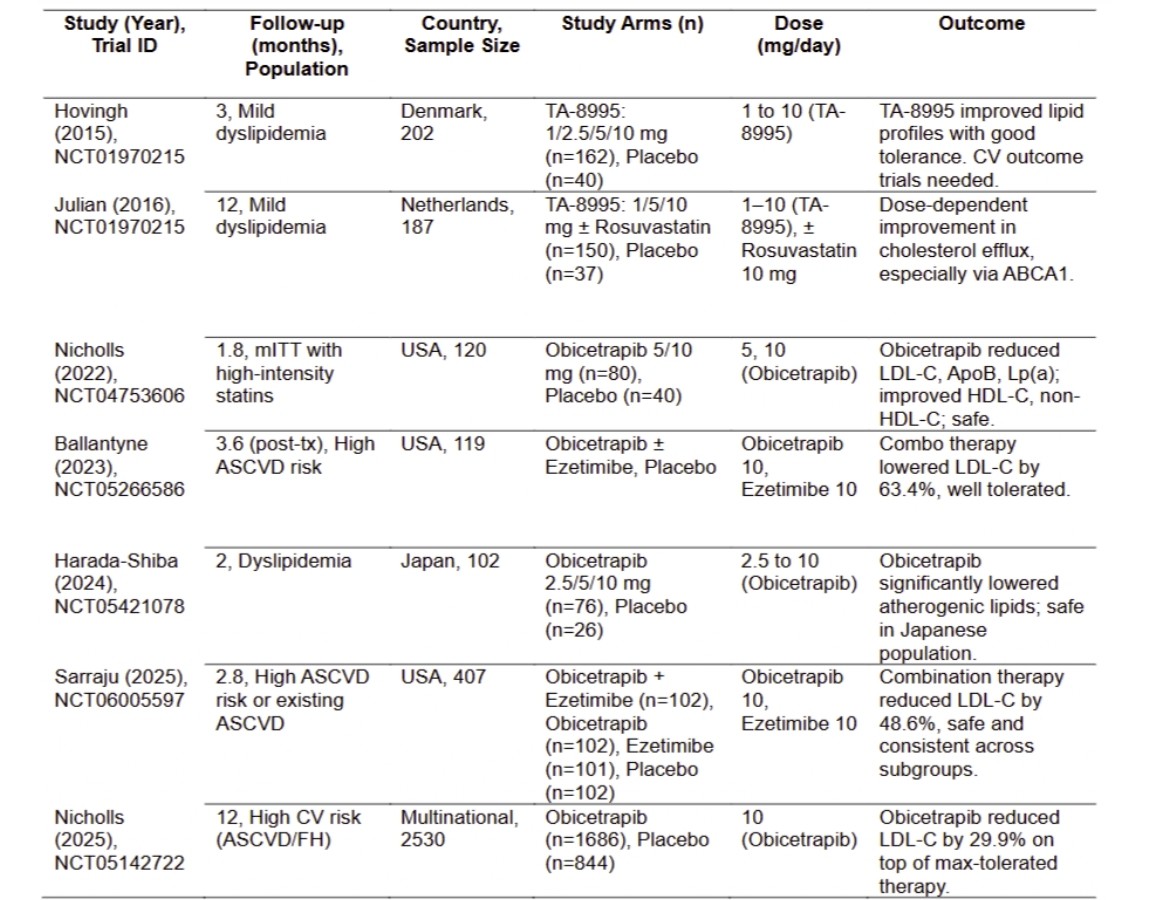
Results: Seven RCTs encompassing 3483 patients were included. Obicetrapib significantly improved lipid parameters. It reduced LDL-C (MSD: –35.43; 95% CI: –40.14 to –30.17; I2 = 93.26%), non-HDL-C (MSD: –36.42; 95% CI: –42.77 to –30.07; I2 = 99.06%), ApoB (MSD: –23.38; 95% CI: –30.68 to –16.08; I2 = 88.56%), and Lp(a) (MSD: –23.95; 95% CI: –35.26 to –12.63; I2 = 77.14%). Obicetrapib also led to a reduction in TG levels (MSD: –0.12; 95% CI: –0.19 to –0.05; I2 = 0.00%). In contrast, favorable increases were observed in HDL-C (MSD: 77.35; 95% CI: 64.56 to 90.13; I2 = 95.82%) and ApoA1 (MSD: 63.93; 95% CI: 53.65 to 74.21; I2 = 81.89%). Despite high heterogeneity, these results support Obicetrapib’s effectiveness in improving atherogenic lipid markers.
Obicetrapib demonstrated a safety profile comparable to placebo. The overall risk of any adverse event was slightly reduced in the Obicetrapib group compared to placebo, but the 95% CI included 1, (RR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.76 to 1.21; I2 = 66.3%; p = 0.01). Specific adverse events such as diarrhea (OR: 1.56; 95% CI: 0.34 to 7.11; I2 = 5.16%; p = 0.57), headache (OR: 1.17; 95% CI: 0.74 to 1.84; I2 = 0.00%; p = 0.50), and back pain (RR: 0.36; 95% CI: 0.11 to 1.16; I2 = 18.3%; p = 0.26) were also not significantly different between groups. Overall, Obicetrapib appears well-tolerated without increased adverse events.
Conclusion: Obicetrapib significantly improved lipid parameters, notably reducing LDL-C, non-HDL-C, ApoB, Lp(a), and triglycerides, while increasing HDL-C and ApoA1, with a favorable and comparable safety profile.
Methods: A systematic search of databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Clinical Trials, and Cochrane Library, was conducted to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Outcomes included the assessment of LDL-C reduction, changes in ApoB, non-HDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, Lp(a), MACE, as well as the safety and tolerability profile of Obicetrapib in patients with dyslipidemia or ASCVD. Standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were pooled using random-effects.
Results: Seven RCTs encompassing 3483 patients were included. Obicetrapib significantly improved lipid parameters. It reduced LDL-C (MSD: –35.43; 95% CI: –40.14 to –30.17; I2 = 93.26%), non-HDL-C (MSD: –36.42; 95% CI: –42.77 to –30.07; I2 = 99.06%), ApoB (MSD: –23.38; 95% CI: –30.68 to –16.08; I2 = 88.56%), and Lp(a) (MSD: –23.95; 95% CI: –35.26 to –12.63; I2 = 77.14%). Obicetrapib also led to a reduction in TG levels (MSD: –0.12; 95% CI: –0.19 to –0.05; I2 = 0.00%). In contrast, favorable increases were observed in HDL-C (MSD: 77.35; 95% CI: 64.56 to 90.13; I2 = 95.82%) and ApoA1 (MSD: 63.93; 95% CI: 53.65 to 74.21; I2 = 81.89%). Despite high heterogeneity, these results support Obicetrapib’s effectiveness in improving atherogenic lipid markers.
Obicetrapib demonstrated a safety profile comparable to placebo. The overall risk of any adverse event was slightly reduced in the Obicetrapib group compared to placebo, but the 95% CI included 1, (RR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.76 to 1.21; I2 = 66.3%; p = 0.01). Specific adverse events such as diarrhea (OR: 1.56; 95% CI: 0.34 to 7.11; I2 = 5.16%; p = 0.57), headache (OR: 1.17; 95% CI: 0.74 to 1.84; I2 = 0.00%; p = 0.50), and back pain (RR: 0.36; 95% CI: 0.11 to 1.16; I2 = 18.3%; p = 0.26) were also not significantly different between groups. Overall, Obicetrapib appears well-tolerated without increased adverse events.
Conclusion: Obicetrapib significantly improved lipid parameters, notably reducing LDL-C, non-HDL-C, ApoB, Lp(a), and triglycerides, while increasing HDL-C and ApoA1, with a favorable and comparable safety profile.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled Hypertension
Nandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan
AHA Life's essential 8 and ideal cardiovascular health among adult swimmersTiozzo Eduard, Henley Cynthia, Jones Caroline, Perry Fredrick, Viscovich Isabella, Johnson Giana, Gardener Hannah, Yu Kerstin