Final ID: MP1965
Impact of Hyper-Polypharmacy on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome: Analysis Form the ATLAS ACS 2-TIMI 51 Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Polypharmacy is increasingly prevalent among patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) due to the burden of multimorbidity and guideline-recommended therapies. However, the impact of polypharmacy on cardiovascular (CV) outcomes in ACS remains uncertain.
Aims:
To determine the relationship between polypharmacy and major adverse CV events (MACE, defined as the composite of CV death, myocardial infarction [MI], or stroke) among patients with ACS.
Methods:
The ATLAS ACS 2-TIMI 51 trial randomized patients with recent ACS to receive twice-daily doses of either 2.5 mg or 5 mg of rivaroxaban or placebo. Patients were categorized into three groups based on the number of baseline concomitant medications: non-polypharmacy (0–4), polypharmacy (5–9), and hyper-polypharmacy (≥10). Cumulative incidence of events over 720 days was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The association between polypharmacy status and MACE was assessed using the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards models.
Results:
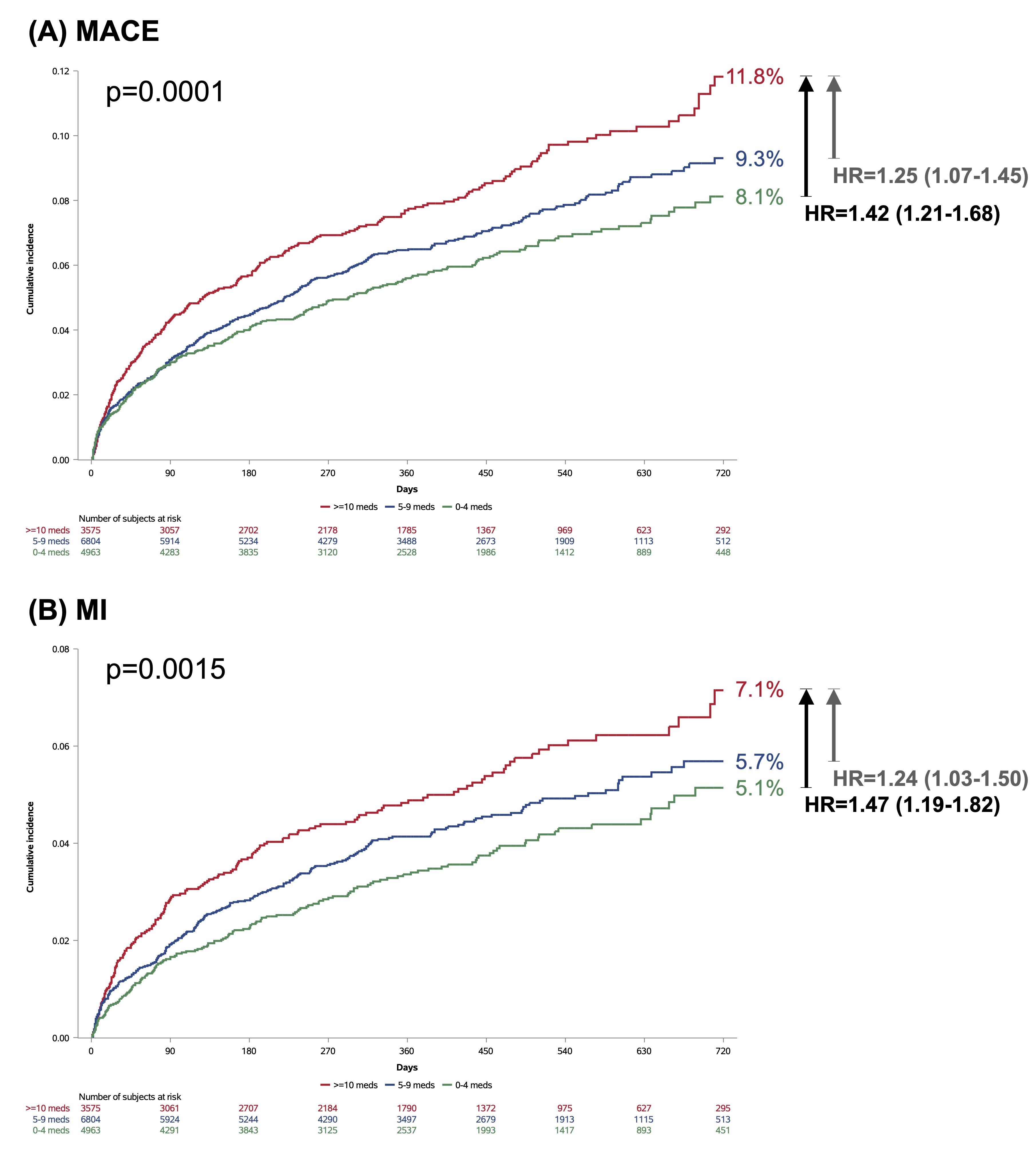
Among 15,342 ACS patients, 6,804 (44.3%) were in the polypharmacy group and 3,575 (23.3%) in the hyper-polypharmacy group. Hyper-polypharmacy was associated with a greater risk of MACE compared to both polypharmacy and non-polypharmacy groups (11.8% vs. 9.3% vs. 8.1%; p = 0.0001; HR = 1.25 [95% CI: 1.07–1.45] and HR = 1.42 [95% CI: 1.21–1.68], respectively). A similar pattern was observed for MI (7.1% vs. 5.7% vs. 5.1%; p = 0.0015; HR = 1.24 [95% CI: 1.03–1.50] and HR = 1.47 [95% CI: 1.19–1.82]). There were no significant differences in the incidence of CV death or stroke across polypharmacy categories. The efficacy of rivaroxaban was not significantly modified by polypharmacy status (p for interaction = 0.93).
Conclusions:
Among patients with ACS, hyper-polypharmacy was common and associated with an increased risk of MACE, primarily driven by a higher incidence of MI. These findings underscore the need for future research to investigate how medication burden, treatment appropriateness, and potential drug–drug interactions influence CV outcomes in this population.
Polypharmacy is increasingly prevalent among patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) due to the burden of multimorbidity and guideline-recommended therapies. However, the impact of polypharmacy on cardiovascular (CV) outcomes in ACS remains uncertain.
Aims:
To determine the relationship between polypharmacy and major adverse CV events (MACE, defined as the composite of CV death, myocardial infarction [MI], or stroke) among patients with ACS.
Methods:
The ATLAS ACS 2-TIMI 51 trial randomized patients with recent ACS to receive twice-daily doses of either 2.5 mg or 5 mg of rivaroxaban or placebo. Patients were categorized into three groups based on the number of baseline concomitant medications: non-polypharmacy (0–4), polypharmacy (5–9), and hyper-polypharmacy (≥10). Cumulative incidence of events over 720 days was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The association between polypharmacy status and MACE was assessed using the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards models.
Results:
Among 15,342 ACS patients, 6,804 (44.3%) were in the polypharmacy group and 3,575 (23.3%) in the hyper-polypharmacy group. Hyper-polypharmacy was associated with a greater risk of MACE compared to both polypharmacy and non-polypharmacy groups (11.8% vs. 9.3% vs. 8.1%; p = 0.0001; HR = 1.25 [95% CI: 1.07–1.45] and HR = 1.42 [95% CI: 1.21–1.68], respectively). A similar pattern was observed for MI (7.1% vs. 5.7% vs. 5.1%; p = 0.0015; HR = 1.24 [95% CI: 1.03–1.50] and HR = 1.47 [95% CI: 1.19–1.82]). There were no significant differences in the incidence of CV death or stroke across polypharmacy categories. The efficacy of rivaroxaban was not significantly modified by polypharmacy status (p for interaction = 0.93).
Conclusions:
Among patients with ACS, hyper-polypharmacy was common and associated with an increased risk of MACE, primarily driven by a higher incidence of MI. These findings underscore the need for future research to investigate how medication burden, treatment appropriateness, and potential drug–drug interactions influence CV outcomes in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning-Based Novel Risk Score Model for Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
Agrawal Ankit, Arockiam Aro Daniela, Bhagat Umesh, Haroun Elio, Majid Muhammad, Wang Tom Kai Ming
2-Deoxyuridine Associates with Recurrent Coronary EventsPistritu Dan, Castano David, Liehn Elisa, Koh Cho Yeow, Gerszten Robert, Singaraja Roshni, Chan Mark, Shah Svati