Final ID: MP260
Multimodal Radiomics and Machine Learning for Predicting Hemorrhagic Transformation After Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis and External Validation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Hemorrhagic transformation (HT) is a common outcome of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), especially following thrombolytic or endovascular reperfusion therapy. Early detection of HT may guide therapeutic decisions and reduce risk. With the advancement of artificial intelligence in neuroimaging, several studies have investigated machine learning (ML) and radiomics models for predicting HT using imaging and clinical data.
Objective:
The purpose of this meta-analysis was to analyze the diagnostic efficacy of ML-based radiomic models for predicting HT after AIS and their generalizability via external validation.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of works published until May 2025 using PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, and IEEE Xplore. The inclusion criteria were studies that used ML-based radiomic or deep learning models with CT, MRI, or multimodal imaging to predict HT in AIS patients. A bivariate random-effects model was used to examine the pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-SROC). The risk of bias was assessed using the QUADAS-2 method. Subgroup analyses were performed based on the imaging modality and algorithm type. An external validation cohort (n=1,150) was used to assess the generalizability of top-performing models.
Results:
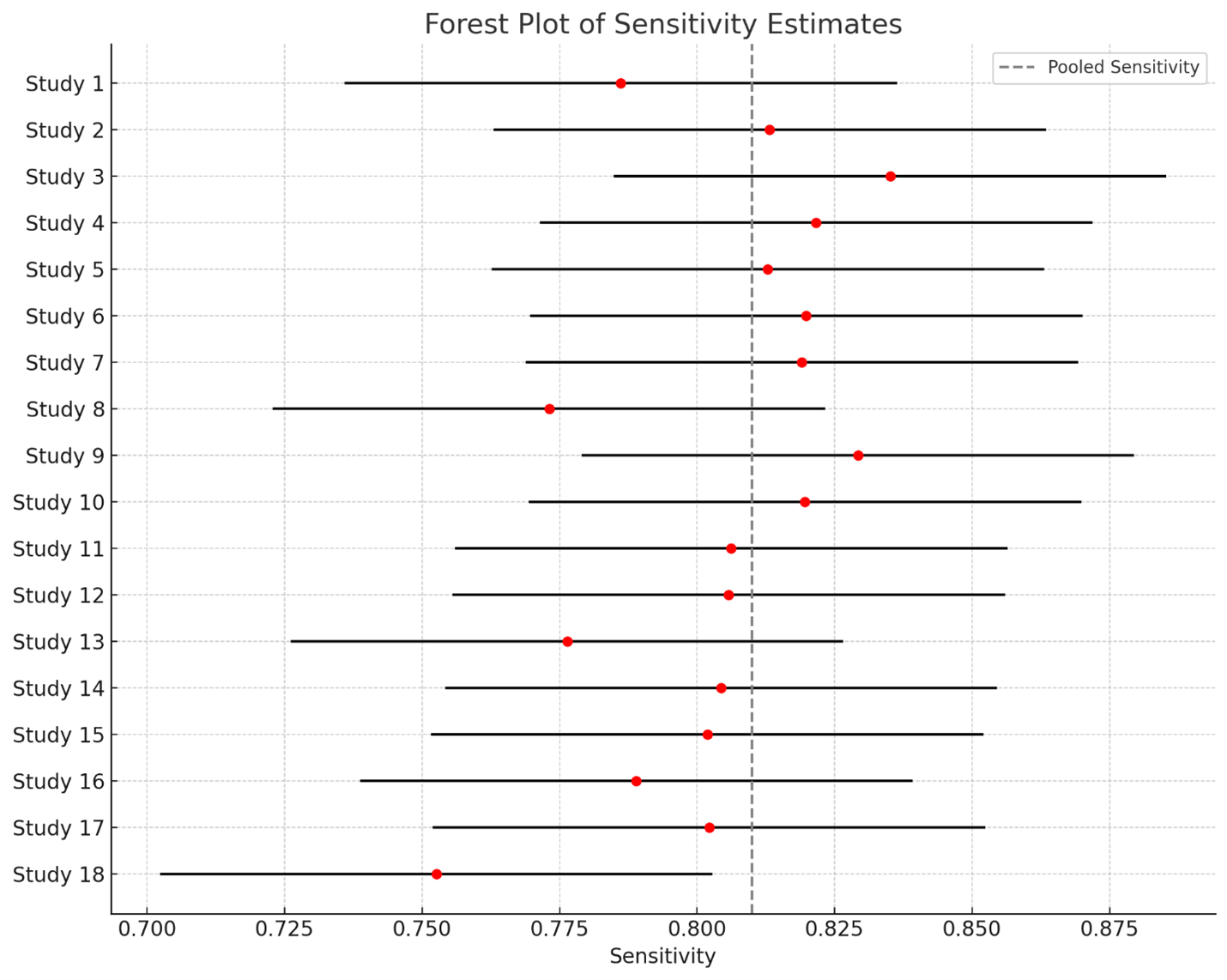
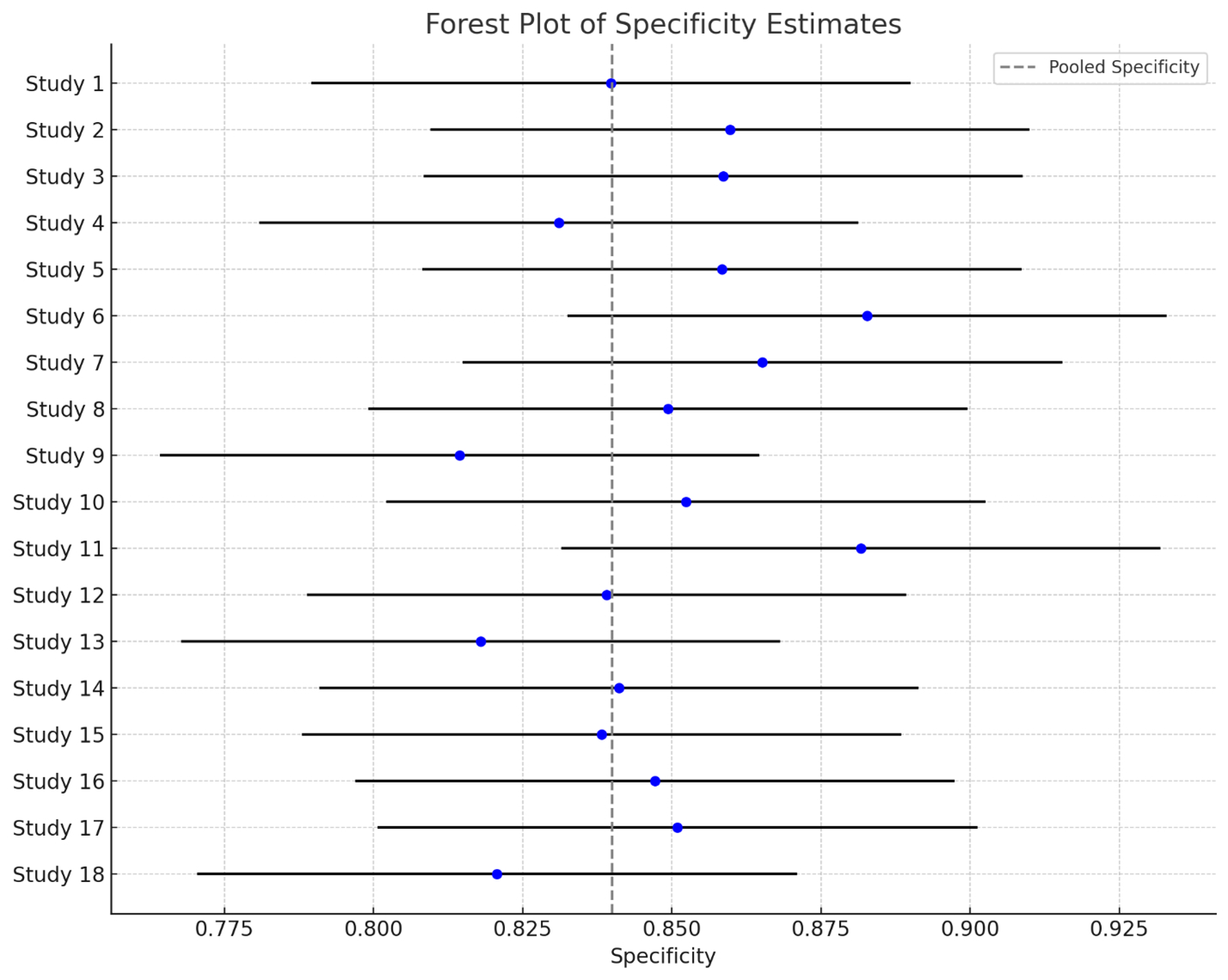
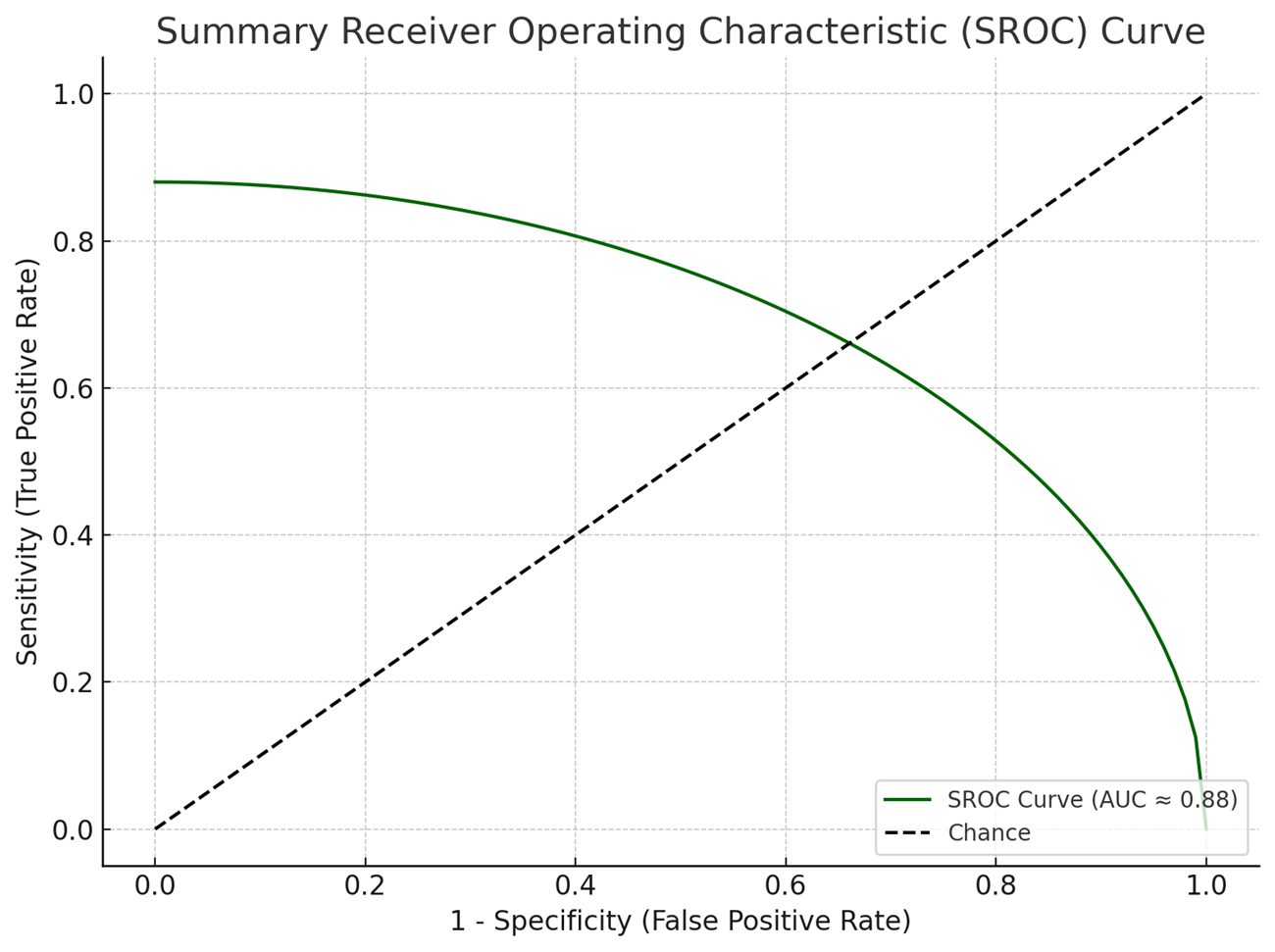
18 studies (n = 3,945 patients; ~455 with HT) met the inclusion criteria. The pooled sensitivity and specificity for machine learning-based radiomics models were 0.81 (95% CI: 0.78-0.84) and 0.84 (95% CI: 0.80-0.88), respectively, with a diagnostic odds ratio of 22.5 (95% CI: 15.0-33.8). The overall AUC-SROC value was 0.88 (95% CI: 0.85–0.91). MRI-based models outperformed CT-only models (AUC: 0.85; p = 0.01). yielded an AUC of 0.87, sensitivity of 0.83, and specificity of 0.82, indicating generalizability. There was no significant publication bias, and heterogeneity was large (I square = 46%).
Conclusion:
ML-based radiomics models that use multimodal neuroimaging show high prediction for hemorrhagic transition after AIS, with consistent results across modalities and external datasets. MRI-based models provide marginally higher diagnosis accuracy.
Hemorrhagic transformation (HT) is a common outcome of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), especially following thrombolytic or endovascular reperfusion therapy. Early detection of HT may guide therapeutic decisions and reduce risk. With the advancement of artificial intelligence in neuroimaging, several studies have investigated machine learning (ML) and radiomics models for predicting HT using imaging and clinical data.
Objective:
The purpose of this meta-analysis was to analyze the diagnostic efficacy of ML-based radiomic models for predicting HT after AIS and their generalizability via external validation.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of works published until May 2025 using PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, and IEEE Xplore. The inclusion criteria were studies that used ML-based radiomic or deep learning models with CT, MRI, or multimodal imaging to predict HT in AIS patients. A bivariate random-effects model was used to examine the pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-SROC). The risk of bias was assessed using the QUADAS-2 method. Subgroup analyses were performed based on the imaging modality and algorithm type. An external validation cohort (n=1,150) was used to assess the generalizability of top-performing models.
Results:
18 studies (n = 3,945 patients; ~455 with HT) met the inclusion criteria. The pooled sensitivity and specificity for machine learning-based radiomics models were 0.81 (95% CI: 0.78-0.84) and 0.84 (95% CI: 0.80-0.88), respectively, with a diagnostic odds ratio of 22.5 (95% CI: 15.0-33.8). The overall AUC-SROC value was 0.88 (95% CI: 0.85–0.91). MRI-based models outperformed CT-only models (AUC: 0.85; p = 0.01). yielded an AUC of 0.87, sensitivity of 0.83, and specificity of 0.82, indicating generalizability. There was no significant publication bias, and heterogeneity was large (I square = 46%).
Conclusion:
ML-based radiomics models that use multimodal neuroimaging show high prediction for hemorrhagic transition after AIS, with consistent results across modalities and external datasets. MRI-based models provide marginally higher diagnosis accuracy.
More abstracts on this topic:
3-HKA Promotes the Vascular Remodeling after Stroke by Modulating the Activation of A1/A2 Reactive Astrocytes
Chen Jun-min, Shi Guang, Yu Lulu, Shan Wei, Zhang Xiangjian, Wang Qun
A Case Series of Papillary Fibroelastomas on the Coumadin ridgeAboukhatwa Omar, Akiki Elias, Kurmann Reto, Larson Kathryn, Keeney Michael, Bois Melanie, Klarich Kyle