Final ID: MP958
Effective Atomic Numbers and Electron Density of Focal Peri-Pulmonary Arterial Adipose Tissue on Spectral CT Can Predict Elevated Pulmonary Arterial Systolic Pressure in Patients without Coronary Arterial, Myocardial, and Valvular Diseases
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Inflammation in pericoronary adipose tissue may occur focally at adjacent plaque sites in the coronary arterial system. Similarly, inflammation in peri-pulmonary arterial (PA) adipose tissue may occur focally at pulmonary arterial (PA) system.
Hypothesis: Using effective atomic numbers (EANs) and electron density (ED) determined by spectral CT as new parameters, the focal characteristics of peri-PA adipose tissue is useful to predict elevated PA systolic pressure.
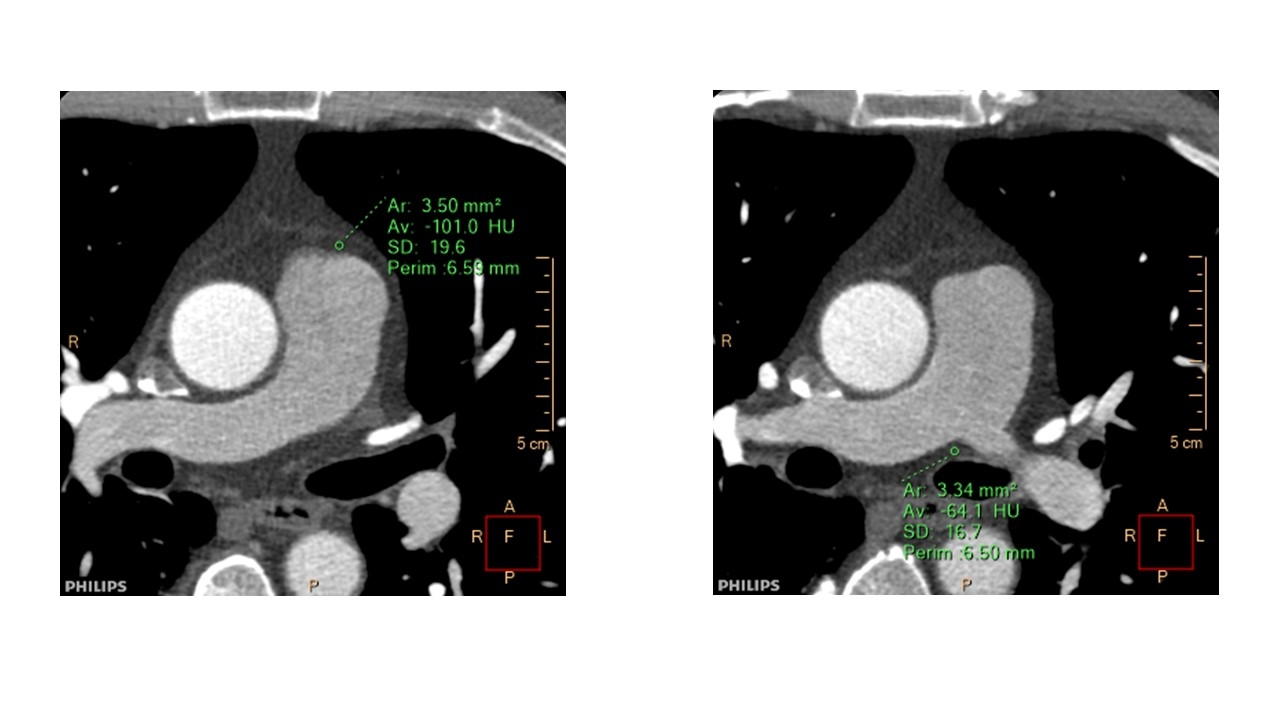
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis of 20 patients (7 male, mean age 54 year old) who underwent dual energy CT (7500, Philips) because of clinically suspected coronary artery diseases, but no significant stenosis in the coronary arteries on CT, and with normal ECG and transthoracic echocardiogram findings. From non-contrast and contrast data, EANs and EDs (% electron density relative to water) of peri-PA adipose tissue were determined at two sites in each patient as represented in Figure 1. We compared tricuspid regurgitation pressure gradient (mmHg).
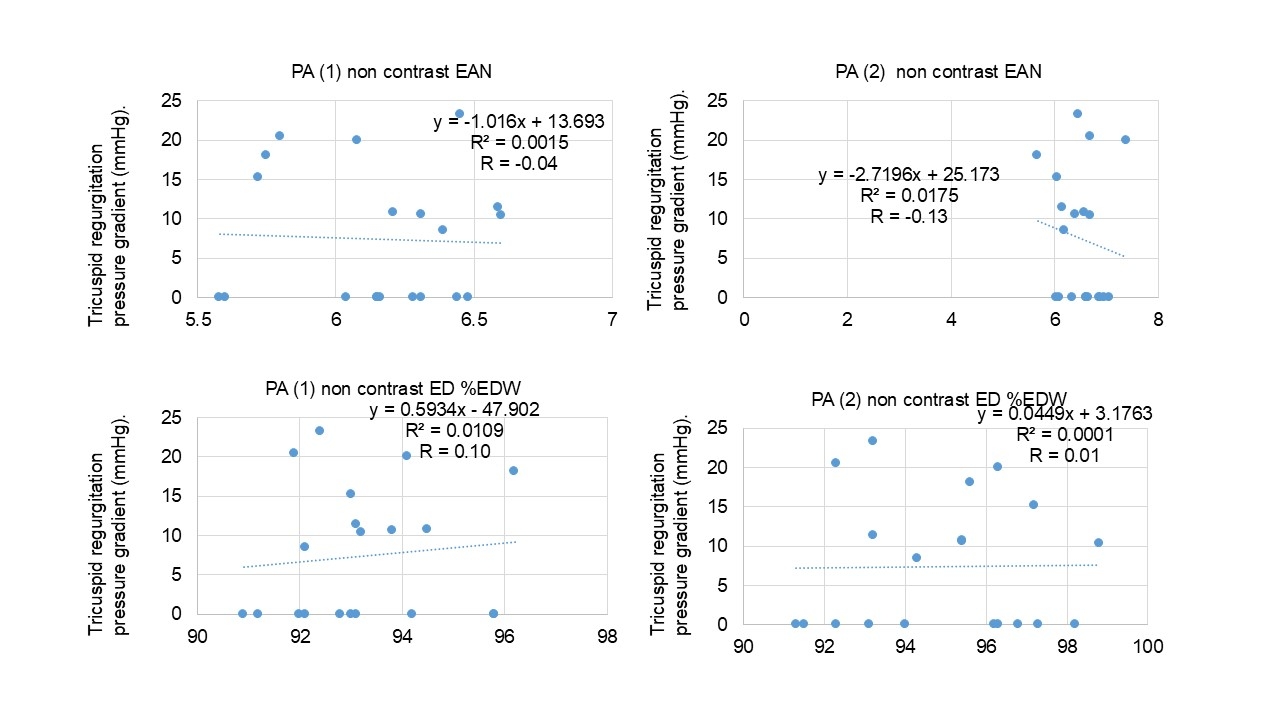
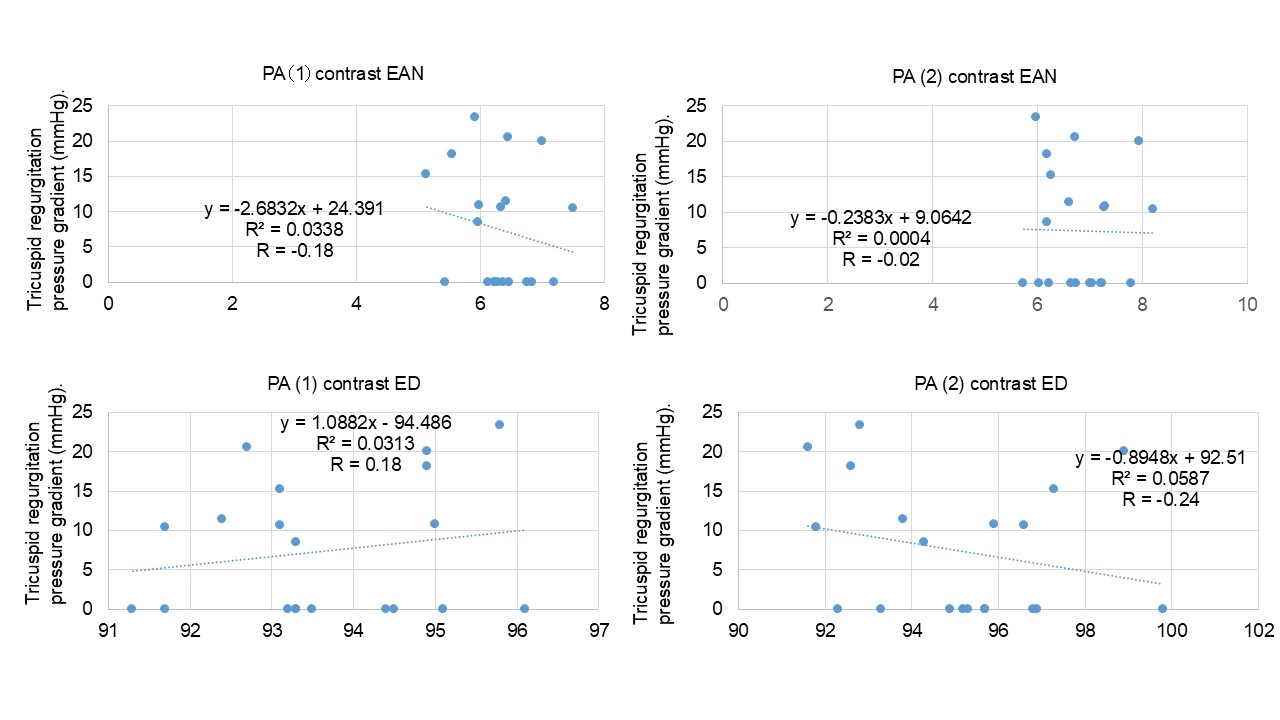
Results: Mean EANs, and EDs of peri-PA adipose tissue at corresponding sites, were 6.15, and 6.52 (EANs), and 93.2 and 94.9 at in site 1 and 2, respectively in non-contrast phase, and 6.32, and 6.82 (EANs) in site 1 and 2, respectively in early phase. Correlation coefficients of each EAN and ED against tricuspid regurgitation pressure gradient on transthoracic echocardiogram were -0.04 and -0.13 (EANs), and 0.10 and 0.01 at in site 1 and 2, respectively in non-contrast phase, and -0.18 and -0.02 (EANs), and 0.18 and -0.24 at in site 1 and 2, respectively in early phase (Figure 2 and 3).
Conclusion: This is the first study to evaluate focal peri-PA adipose tissue by EANs, and EDs and its relationship to estimated PA systolic pressure. Right sided heart is low pressure system, but these new CT parameters may be useful to predict future occurrence of pulmonary hypertension, which is related to peri-PA adipose tissue inflammation.
Hypothesis: Using effective atomic numbers (EANs) and electron density (ED) determined by spectral CT as new parameters, the focal characteristics of peri-PA adipose tissue is useful to predict elevated PA systolic pressure.
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis of 20 patients (7 male, mean age 54 year old) who underwent dual energy CT (7500, Philips) because of clinically suspected coronary artery diseases, but no significant stenosis in the coronary arteries on CT, and with normal ECG and transthoracic echocardiogram findings. From non-contrast and contrast data, EANs and EDs (% electron density relative to water) of peri-PA adipose tissue were determined at two sites in each patient as represented in Figure 1. We compared tricuspid regurgitation pressure gradient (mmHg).
Results: Mean EANs, and EDs of peri-PA adipose tissue at corresponding sites, were 6.15, and 6.52 (EANs), and 93.2 and 94.9 at in site 1 and 2, respectively in non-contrast phase, and 6.32, and 6.82 (EANs) in site 1 and 2, respectively in early phase. Correlation coefficients of each EAN and ED against tricuspid regurgitation pressure gradient on transthoracic echocardiogram were -0.04 and -0.13 (EANs), and 0.10 and 0.01 at in site 1 and 2, respectively in non-contrast phase, and -0.18 and -0.02 (EANs), and 0.18 and -0.24 at in site 1 and 2, respectively in early phase (Figure 2 and 3).
Conclusion: This is the first study to evaluate focal peri-PA adipose tissue by EANs, and EDs and its relationship to estimated PA systolic pressure. Right sided heart is low pressure system, but these new CT parameters may be useful to predict future occurrence of pulmonary hypertension, which is related to peri-PA adipose tissue inflammation.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-Derived Cardiac Morphometrics from CAC CT for Heart Failure Risk Prediction
Alkhaleefah Mohammad, Balakrishnan Guha, Li Shuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Gullapelli Rakesh, Bose Budhaditya, Rockers Elijah, Modanwal Gourav, Hoori Ammar, Madabhushi Anant, Wilson David, Patel Kershaw
A Novel Animal Model for Pulmonary Hypertension: Lung Endothelial Specific Deletion of Egln1 in MiceLiu Bin, Yi Dan, Ramirez Karina, Fallon Michael, Dai Zhiyu