Final ID: MP1371
Elevated Peri-coronary Adipose Tissue attenuation association with Coronary Plaque Progression in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Peri-coronary adipose tissue (PCAT) attenuation, quantified by Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA), is a validated non-invasive marker for assessing coronary inflammation. It has been predictive of adverse outcomes including myocardial infarction and cardiovascular death. This is pertinent especially for type 2 diabetic patients given increased systemic inflammation and increased risk of coronary artery disease. Given that increased inflammation has been associated with coronary atherogenesis, our aim was to investigate whether progression in PCAT attenuation was associated with coronary plaque burden progression.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesize that elevated PCAT attenuation, suggestive of increased vascular inflammation, is associated with increased coronary plaque burden and progression, in a high-risk cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus enrolled in STOP (Semaglutide Treatment Effect On Coronary Atherosclerosis Progression In Diabetes) trial.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective analysis of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus from the STOP trial who underwent serial CCTA at baseline visit and 12-month follow up. PCAT attenuation (HU) was measured around the proximal right coronary artery from the 10-50th mm from the ostium, the current standardized method for PCAT analysis. Compositional plaque changes were measured as change in percent atheroma volume (PAV%) comparing baseline to 12-month follow up through analysis with QAngio and Medis. Spearman correlation and multivariable linear regression models assessed the association between PCAT and change in PAV. In addition, multivariable models adjusted for traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
Results:
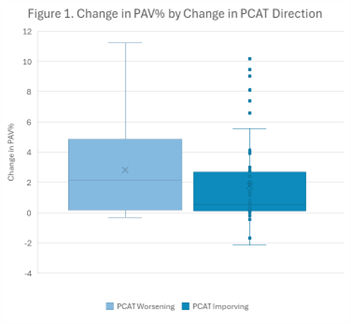
We analyzed 98 participants (mean age 57.1±8.2 years, 62% male). Patients with an increase in PCAT attenuation (measures as higher HU) showed an increase in PAV progression (r=0.259, p=0.01). Changes in PCAT attenuation correlated with changes in the burden of total plaque (r=0.22, p=0.029) and calcified plaque (r=0.219, p=0.03), but not with other morphologies.
Conclusion:
In this high-risk cohort of patients with diabetes and extensive atherosclerosis, we found that an increase in PCAT was associated with rapid progression of total plaque volumes. These findings support the role of vascular inflammation in the progression of atherosclerosis and the need to characterize vascular inflammation, as potential therapeutic targets.
Peri-coronary adipose tissue (PCAT) attenuation, quantified by Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA), is a validated non-invasive marker for assessing coronary inflammation. It has been predictive of adverse outcomes including myocardial infarction and cardiovascular death. This is pertinent especially for type 2 diabetic patients given increased systemic inflammation and increased risk of coronary artery disease. Given that increased inflammation has been associated with coronary atherogenesis, our aim was to investigate whether progression in PCAT attenuation was associated with coronary plaque burden progression.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesize that elevated PCAT attenuation, suggestive of increased vascular inflammation, is associated with increased coronary plaque burden and progression, in a high-risk cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus enrolled in STOP (Semaglutide Treatment Effect On Coronary Atherosclerosis Progression In Diabetes) trial.
Methods:
We performed a retrospective analysis of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus from the STOP trial who underwent serial CCTA at baseline visit and 12-month follow up. PCAT attenuation (HU) was measured around the proximal right coronary artery from the 10-50th mm from the ostium, the current standardized method for PCAT analysis. Compositional plaque changes were measured as change in percent atheroma volume (PAV%) comparing baseline to 12-month follow up through analysis with QAngio and Medis. Spearman correlation and multivariable linear regression models assessed the association between PCAT and change in PAV. In addition, multivariable models adjusted for traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
Results:
We analyzed 98 participants (mean age 57.1±8.2 years, 62% male). Patients with an increase in PCAT attenuation (measures as higher HU) showed an increase in PAV progression (r=0.259, p=0.01). Changes in PCAT attenuation correlated with changes in the burden of total plaque (r=0.22, p=0.029) and calcified plaque (r=0.219, p=0.03), but not with other morphologies.
Conclusion:
In this high-risk cohort of patients with diabetes and extensive atherosclerosis, we found that an increase in PCAT was associated with rapid progression of total plaque volumes. These findings support the role of vascular inflammation in the progression of atherosclerosis and the need to characterize vascular inflammation, as potential therapeutic targets.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comprehensive Study on Machine Learning Models Combining with Oversampling for One-year Persistent Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease
Liang Kaizhi, Pang Yusheng, Su Danyan
A novel method for measuring HDL-bound unconjugated bilirubin using an eel fluorescent protein reveals its association with reduced coronary artery diseaseFujioka Tomoo, Iino Takuya, Toh Ryuji, Harada Amane, Nagao Manabu, Shinohara Masakazu, Ishida Tatsuro, Otake Hiromasa