Final ID: MP2111
Association of Ramus Intermedius Variant with Greater Coronary Plaque and Stenosis Burden
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The ramus intermedius (RI) is a variant artery arising from the trifurcation of the left main (LM) coronary artery. While RI has been found to be associated with greater LM plaque burden, its relationship with total coronary atherosclerotic plaque burden across the coronary tree remains unclear. We aimed to assess whether the presence of RI is associated with greater plaque, stenosis, and segment involvement across the coronary tree.
Methods: We conducted a large retrospective single-center study of 11,497 adults who underwent coronary CT angiography between October 2006 and December 2022 in Los Angeles, California. Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare total plaque score (TPS), total stenosis score (TSS), and segment involvement score (SIS) among individuals with and without RI. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to evaluate the association between the presence of RI and overall coronary plaque burden, adjusting for traditional cardiovascular risk factors, including age, ethnicity, sex, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and smoking status.
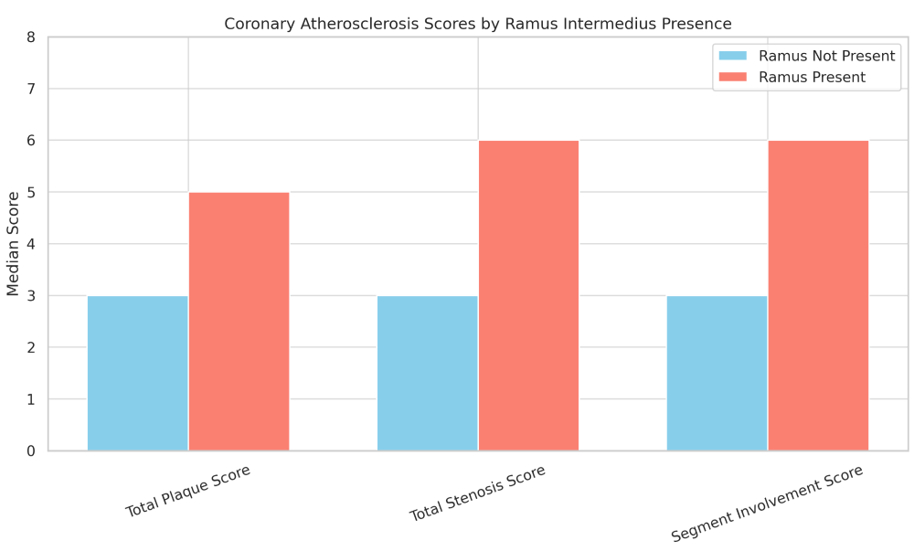
Results: Among the 11,497 subjects (mean age 62.0 ± 12.4 years, 64% male), 11% had a ramus intermedius present. Individuals with RI had significantly higher total plaque scores [median 5.0, IQR 2.0 - 8.0 vs. 3.0, IQR 0.0 - 8.0], total stenosis scores [6.0, IQR 2.0 - 11.0 vs. 3.0, IQR 0.0 - 9.0], and segment involvement scores [6.0, IQR 2.0 - 12.0 vs. 3.0, IQR 0.0 - 6.0] compared to those without RI (all p < 0.0001). In a multivariable logistic regression model adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors, the presence of an RI was associated with the presence of any coronary plaque (OR 1.71 [1.51,1.95] p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The presence of the ramus intermedius variant is associated with significantly greater overall coronary plaque burden, stenosis severity, and segment involvement. These findings suggest that RI may be linked to more diffuse coronary atherosclerosis, potentially due to altered hemodynamic stability in the coronary vasculature.
Methods: We conducted a large retrospective single-center study of 11,497 adults who underwent coronary CT angiography between October 2006 and December 2022 in Los Angeles, California. Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare total plaque score (TPS), total stenosis score (TSS), and segment involvement score (SIS) among individuals with and without RI. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to evaluate the association between the presence of RI and overall coronary plaque burden, adjusting for traditional cardiovascular risk factors, including age, ethnicity, sex, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and smoking status.
Results: Among the 11,497 subjects (mean age 62.0 ± 12.4 years, 64% male), 11% had a ramus intermedius present. Individuals with RI had significantly higher total plaque scores [median 5.0, IQR 2.0 - 8.0 vs. 3.0, IQR 0.0 - 8.0], total stenosis scores [6.0, IQR 2.0 - 11.0 vs. 3.0, IQR 0.0 - 9.0], and segment involvement scores [6.0, IQR 2.0 - 12.0 vs. 3.0, IQR 0.0 - 6.0] compared to those without RI (all p < 0.0001). In a multivariable logistic regression model adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors, the presence of an RI was associated with the presence of any coronary plaque (OR 1.71 [1.51,1.95] p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The presence of the ramus intermedius variant is associated with significantly greater overall coronary plaque burden, stenosis severity, and segment involvement. These findings suggest that RI may be linked to more diffuse coronary atherosclerosis, potentially due to altered hemodynamic stability in the coronary vasculature.
More abstracts on this topic:
2-Deoxyuridine Associates with Recurrent Coronary Events
Pistritu Dan, Castano David, Liehn Elisa, Koh Cho Yeow, Gerszten Robert, Singaraja Roshni, Chan Mark, Shah Svati
9p21.3 variants drive coronary calcification by suppressing statherin expressionSoheili Fariborz, Almontashiri Naif, Heydarikhorneh Niloufar, Vilmundarson Ragnar, Chen Hsiao-huei, Stewart Alexandre