Final ID: MP86
Pembrolizumab-Induced Myositis Unmasking Double M Syndrome with Smoldering Myocarditis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as pembrolizumab, have revolutionized cancer therapy but can trigger immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including myocarditis and myositis. Double M syndrome, myositis with concurrent myocarditis, is a rare, high-risk phenotype typically presenting acutely, though smoldering presentations are often underrecognized and constitute a diagnostic challenge.
Clinical case
A 67-year-old woman with stage IIb triple-negative breast cancer, treated with pembrolizumab-carboplatin/paclitaxel followed by doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide per KEYNOTE-522 protocol, presented four months after completing ICI therapy with worsening myalgias, weakness, low-grade fever, and transaminitis. Labs revealed elevated CK (7,760 U/L), transaminases (AST 369 U/L, ALT 626 U/L). ECG showed sinus tachycardia and diffuse ST depressions, with troponin-I (>15,000 ng/L), and CK-MB (185 ng/mL). TTE demonstrated preserved LVEF without wall motion abnormalities. Differential diagnoses included non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, ICI-related myocarditis, and viral myocarditis.
Decision-Making
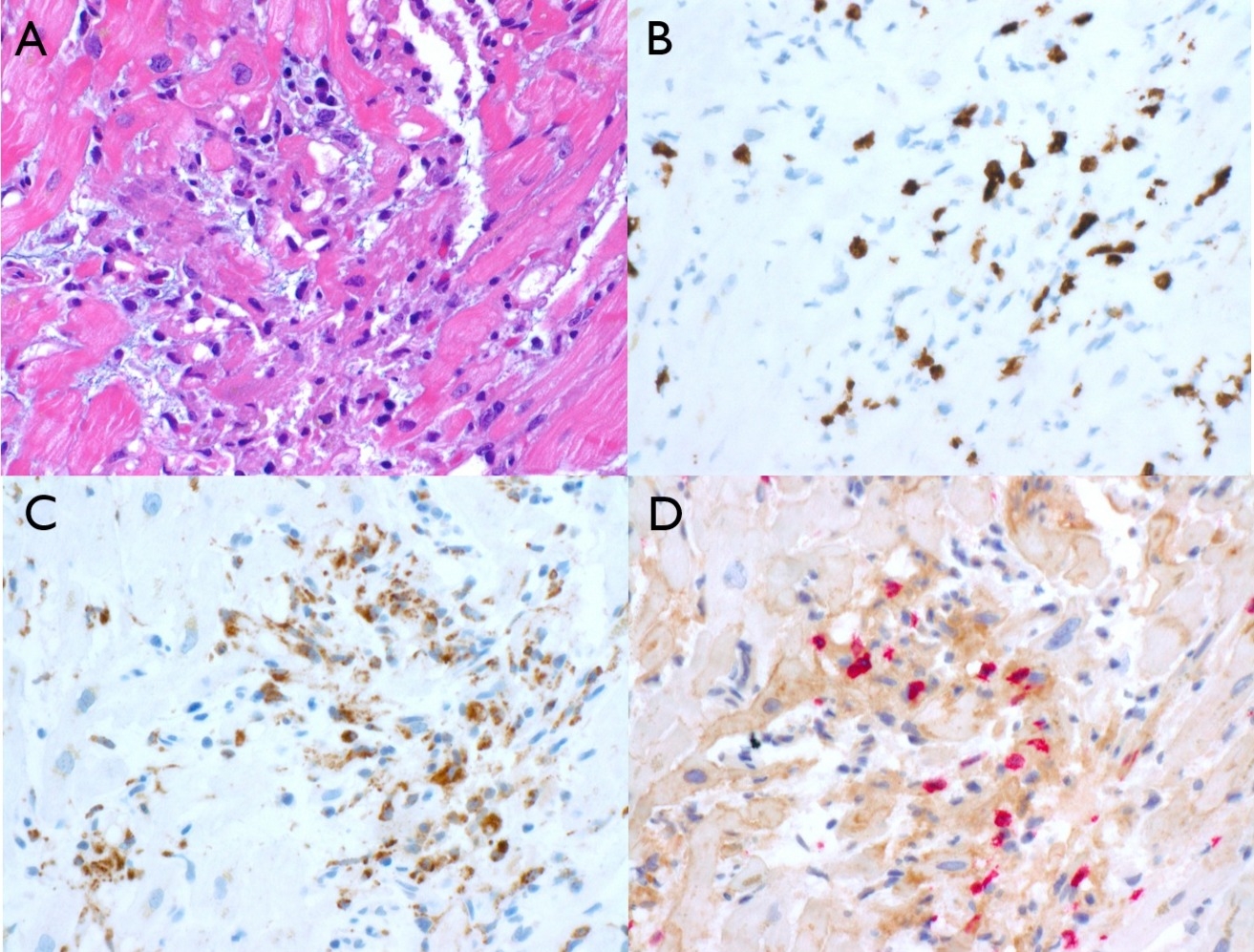
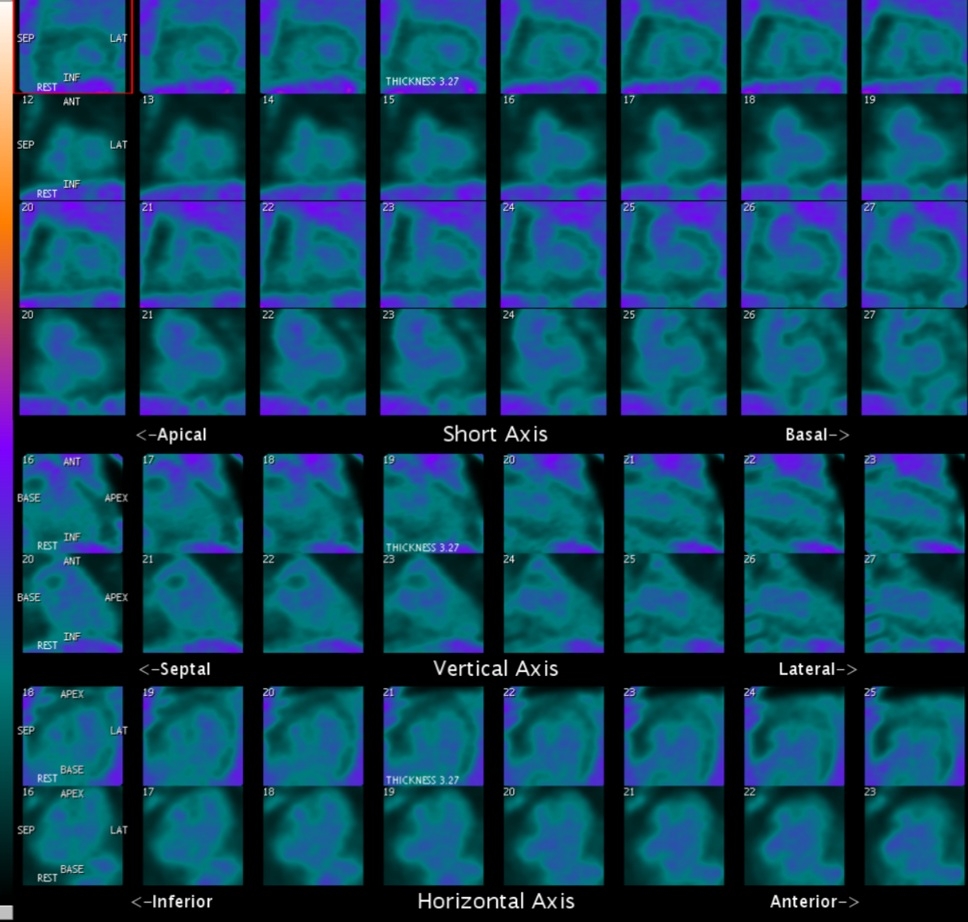
Initial ACS management was initiated but discontinued after coronary angiography showed non-obstructive disease. Endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) revealed lymphocyte-predominant myocarditis with CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell infiltrates and PD-L1 overexpression in myocytes, confirming ICI-associated myocarditis (Figure 1). She was treated with pulse-dose methylprednisolone (1 g/day x 5 days), followed by oral prednisone taper. Follow-up cardiac PET/CT at two months showed complete resolution of myocardial inflammation (Figure 2).
Conclusion
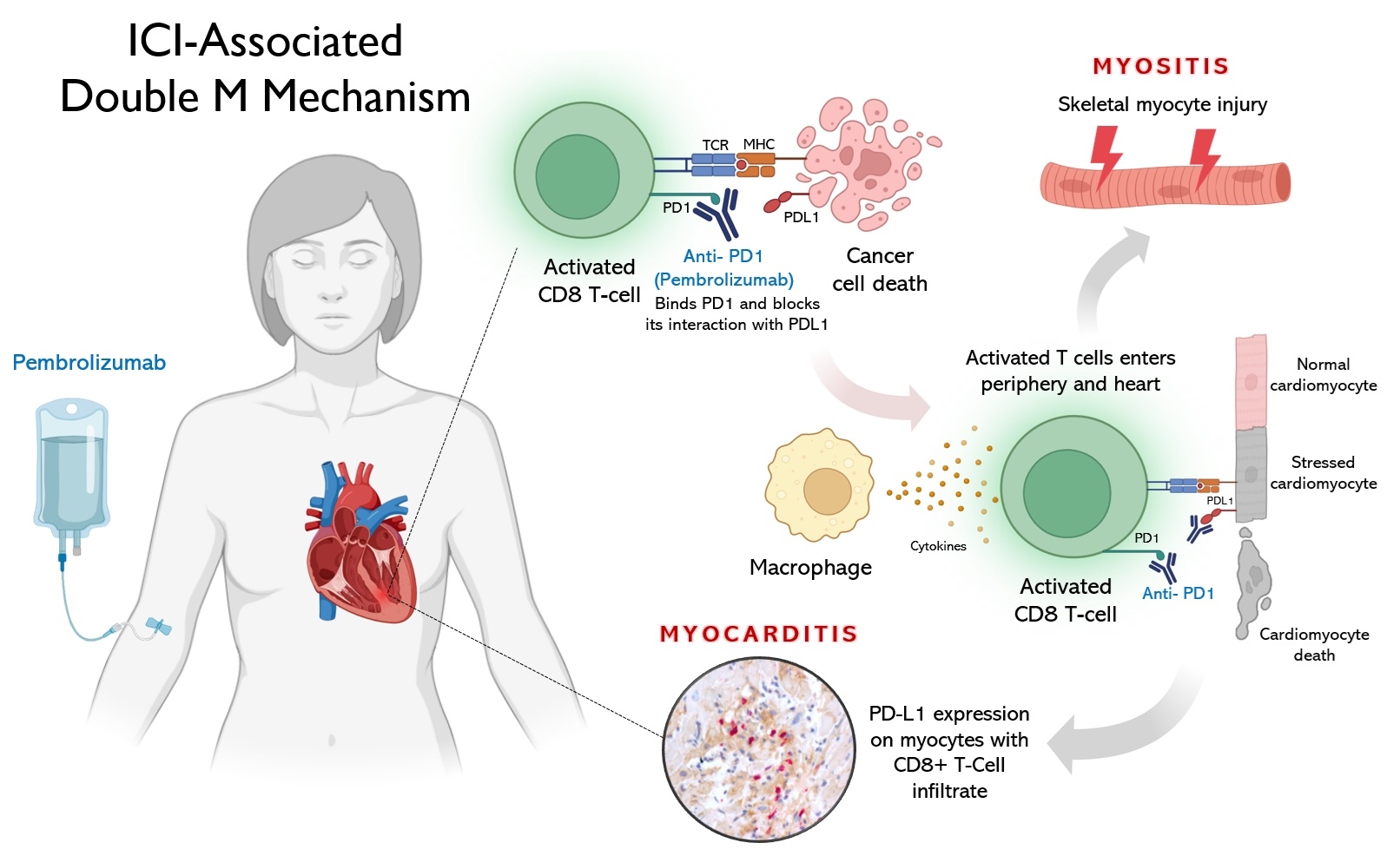
This unique case illustrates a rare, delayed-onset presentation of pembrolizumab-induced Double M syndrome with smoldering myocarditis (Figure 3) and myositis, highlighting the importance of considering ICI-related myocarditis even in asymptomatic or subacute settings post-immunotherapy to avoid fatal cardiac complications. EMB played a critical role in diagnosis and tailored corticosteroid therapy. Timely recognition and coordinated multidisciplinary management are crucial for improving outcomes in ICI-related cardiotoxicity and other irAEs.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as pembrolizumab, have revolutionized cancer therapy but can trigger immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including myocarditis and myositis. Double M syndrome, myositis with concurrent myocarditis, is a rare, high-risk phenotype typically presenting acutely, though smoldering presentations are often underrecognized and constitute a diagnostic challenge.
Clinical case
A 67-year-old woman with stage IIb triple-negative breast cancer, treated with pembrolizumab-carboplatin/paclitaxel followed by doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide per KEYNOTE-522 protocol, presented four months after completing ICI therapy with worsening myalgias, weakness, low-grade fever, and transaminitis. Labs revealed elevated CK (7,760 U/L), transaminases (AST 369 U/L, ALT 626 U/L). ECG showed sinus tachycardia and diffuse ST depressions, with troponin-I (>15,000 ng/L), and CK-MB (185 ng/mL). TTE demonstrated preserved LVEF without wall motion abnormalities. Differential diagnoses included non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, ICI-related myocarditis, and viral myocarditis.
Decision-Making
Initial ACS management was initiated but discontinued after coronary angiography showed non-obstructive disease. Endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) revealed lymphocyte-predominant myocarditis with CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell infiltrates and PD-L1 overexpression in myocytes, confirming ICI-associated myocarditis (Figure 1). She was treated with pulse-dose methylprednisolone (1 g/day x 5 days), followed by oral prednisone taper. Follow-up cardiac PET/CT at two months showed complete resolution of myocardial inflammation (Figure 2).
Conclusion
This unique case illustrates a rare, delayed-onset presentation of pembrolizumab-induced Double M syndrome with smoldering myocarditis (Figure 3) and myositis, highlighting the importance of considering ICI-related myocarditis even in asymptomatic or subacute settings post-immunotherapy to avoid fatal cardiac complications. EMB played a critical role in diagnosis and tailored corticosteroid therapy. Timely recognition and coordinated multidisciplinary management are crucial for improving outcomes in ICI-related cardiotoxicity and other irAEs.
More abstracts on this topic:
A functional survey of postnatal heart maturation with in vivo Perturb-seq in spatial and temporal resolution
Wang Haofei, Liu Jiandong, Dong Yanhan, Shi Huitong, Colon Marazzano, Liu Xingyan, Farber Gregory, Qian Yunzhe, Anthony Nicholas, Qian Li
3D spheroids composed by induced Skeletal Muscle Progenitor Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from human Pluripotent Stem Cells can recapitulate embryonic niches in hindlimb ischemia modelKim Jinju, Park Jae-hyun, Choi Yeon-jik, Park Hun