Final ID: MP2158
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Pembrolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), is a monoclonal antibody that binds to PD-1 receptors on T-cells and prevents their inhibition by certain tumors, augmenting the immune system’s ability to kill malignant cells. ICI-myocarditis is a rare but serious side effect with high mortality rates. This is a report focusing on ICI-myocarditis that highlights a treatment regimen in a fulminant steroid-refractory case.
Clinical Course:
A 54-year-old man with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue presented to the hospital days after completing his 13th cycle of pembrolizumab with dyspnea. EKG was unremarkable, but high-sensitivity troponin-T (HSTn-T) was elevated at 351 ng/L. TTE revealed an ejection fraction (EF) of 27%. Given concern for ICI myocarditis, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) was obtained which showed myocardial edema with extensive early and late gadolinium enhancement involving 40% of the myocardium. After 3 days of 1g IV methylprednisolone his symptoms improved and HSTn-T fell to 220 ng/L. He was transitioned to prednisone and discharged. In follow-up, dyspnea and weight gain were noted, HSTn-T was persistently elevated to 208 ng/L despite interval increase in prednisone.
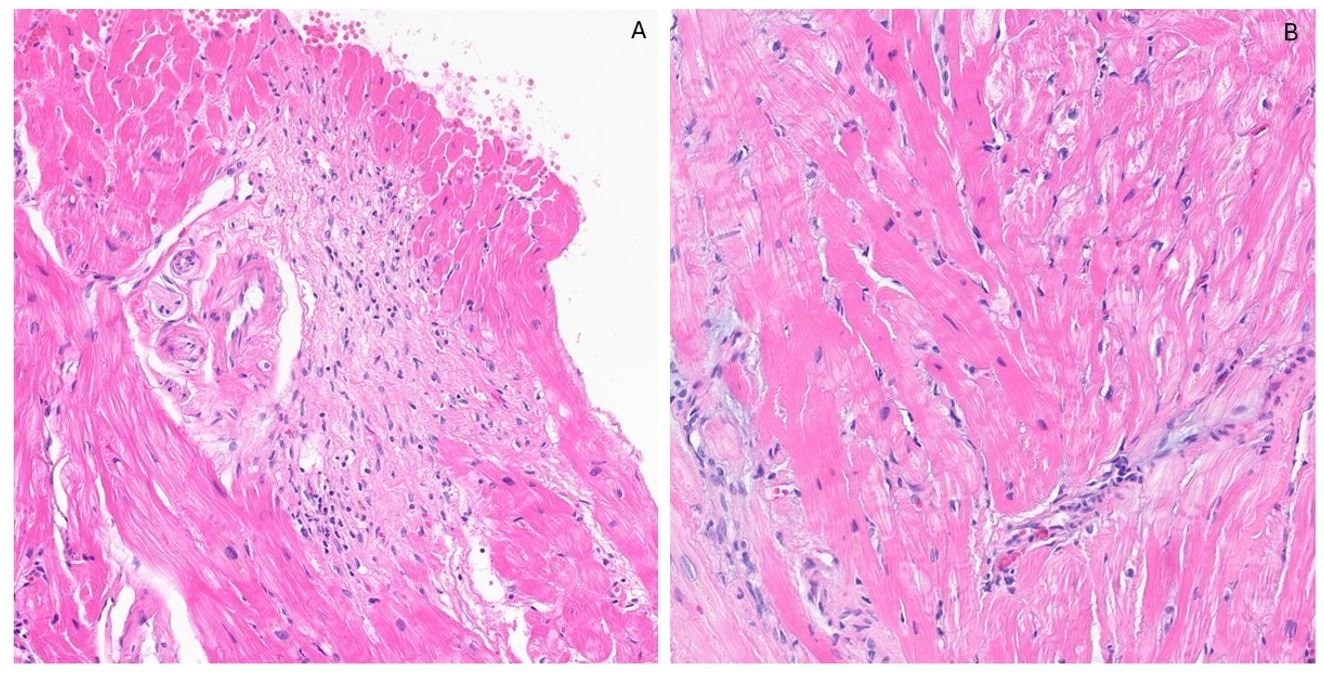
On readmission, he was found to be in cardiogenic shock requiring milrinone with a lactate of 3.9 and HSTn-T of 142 ng/L. EKG was unremarkable for conduction disease. Repeat TTE revealed a decline in EF to 19%. An endomyocardial biopsy revealed subendocardial and interstitial fibrosis with associated lymphocytic inflammation. He received a 3-day course of methylprednisolone 1g IV followed by prednisone and a 5-day course of rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (Thymoglobulin). As he completed the thymoglobulin, his symptoms improved and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) was added. Repeat CMR revealed a decrease in late gadolinium enhancement to 27%. A right ventricular thrombus prevented a repeat biopsy. By discharge, he was asymptomatic and inotropes were weaned off.
Conclusions:
High dose steroids are the standard of treatment for ICI-myocarditis, leading to improved outcomes with respect to cardiovascular death, cardiac arrest, and cardiogenic shock. However, data is sparse on treatment options when steroids fail. Limited case reports exist documenting the use of plasmapheresis, IV immunoglobulin, anti-thymocyte globulin, and MMF. Here we illustrated successful treatment of steroid-refractory myocarditis with the addition of MMF and thymoglobulin.
Pembrolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), is a monoclonal antibody that binds to PD-1 receptors on T-cells and prevents their inhibition by certain tumors, augmenting the immune system’s ability to kill malignant cells. ICI-myocarditis is a rare but serious side effect with high mortality rates. This is a report focusing on ICI-myocarditis that highlights a treatment regimen in a fulminant steroid-refractory case.
Clinical Course:
A 54-year-old man with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue presented to the hospital days after completing his 13th cycle of pembrolizumab with dyspnea. EKG was unremarkable, but high-sensitivity troponin-T (HSTn-T) was elevated at 351 ng/L. TTE revealed an ejection fraction (EF) of 27%. Given concern for ICI myocarditis, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) was obtained which showed myocardial edema with extensive early and late gadolinium enhancement involving 40% of the myocardium. After 3 days of 1g IV methylprednisolone his symptoms improved and HSTn-T fell to 220 ng/L. He was transitioned to prednisone and discharged. In follow-up, dyspnea and weight gain were noted, HSTn-T was persistently elevated to 208 ng/L despite interval increase in prednisone.
On readmission, he was found to be in cardiogenic shock requiring milrinone with a lactate of 3.9 and HSTn-T of 142 ng/L. EKG was unremarkable for conduction disease. Repeat TTE revealed a decline in EF to 19%. An endomyocardial biopsy revealed subendocardial and interstitial fibrosis with associated lymphocytic inflammation. He received a 3-day course of methylprednisolone 1g IV followed by prednisone and a 5-day course of rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (Thymoglobulin). As he completed the thymoglobulin, his symptoms improved and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) was added. Repeat CMR revealed a decrease in late gadolinium enhancement to 27%. A right ventricular thrombus prevented a repeat biopsy. By discharge, he was asymptomatic and inotropes were weaned off.
Conclusions:
High dose steroids are the standard of treatment for ICI-myocarditis, leading to improved outcomes with respect to cardiovascular death, cardiac arrest, and cardiogenic shock. However, data is sparse on treatment options when steroids fail. Limited case reports exist documenting the use of plasmapheresis, IV immunoglobulin, anti-thymocyte globulin, and MMF. Here we illustrated successful treatment of steroid-refractory myocarditis with the addition of MMF and thymoglobulin.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Self-Resolving Pheochromocytoma-Induced Reverse Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Due to Tumor Hemorrhagic Conversion
Cedeno Serna Juan, Jayant Girish, Joseph Christy, Contreras Yametti Felipe, Lorenzatti Daniel, Mangeshkar Shaunak, Morales Nieves, Carruthers David, Sims Daniel
A Pressure-Volume Loops Approach Predicts Outcomes After Double Switch Operation For Congenitally Corrected Transposition Of The Great Arteries with Intact Ventricular SeptumThatte Nikhil, Del Nido Pedro, Ghelani Sunil, Hammer Peter, Marx Gerald, Beroukhim Rebecca, Gauvreau Kimberlee, Callahan Ryan, Prakash Ashwin, Emani Sitaram, Hoganson David