Final ID: Mo3015
COMPARISON OF CARDIOTOXIC EFFECTS AMONG BTK (BRUTON TYROSINE KINASE) INHIBITORS: A PHARMACOVIGILANCE ANALYSIS
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: First-generation BTK inhibitors (BTKi) Ibrutinib showed benefits in the RESONATE-2 trial and have been widely used since then. However, its associated Cardiovascular (CV) side effects limit its use in certain populations. Newer generation BTKis like Acalabrutinib and Zanubrutinib have been shown to have a relatively better CV safety profile, yet post-marketing surveillance data is limited.
Methods: We analyzed CV Adverse Events (AEs) reported to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)’s Adverse Events (FAERS) database, WHO’s VigiAccess database, and the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) EudraVigilance database, for Ibrutinib and newer generation BTKi Acalabrutinib and Zanubrutinib using descriptive statistics. Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) was calculated for all reported CV AEs, and both newer generation BTKis were compared with Ibrutinib. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare and look for differences among new-generation BTKis.
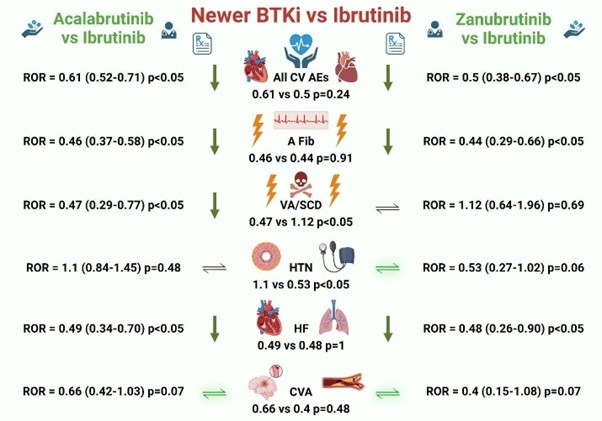
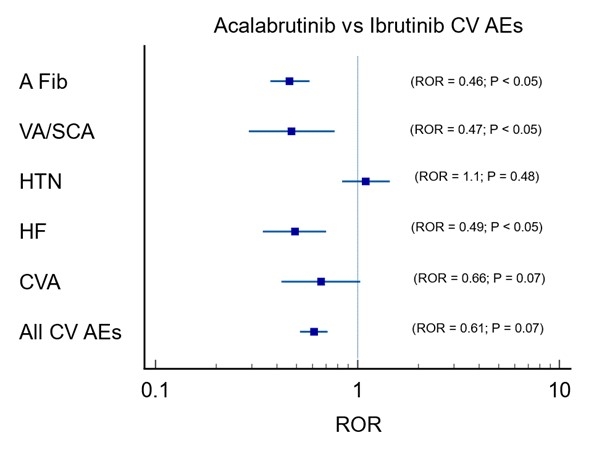
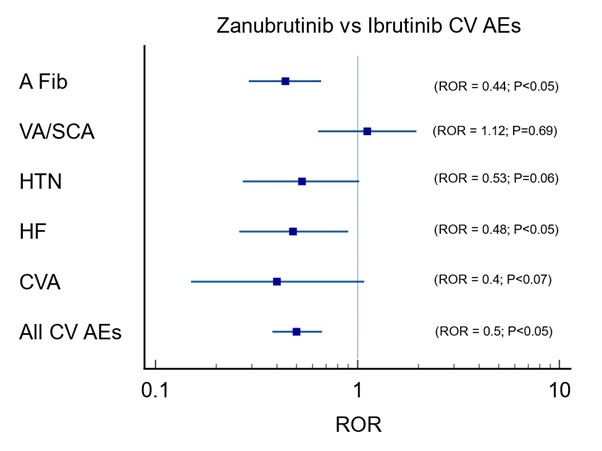
Results: On FAERS database, BTKis had increased CV AEs reported with AFib being the highest [2,146 (6.76%)] followed by HF [808 (2.54%)], HTN [688 (2.17%)], VA/SCD (Ventricular Arrhythmia/Sudden Cardiac Arrest) [461 (1.45%), and CVA [395 (1.24%)]. All CV AEs [ROR:5.42 (5.23-5.63) P<0.05] were significantly higher, with the most common association noted with AFib [ROR:21.5 (20.57-22.50) P<0.05]. While comparing Acalabrutinib with Ibrutinib, fewer AFib, VA/SCA, and HF were reported, whereas reported HTN was not significantly different between them. While comparing Zanubrutinib with Ibrutinib, a smaller number of AFib and HF were observed, while reported VA/SCA was not significantly different between them. Both newer generation BTK inhibitors, Acalabrutinib and Zanubrutinib, had overall equal reduction (ROR = 0.61 vs 0.5, P=0.24) in reported CV AEs. Zanubrutinib had higher VA/SCA than Acalabrutinib (ROR = 1.12 vs. 0.47, P<0.05). At the same time, Zanubrutinib had less HTN than Acalabrutinib (ROR = 0.47 vs. 1.12, P<0.05). Most of these findings were supported by coinciding findings from VigiAccess and EudraVigilance databases.
Conclusion: The Newer generation BTKis have fewer CV AEs when compared to Ibrutinib, which was consistent with current data. Among the newer generation BTKis, Acalabrutinib signaled for relatively higher reported HTN, while Zanubrutinib signaled for relatively higher reported VA/SCAs. Further surveillance of CV AEs associated with newer BTKi from different populations will add value to our research.
Methods: We analyzed CV Adverse Events (AEs) reported to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)’s Adverse Events (FAERS) database, WHO’s VigiAccess database, and the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) EudraVigilance database, for Ibrutinib and newer generation BTKi Acalabrutinib and Zanubrutinib using descriptive statistics. Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) was calculated for all reported CV AEs, and both newer generation BTKis were compared with Ibrutinib. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare and look for differences among new-generation BTKis.
Results: On FAERS database, BTKis had increased CV AEs reported with AFib being the highest [2,146 (6.76%)] followed by HF [808 (2.54%)], HTN [688 (2.17%)], VA/SCD (Ventricular Arrhythmia/Sudden Cardiac Arrest) [461 (1.45%), and CVA [395 (1.24%)]. All CV AEs [ROR:5.42 (5.23-5.63) P<0.05] were significantly higher, with the most common association noted with AFib [ROR:21.5 (20.57-22.50) P<0.05]. While comparing Acalabrutinib with Ibrutinib, fewer AFib, VA/SCA, and HF were reported, whereas reported HTN was not significantly different between them. While comparing Zanubrutinib with Ibrutinib, a smaller number of AFib and HF were observed, while reported VA/SCA was not significantly different between them. Both newer generation BTK inhibitors, Acalabrutinib and Zanubrutinib, had overall equal reduction (ROR = 0.61 vs 0.5, P=0.24) in reported CV AEs. Zanubrutinib had higher VA/SCA than Acalabrutinib (ROR = 1.12 vs. 0.47, P<0.05). At the same time, Zanubrutinib had less HTN than Acalabrutinib (ROR = 0.47 vs. 1.12, P<0.05). Most of these findings were supported by coinciding findings from VigiAccess and EudraVigilance databases.
Conclusion: The Newer generation BTKis have fewer CV AEs when compared to Ibrutinib, which was consistent with current data. Among the newer generation BTKis, Acalabrutinib signaled for relatively higher reported HTN, while Zanubrutinib signaled for relatively higher reported VA/SCAs. Further surveillance of CV AEs associated with newer BTKi from different populations will add value to our research.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Simple One-Item Nursing Falls Assessment Predicts Outcomes For Patients With Stage D Heart Failure Undergoing Surgical Advanced Therapies
Salvador Vincent, Perez Jaime Abraham, Hudec Paige, Gorodeski Eiran, Oneill Thomas
Adipose tissue extracellular vesicles mediate pro-arrhythmic changes in atrial cardiomyocytesLimpitikul Worawan, Garcia Contreras Marta, Betti Michael, Sheng Quanhu, Xiao Ling, Chatterjee Emeli, Gamazon Eric, Shah Ravi, Das Saumya