Final ID: MP1016
COMPARISON OF CARDIOTOXIC EFFECTS BETWEEN AIs AEROMATASE INHIBITORS) AND SERMs (SELECTIVE ESTROGEN RECEPTOR INHIBITORS): A PHARMACOVIGILANCE ANALYSIS
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Cardiovascular (CV) diseases are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in breast cancer survivors. Side effects of antineoplastic agents used in treating breast cancer have been known to be a culprit for the development of CV diseases. Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs) and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators(SERMs) are widely used for Estrogen receptor positive breast cancer, but limited data is available on the CV risk profiles of these classes. We aimed to compare CV risk profiles of AIs and SERMs.
Methods: We queried the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)’s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database for CV AEs of AIs and SERMs from 1996-2023. We included Anastrozole, Letrozole, and Exemestane for AIs and Raloxifene, Tamoxifen, Fulvestrant, and Toremifene for SERMs. The data on CV risk profiles were collected, analyzed, and compared for both classes using descriptive statistics. Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) was calculated for all reported CV AEs and both AIs and SERMs. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare and look for differences among AIs and SERMs.
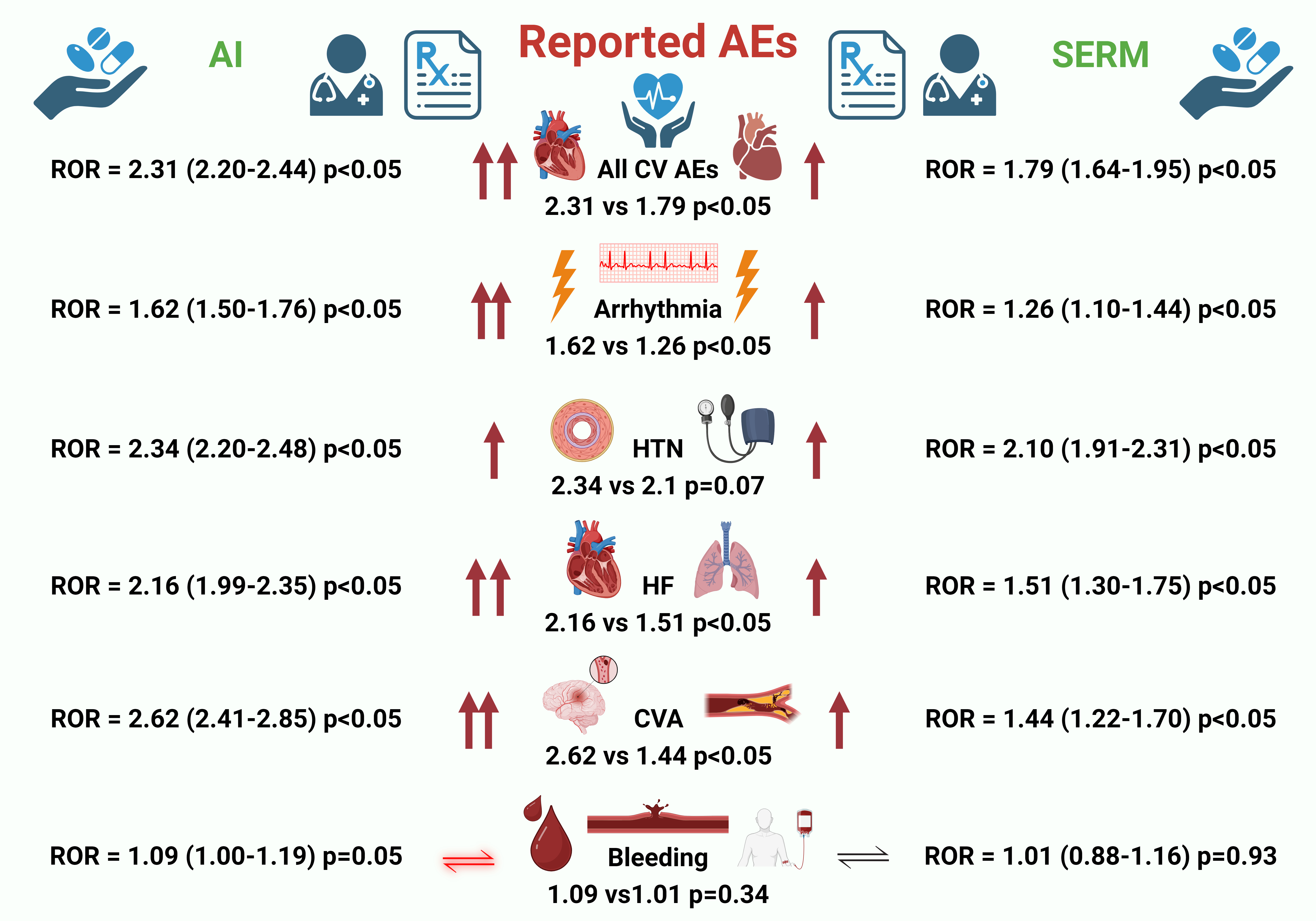
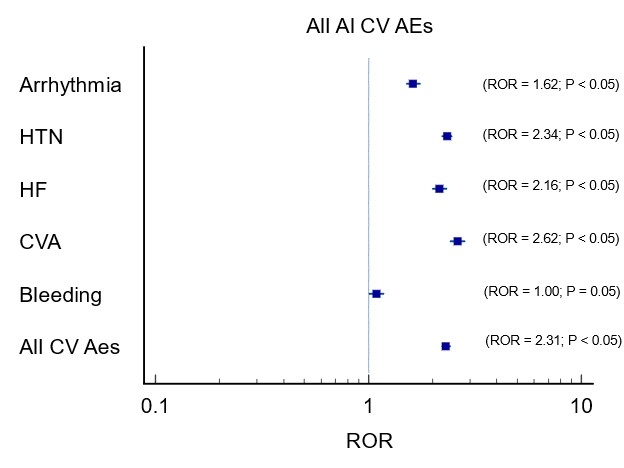
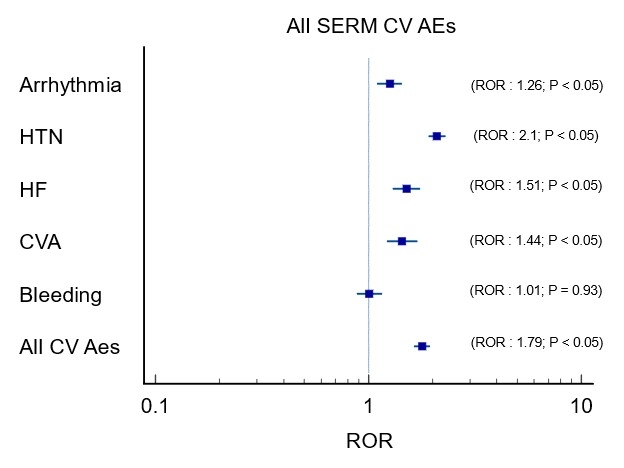
Results: On the FAERS database, a total of 37,128 events were reported for AIs, while 16,616 events were reported for SERMs. 2,499 CV AEs were reported for AIs, and 865 CV AEs were reported for SERMs. Though both AIs [ROR:2.31 (2.20-2.44) P<0.05], and SERMs [ROR:1.79 (1.64-1.95) P<0.05], had increasingly reported CV AEs, when comparing the adjusted ratio, AIs had more reported CV AEs compared to SERMs (ROR = 2.31 vs 1.79, P<0.05). On subsequent analysis, CVA (ROR = 2.62 vs 1.44, P<0.05), HF (ROR = 2.16 vs 1.51, P<0.05), and Arrhythmia (ROR = 1.62 vs 1.26, P<0.05) were also reported more with AIs compared to SERMs. HTN was found to be equally reported among both classes. Most of these findings were supported by coinciding findings from VigiAccess and EudraVigilance databases. More cardiac AEs were seen with AIs when compared with SERMs on VigiAccess [(3.92% vs 3.44%); ROR = 1.15 (1.08-1.22, p<0.05)] as well as EudraVigilance [(5.02% vs 4.07%); ROR = 1.24 (1.15-1.34, p<0.05)] databases.
Conclusion: AIs are observed to be associated with higher rates of CV AEs compared to SERMs. Further studies are warranted to establish the CV risk profile of these agents.
Methods: We queried the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)’s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database for CV AEs of AIs and SERMs from 1996-2023. We included Anastrozole, Letrozole, and Exemestane for AIs and Raloxifene, Tamoxifen, Fulvestrant, and Toremifene for SERMs. The data on CV risk profiles were collected, analyzed, and compared for both classes using descriptive statistics. Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) was calculated for all reported CV AEs and both AIs and SERMs. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare and look for differences among AIs and SERMs.
Results: On the FAERS database, a total of 37,128 events were reported for AIs, while 16,616 events were reported for SERMs. 2,499 CV AEs were reported for AIs, and 865 CV AEs were reported for SERMs. Though both AIs [ROR:2.31 (2.20-2.44) P<0.05], and SERMs [ROR:1.79 (1.64-1.95) P<0.05], had increasingly reported CV AEs, when comparing the adjusted ratio, AIs had more reported CV AEs compared to SERMs (ROR = 2.31 vs 1.79, P<0.05). On subsequent analysis, CVA (ROR = 2.62 vs 1.44, P<0.05), HF (ROR = 2.16 vs 1.51, P<0.05), and Arrhythmia (ROR = 1.62 vs 1.26, P<0.05) were also reported more with AIs compared to SERMs. HTN was found to be equally reported among both classes. Most of these findings were supported by coinciding findings from VigiAccess and EudraVigilance databases. More cardiac AEs were seen with AIs when compared with SERMs on VigiAccess [(3.92% vs 3.44%); ROR = 1.15 (1.08-1.22, p<0.05)] as well as EudraVigilance [(5.02% vs 4.07%); ROR = 1.24 (1.15-1.34, p<0.05)] databases.
Conclusion: AIs are observed to be associated with higher rates of CV AEs compared to SERMs. Further studies are warranted to establish the CV risk profile of these agents.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel risk score predicts the prevalence of left atrial low-voltage areas and rhythm outcome in patients undergoing long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation
Ooka Hirotaka, Nakao Sho, Kusuda Masaya, Ariyasu Wataru, Kudo Satoshi, Fujii Subaru, Mano Toshiaki, Matsuda Yasuhiro, Masuda Masaharu, Okamoto Shin, Ishihara Takayuki, Nanto Kiyonori, Tsujimura Takuya, Hata Yosuke, Uematsu Hiroyuki
1-Year Outcomes After Cardioversion With and Without Anticoagulation in Patients With Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Propensity-Matched AnalysisThangjui Sittinun, Trongtorsak Angkawipa, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Thyagaturu Harshith, Watson Hangyu, Mensah Samuel, Balla Sudarshan, Navaravong Leenhapong