Final ID: MP1405
Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors Effectively Lower Blood Pressure but Increase Hyperkalemia Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background. Aldosterone synthase inhibitors (ASIs) are a novel class targeting aldosterone biosynthesis, offering a mechanistically distinct approach from mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
Research Question. Do ASIs significantly reduce blood pressure compared to placebo in patients with hypertension, and what is their associated safety profile?
Methods. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating ASIs versus placebo in hypertensive patients. A comprehensive search was performed in Cochrane CENTRAL, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science up to April 15, 2025. All available dosages of each agent were pooled into a single treatment node. The primary efficacy outcome was the change in mean seated systolic blood pressure (SBP), while the safety outcome was hyperkalemia. Secondary outcomes included changes in mean seated diastolic blood pressure (DBP), 24-hour ambulatory SBP, serious adverse events (SAEs), and hyponatremia. Data were synthesized using inverse-variance random-effects models.
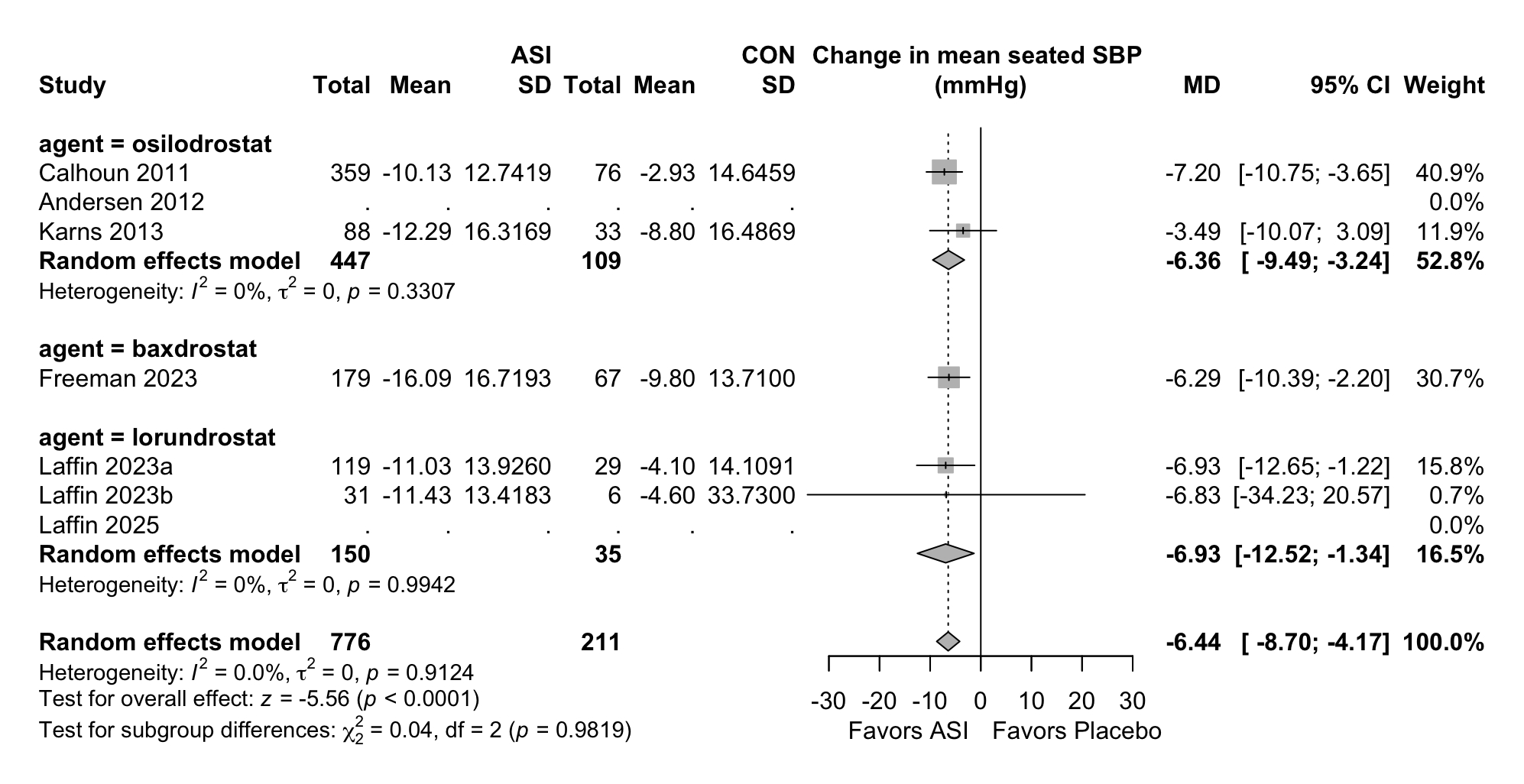
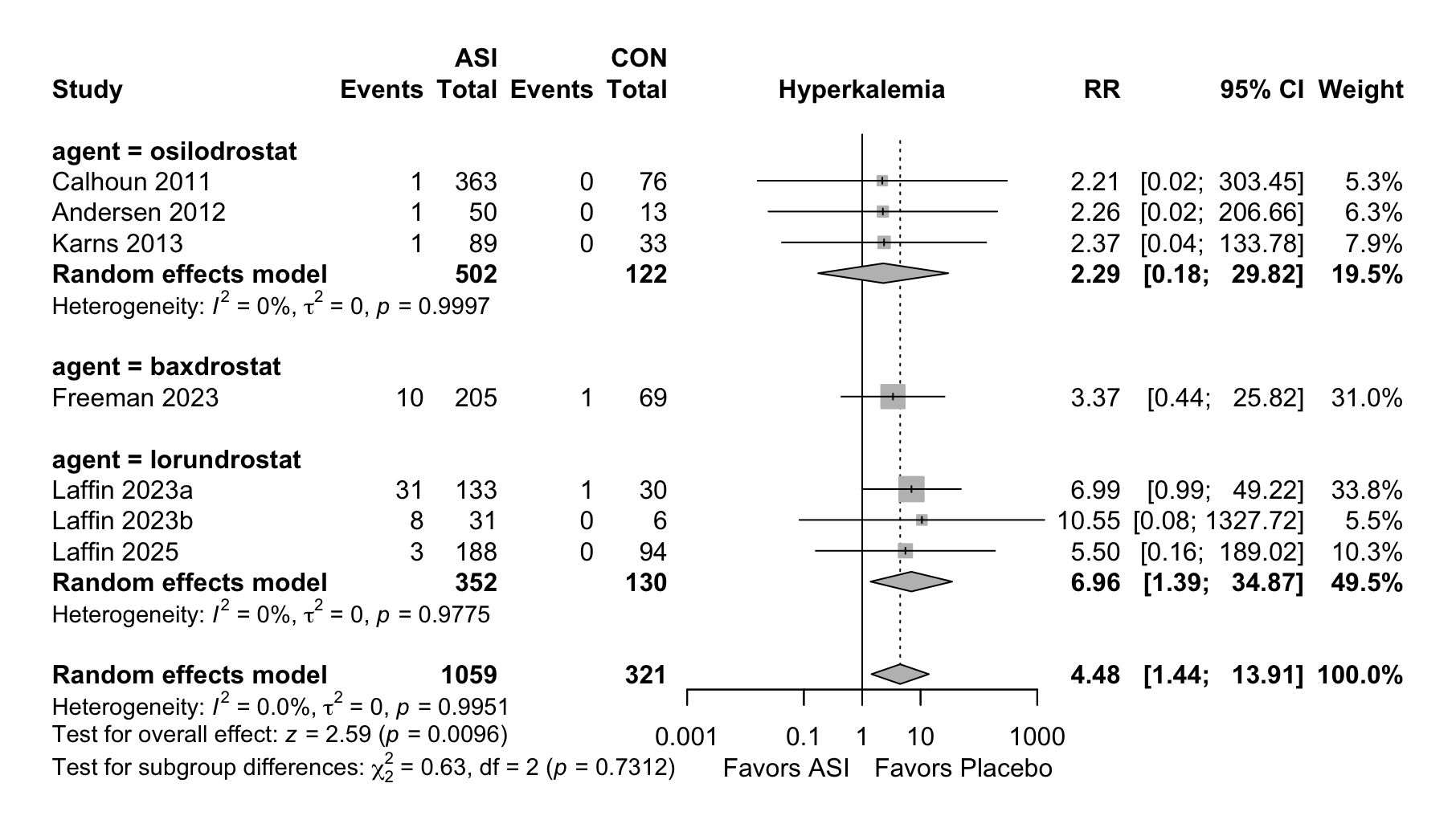
Results. Six RCTs comprising 1,382 participants were included from an initial screening of 855 records. Compared with placebo, ASIs significantly reduced mean seated SBP (mean difference [MD] −6.44 mmHg; 95% CI −8.7 to −4.17; I2=0%; p<0.0001). Mean seated DBP was also significantly reduced (MD −2.15 mmHg; 95% CI −3.48 to −0.82; p=0.0015), as was 24-hour ambulatory SBP (MD −6.82 mmHg; 95% CI −8.81 to −4.84; p<0.001). These SBP and DBP reductions were consistent across hypertension subtypes (primary, resistant, and uncontrolled) and among different ASI agents (p for interaction >0.1). The risk of hyperkalemia was significantly elevated (RR 4.48; 95% CI 1.44 to 13.91), primarily driven by lorundrostat (RR 6.96; 95% CI 1.39 to 34.87). However, ASIs were not associated with a significant increase in SAEs (RR: 2.11; 95% CI 0.82 to 5.43; p=0.62) or non-SAEs (RR 1.10; 95% CI 0.76 to 1.57; p=0.62) compared to placebo. No significant increase was observed in hyponatremia risk (RR 1.24; 95% CI 0.34 to 4.46).
Conclusions. ASIs significantly and mildly reduced both SBP and DBP in hypertensive patients, with an overall manageable safety profile. The increased risk of hyperkalemia—particularly with lorundrostat—warrants monitoring. These agents may hold promise for enhanced efficacy when combined with other antihypertensive therapies in future trials.
Research Question. Do ASIs significantly reduce blood pressure compared to placebo in patients with hypertension, and what is their associated safety profile?
Methods. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating ASIs versus placebo in hypertensive patients. A comprehensive search was performed in Cochrane CENTRAL, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science up to April 15, 2025. All available dosages of each agent were pooled into a single treatment node. The primary efficacy outcome was the change in mean seated systolic blood pressure (SBP), while the safety outcome was hyperkalemia. Secondary outcomes included changes in mean seated diastolic blood pressure (DBP), 24-hour ambulatory SBP, serious adverse events (SAEs), and hyponatremia. Data were synthesized using inverse-variance random-effects models.
Results. Six RCTs comprising 1,382 participants were included from an initial screening of 855 records. Compared with placebo, ASIs significantly reduced mean seated SBP (mean difference [MD] −6.44 mmHg; 95% CI −8.7 to −4.17; I2=0%; p<0.0001). Mean seated DBP was also significantly reduced (MD −2.15 mmHg; 95% CI −3.48 to −0.82; p=0.0015), as was 24-hour ambulatory SBP (MD −6.82 mmHg; 95% CI −8.81 to −4.84; p<0.001). These SBP and DBP reductions were consistent across hypertension subtypes (primary, resistant, and uncontrolled) and among different ASI agents (p for interaction >0.1). The risk of hyperkalemia was significantly elevated (RR 4.48; 95% CI 1.44 to 13.91), primarily driven by lorundrostat (RR 6.96; 95% CI 1.39 to 34.87). However, ASIs were not associated with a significant increase in SAEs (RR: 2.11; 95% CI 0.82 to 5.43; p=0.62) or non-SAEs (RR 1.10; 95% CI 0.76 to 1.57; p=0.62) compared to placebo. No significant increase was observed in hyponatremia risk (RR 1.24; 95% CI 0.34 to 4.46).
Conclusions. ASIs significantly and mildly reduced both SBP and DBP in hypertensive patients, with an overall manageable safety profile. The increased risk of hyperkalemia—particularly with lorundrostat—warrants monitoring. These agents may hold promise for enhanced efficacy when combined with other antihypertensive therapies in future trials.
More abstracts on this topic:
Multicultural Recommendations to Guide Stroke Care: A Document Review of International Stroke Guidelines
Baih Shegaw, Drury Peta, Allida Sabine, Ferguson Caleb
Aldosterone levels are associated with hypertension in post-menopausal women: the Study of Women’s Health Across the NationByrd J Brian, Karvonen-gutierrez Carrie, Leis Aleda, Hood Michelle, Dhar Shichi, Rao Satish, El Khoudary Samar, Thurston Rebecca, Mcconnell Daniel, Auchus Richard