Final ID: Mo2075
Increased Utilization of Home-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs among Veterans with Ischemic Heart Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objectives: Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) is a guideline recommended secondary prevention program that has been vastly underutilized despite evidence of reducing morbidity and mortality in patients with ischemic heart disease (IHD), including Veterans. Alternative programs such as home-based CR (HBCR) have been available to Veterans since 2012, as well as non-VA community programs. We examined patient characteristics associated with CR participation and compared trends amond Veterans from 2012 to 2022 across different CR delivery methods.
Methods: We examined national VA electronic health record data and Medicare claims data from a 5% sample to identify patients with outpatient ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes for IHD. We accounted for CR participation using CPT codes within 12-months following IHD diagnosis. We used t-tests and chi-square tests to compare patient characteristics associated with CR participation vs. non-participation.
Results: From 2012 to 2022, 63,185 Veterans out of 405,907 who were hospitalized with IHD participated in CR, increasing participation rates from 10% to 17% overall. The peak rate of 20% CR participation occurred in 2018 with a dip in participation beginning in 2020, followed by steady increases thereafter. Veterans who participated in CR were slightly younger, more obese, male, white, married, had higher income, non-smokers, and had a history of cardiometabolic disease, except for MI, heart failure, and peripheral vascular disease (p<0.001 for all).
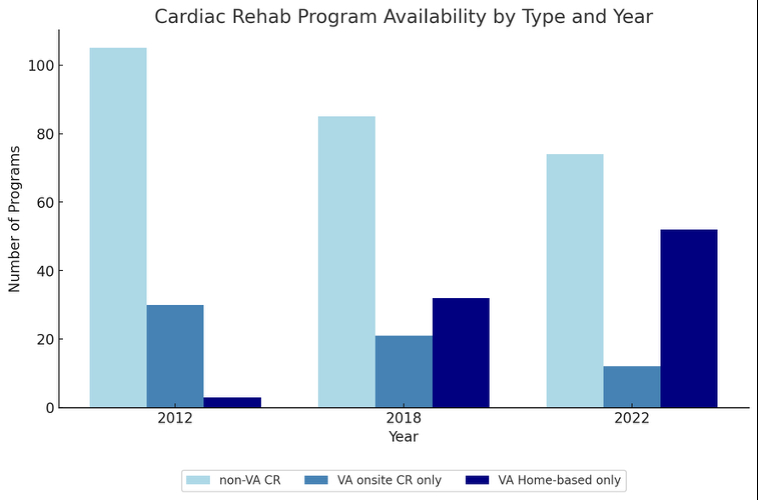
Conclusions: While the overall increase in participation is encouraging, the fact that fewer than 1 in 5 eligible Veterans with IHD participated in any CR remains a significant gap in care given the various modalities that are available (i.e., facility-based, home-based, non-VA community care). HBCR programs in the VA grew from 3 to 52 programs over 10 years, indicating strong institutional support in alternative programs. It is unknown whether the decline in facility-based VA CR programs and reduced reliance on non-VA community programs occurred due to more attention to virtual programs, yet offers a tremendous opportunity to provide more care for Veterans.
Methods: We examined national VA electronic health record data and Medicare claims data from a 5% sample to identify patients with outpatient ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes for IHD. We accounted for CR participation using CPT codes within 12-months following IHD diagnosis. We used t-tests and chi-square tests to compare patient characteristics associated with CR participation vs. non-participation.
Results: From 2012 to 2022, 63,185 Veterans out of 405,907 who were hospitalized with IHD participated in CR, increasing participation rates from 10% to 17% overall. The peak rate of 20% CR participation occurred in 2018 with a dip in participation beginning in 2020, followed by steady increases thereafter. Veterans who participated in CR were slightly younger, more obese, male, white, married, had higher income, non-smokers, and had a history of cardiometabolic disease, except for MI, heart failure, and peripheral vascular disease (p<0.001 for all).
Conclusions: While the overall increase in participation is encouraging, the fact that fewer than 1 in 5 eligible Veterans with IHD participated in any CR remains a significant gap in care given the various modalities that are available (i.e., facility-based, home-based, non-VA community care). HBCR programs in the VA grew from 3 to 52 programs over 10 years, indicating strong institutional support in alternative programs. It is unknown whether the decline in facility-based VA CR programs and reduced reliance on non-VA community programs occurred due to more attention to virtual programs, yet offers a tremendous opportunity to provide more care for Veterans.
More abstracts on this topic:
Co-Created Intervention Promotes Uptake of Low Sodium Iodized Salt Substitute to Control Hypertension: Results from a Large Community-based Quasi-Experimental Study from India
Srinivasapura Venkateshmurthy Nikhil, Mohan Sailesh, Dubey Manisha, Sehgal Reena, Jarhyan Prashant, Khatkar Rajesh, Konkati Shiva Prasad, Sharma Manika, Ide Nicole, Prabhakaran Dorairaj
Cardiac Rehabilitation In a Safety Net Population - Effects on Hypertension ManagementBurke Morgan, Gan Arnold, Jinno Stephanie, Ge Brandon, Haq Ubayd, Balasubramanian Satish, Chen Grace, Gordon Samuel