Final ID: MP2386
Efficacy of Obicetrapib on Lipid Parameters: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibition has re-emerged as a promising strategy in lipid management, particularly in patients with residual atherogenic risk despite statin therapy. Obicetrapib is a selective CETP inhibitor recently evaluated in multiple randomized trials. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) being a major modifiable risk factor; necessitating the development of additional lipid-lowering agents.
Objective:
This meta-analysis aimed to assess the lipid-modifying efficacy of obicetrapib across key atherogenic and protective lipid markers.
Methods:
We searched the Cochrane Central Registry of Controlled Trials, PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and clinicalTrials.gov databases for all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published up to May 2025 comparing sotatercept to placebo .Lipid outcomes evaluated included low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non–HDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglycerides. Standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I squared statistic.
Results:
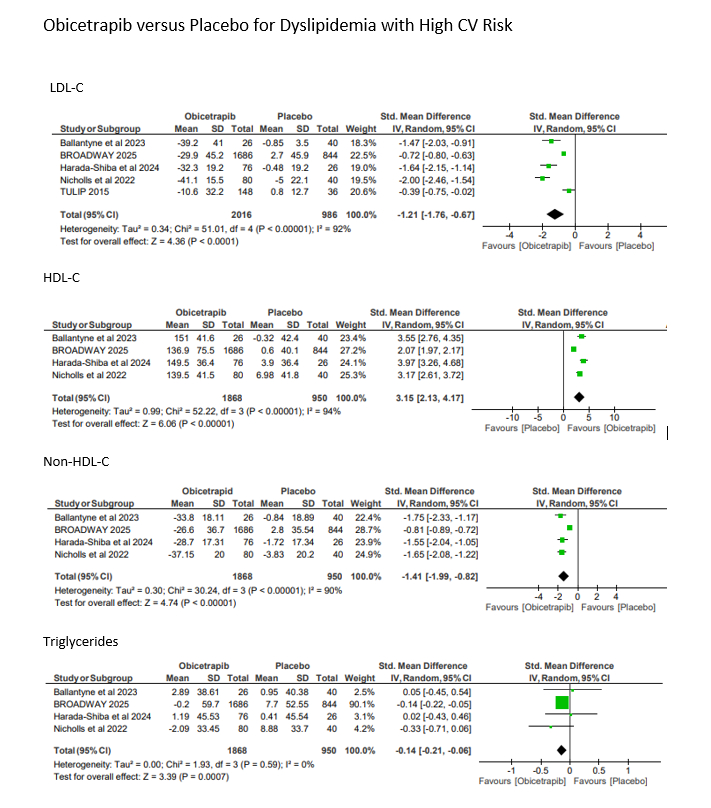
Five randomized controlled trials were included with a population of 3002 Obicetrapib, n = 2016; placebo, n=986) with mean age of 64.4 years. Obicetrapib significantly reduced LDL-C (SMD: –1.21; 95% CI: –1.76 to –0.67) and non–HDL-C (SMD: –1.41; 95% CI: –1.99 to –0.82) compared with placebo. HDL-C levels were significantly increased (SMD: +3.15; 95% CI: 2.13 to 4.17). A modest reduction in triglycerides was also observed (SMD: –0.14; 95% CI: –0.21 to –0.06). Heterogeneity was high for LDL-C, HDL-C, and non–HDL-C outcomes (I squared > 90%) but negligible for triglycerides (I squared = 0%).
Conclusion:
Obicetrapib significantly improves atherogenic lipid profiles, including marked reductions in LDL-C and non–HDL-C, as well as a substantial increase in HDL-C. These findings support obicetrapib as a potent adjunctive therapy in patients with dyslipidemia.
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibition has re-emerged as a promising strategy in lipid management, particularly in patients with residual atherogenic risk despite statin therapy. Obicetrapib is a selective CETP inhibitor recently evaluated in multiple randomized trials. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) being a major modifiable risk factor; necessitating the development of additional lipid-lowering agents.
Objective:
This meta-analysis aimed to assess the lipid-modifying efficacy of obicetrapib across key atherogenic and protective lipid markers.
Methods:
We searched the Cochrane Central Registry of Controlled Trials, PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and clinicalTrials.gov databases for all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published up to May 2025 comparing sotatercept to placebo .Lipid outcomes evaluated included low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non–HDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglycerides. Standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I squared statistic.
Results:
Five randomized controlled trials were included with a population of 3002 Obicetrapib, n = 2016; placebo, n=986) with mean age of 64.4 years. Obicetrapib significantly reduced LDL-C (SMD: –1.21; 95% CI: –1.76 to –0.67) and non–HDL-C (SMD: –1.41; 95% CI: –1.99 to –0.82) compared with placebo. HDL-C levels were significantly increased (SMD: +3.15; 95% CI: 2.13 to 4.17). A modest reduction in triglycerides was also observed (SMD: –0.14; 95% CI: –0.21 to –0.06). Heterogeneity was high for LDL-C, HDL-C, and non–HDL-C outcomes (I squared > 90%) but negligible for triglycerides (I squared = 0%).
Conclusion:
Obicetrapib significantly improves atherogenic lipid profiles, including marked reductions in LDL-C and non–HDL-C, as well as a substantial increase in HDL-C. These findings support obicetrapib as a potent adjunctive therapy in patients with dyslipidemia.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiologist Attitude to Lipid Control in Patients with ASCVD without Major Cardiovascular Events: Insights from the 2024 ACS EuroPath Survey
Zaman Azfar, De Caterina Raffaele, Schiele Francois, Sionis Alessandro, Catapano Alberico, Laufs Ulrich
A Focus for Improvement - Factors for Lab Adherence in a Pediatric Preventive Cardiology ProgramHolsinger Hunter, Porterfield Ronna, Taylor Makenna, Dresbach Bethany, Seipel Brittany, Igwe Chukwuemeka, Alvarado Chance, Tran Andrew