Final ID: Sa2092
Characterizing the Continuum of Untreated Cardiovascular Risk Among Young Adults Without Established Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from a Real-World Health System and a Population-Based Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Contemporary cardiovascular (CV) prevention frameworks prioritize individuals who meet treatment thresholds based on estimated risk or clinical indicators. However, a large proportion of midlife adults—though classified as “low-risk” and therapy-ineligible group remain poorly defined. Leveraging data from a real-world health system and a population-based cohort, we evaluated the distribution and trajectory CV-risk across the untreated risk continuum, with a focus on the primordial prevention population.
Methods
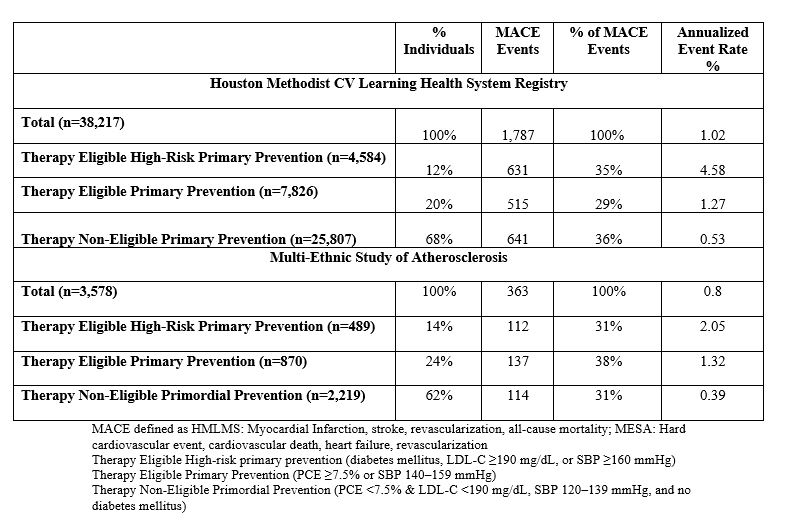
We analyzed adults aged 45–64 years without baseline ASCVD or use of lipid-lowering/antihypertensive therapy from (1) the Houston Methodist Learning Health System Registry (HMLHS, baseline 2016–2017), and (2) the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, baseline 2000–2002). Participants were categorized into 3 exclusive groups: therapy eligible high-risk primary prevention, therapy eligible intermediate risk primary prevention, and therapy ineligible primordial prevention (table). The primary outcome was the major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) with incidence rates calculated per 100 person-years (PYs).
Results
Across both cohorts, therapy ineligible primordial prevention group represented the largest segment of untreated population (HMLHS: 68%; MESA: 62%). The overall incidence of MACE was 1.02/100 PY in HMLMS and 0.80/100 PY’s in MESA over a respective median follow-up of 3.8 years and 14.2 years respectively. In both cohorts, the high-risk group exhibited the highest event rates (HMLHS: 4.58; MESA: 2.05 per 100 PYs). Primordial prevention cohort accounted for a substantial proportion of MACE events (HMLHS: 36%; MESA: 31%), despite having the lowest event rates (HMLHS: 0.53; MESA: 0.39 per 100 PYs).
Conclusion
In both a clinical and epidemiologic setting, therapy-ineligible individuals represented the largest segment of untreated adults and accounted for nearly one-third of ASCVD events, despite their lower short-term risk profiles. These findings expose a critical gap in current risk-based treatment paradigms and emphasize the need for scalable, earlier-stage prevention strategies targeting this group to improve population-level CV outcomes.
Contemporary cardiovascular (CV) prevention frameworks prioritize individuals who meet treatment thresholds based on estimated risk or clinical indicators. However, a large proportion of midlife adults—though classified as “low-risk” and therapy-ineligible group remain poorly defined. Leveraging data from a real-world health system and a population-based cohort, we evaluated the distribution and trajectory CV-risk across the untreated risk continuum, with a focus on the primordial prevention population.
Methods
We analyzed adults aged 45–64 years without baseline ASCVD or use of lipid-lowering/antihypertensive therapy from (1) the Houston Methodist Learning Health System Registry (HMLHS, baseline 2016–2017), and (2) the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, baseline 2000–2002). Participants were categorized into 3 exclusive groups: therapy eligible high-risk primary prevention, therapy eligible intermediate risk primary prevention, and therapy ineligible primordial prevention (table). The primary outcome was the major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) with incidence rates calculated per 100 person-years (PYs).
Results
Across both cohorts, therapy ineligible primordial prevention group represented the largest segment of untreated population (HMLHS: 68%; MESA: 62%). The overall incidence of MACE was 1.02/100 PY in HMLMS and 0.80/100 PY’s in MESA over a respective median follow-up of 3.8 years and 14.2 years respectively. In both cohorts, the high-risk group exhibited the highest event rates (HMLHS: 4.58; MESA: 2.05 per 100 PYs). Primordial prevention cohort accounted for a substantial proportion of MACE events (HMLHS: 36%; MESA: 31%), despite having the lowest event rates (HMLHS: 0.53; MESA: 0.39 per 100 PYs).
Conclusion
In both a clinical and epidemiologic setting, therapy-ineligible individuals represented the largest segment of untreated adults and accounted for nearly one-third of ASCVD events, despite their lower short-term risk profiles. These findings expose a critical gap in current risk-based treatment paradigms and emphasize the need for scalable, earlier-stage prevention strategies targeting this group to improve population-level CV outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessment of Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Primary Healthcare Physicians in Provinces of Armenia Towards Hypertension Management: A Cross-sectional Study
Baghoomian Ania, Hovhannisyan Marine, Shekherdimian Shant
A Focus for Improvement - Factors for Lab Adherence in a Pediatric Preventive Cardiology ProgramHolsinger Hunter, Porterfield Ronna, Taylor Makenna, Dresbach Bethany, Seipel Brittany, Igwe Chukwuemeka, Alvarado Chance, Tran Andrew