Final ID: MP2286
Cumulative LDL-C Exposure and Presence of CAC at Midlife: A Combined Predictor of Long-Term Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Emerging evidence suggests that cumulative exposure to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), rather than a single measurement, may be a stronger determinant of future ASCVD. The presence of coronary artery calcium (CAC) at midlife offers a subclinical marker of atherosclerotic burden. Herein, we aim to assess the interplay of early-life LDL-C exposure and CAC in young adults for predicting long-term ASCVD risk.
Methods
We included 2159 participants free of clinical ASCVD from the CARDIA (Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults) study who had longitudinal LDL-C measurements from early adulthood, underwent CAC scanning and were ≥40 years old at exam 15 (mean age: 42.7; 57.3% female; 41.4% Black). LDL-C exposure was quantified as area under the curve (AUC) from age 18-40 and categorized into tertiles. CAC was assessed at exam 15 (CAC=0 or CAC>0). Participants were followed for 18 years for MACE, defined as nonfatal CHD, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute coronary syndrome, revascularization, transient ischemic attack, peripheral artery disease, death, and CHF.
Results
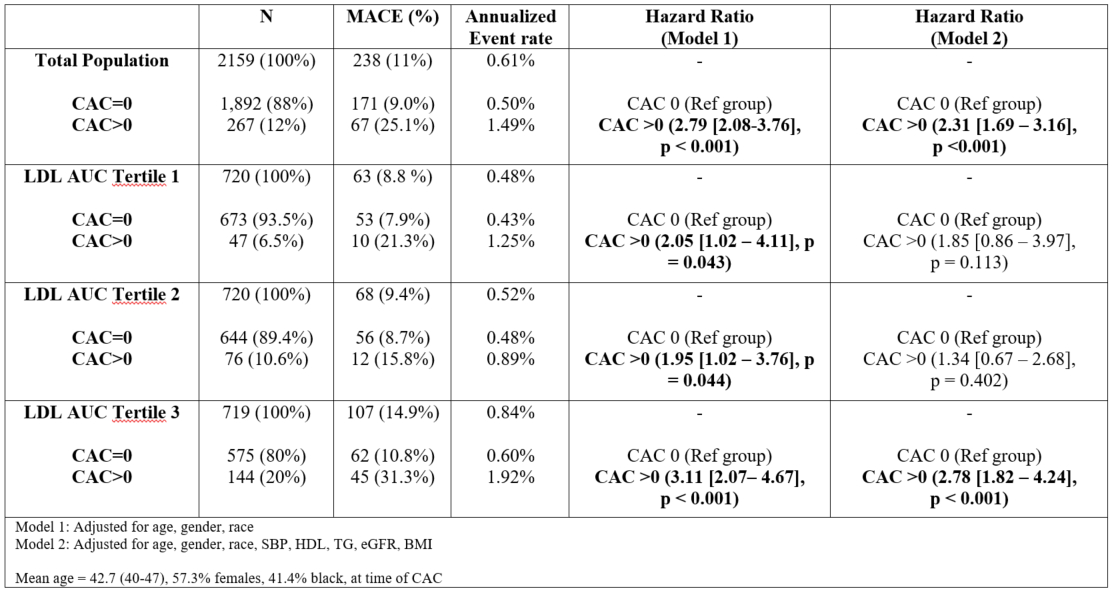
The overall prevalence of CAC>0 at exam 15 increased across LDL-C exposure tertiles (6.5-20%). Compared to tertile 1, adjusted odds of CAC>0 were (OR: 1.47; 95% CI: 0.99-2.17; p=0.051) in tertile 2 and (OR: 2.96; 95% CI: 2.07-4.28; p<0.001) in tertile 3. Over a mean follow-up of 18 years, 238 (11%) MACE events were observed with an annualized event rate of 0.61%. Both higher cumulative LDL exposure and presence of CAC at midlife were associated with higher risk of MACE (Table 1). Among those with CAC=0, MACE rates ranged from 0.43%-0.60% across LDL exposure as compared to those with CAC>0 whose rates ranged from 1.25%-1.92%. In multivariable Cox models adjusting for age, race, sex, SBP, BMI, HDL-C, eGFR, and triglycerides, both higher LDL-C AUC (HR: 1.47; 95% CI: 1.05-2.17; p=0.026) and CAC>0 (HR:2.31; 95% CI: 1.69-3.16; p<0.001) were independently associated with increased risk of MACE.
Conclusion
In this young adult cohort, cumulative LDL-C exposure and presence of CAC were independently associated with future ASCVD events. While higher lifetime LDL-C was linked to increased odds of CAC>0 at midlife, individuals with CAC=0 had low long-term event rates, whereas those with both CAC>0 and elevated LDL-C had the highest absolute risk, highlighting the heterogeneity of risk conferred by LDL-C exposure and the additive prognostic value of CAC in midlife.
Emerging evidence suggests that cumulative exposure to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), rather than a single measurement, may be a stronger determinant of future ASCVD. The presence of coronary artery calcium (CAC) at midlife offers a subclinical marker of atherosclerotic burden. Herein, we aim to assess the interplay of early-life LDL-C exposure and CAC in young adults for predicting long-term ASCVD risk.
Methods
We included 2159 participants free of clinical ASCVD from the CARDIA (Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults) study who had longitudinal LDL-C measurements from early adulthood, underwent CAC scanning and were ≥40 years old at exam 15 (mean age: 42.7; 57.3% female; 41.4% Black). LDL-C exposure was quantified as area under the curve (AUC) from age 18-40 and categorized into tertiles. CAC was assessed at exam 15 (CAC=0 or CAC>0). Participants were followed for 18 years for MACE, defined as nonfatal CHD, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute coronary syndrome, revascularization, transient ischemic attack, peripheral artery disease, death, and CHF.
Results
The overall prevalence of CAC>0 at exam 15 increased across LDL-C exposure tertiles (6.5-20%). Compared to tertile 1, adjusted odds of CAC>0 were (OR: 1.47; 95% CI: 0.99-2.17; p=0.051) in tertile 2 and (OR: 2.96; 95% CI: 2.07-4.28; p<0.001) in tertile 3. Over a mean follow-up of 18 years, 238 (11%) MACE events were observed with an annualized event rate of 0.61%. Both higher cumulative LDL exposure and presence of CAC at midlife were associated with higher risk of MACE (Table 1). Among those with CAC=0, MACE rates ranged from 0.43%-0.60% across LDL exposure as compared to those with CAC>0 whose rates ranged from 1.25%-1.92%. In multivariable Cox models adjusting for age, race, sex, SBP, BMI, HDL-C, eGFR, and triglycerides, both higher LDL-C AUC (HR: 1.47; 95% CI: 1.05-2.17; p=0.026) and CAC>0 (HR:2.31; 95% CI: 1.69-3.16; p<0.001) were independently associated with increased risk of MACE.
Conclusion
In this young adult cohort, cumulative LDL-C exposure and presence of CAC were independently associated with future ASCVD events. While higher lifetime LDL-C was linked to increased odds of CAC>0 at midlife, individuals with CAC=0 had low long-term event rates, whereas those with both CAC>0 and elevated LDL-C had the highest absolute risk, highlighting the heterogeneity of risk conferred by LDL-C exposure and the additive prognostic value of CAC in midlife.
More abstracts on this topic:
Baseline Severity of Coronary Artery Calcium Among Patients Enrolled in the CorCal Trial Compared to those Enrolled in the MESA Study
Muhlestein Joseph, May Heidi, Winslow Tyler, Knight Stacey, Le Viet, Iverson Leslie, Bair Tami, Knowlton Kirk, Anderson Jeffrey
Association of Cardiovascular Health by Life’s Essential 8 with Subsequent Coronary Artery Calcification: A Prospective Cohort StudyAn Hyoeun, Jeon Jooeun, Lee Hyeok-hee, Shim Jee-seon, Kim Hyeon Chang, Lee Hokyou