Final ID: MP1553
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Cardiovascular deaths among individuals with Cancer in the United States (2018-2023): A nationwide analysis from CDC WONDER database
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted healthcare access and delivery for vulnerable populations, including individuals with cancer.
Research Question: What is the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cardiovascular mortality and the shifts in place of death in patients with cancer?
Methodology: We used CDC WONDER data (2018–2023) to identify cancer patients with mortality due to CVD. The study period was categorized into pre-COVID (2018–2019), during COVID (2020–2021), and post-COVID (2022–2023). We extracted age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 population, stratified by age, sex, race, ethnicity, and Census region. Deaths were categorized by location: inpatient, outpatient/emergency department, home, hospice, and nursing home/long-term care.
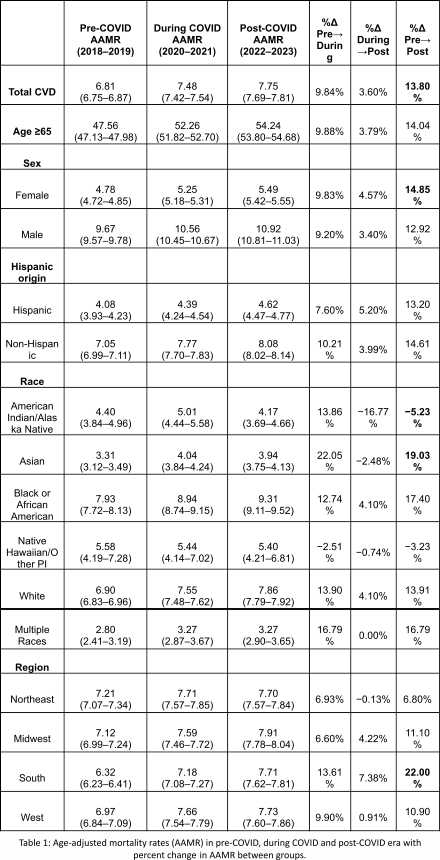
Results: Among 183,256 deaths, the AAMR for CVD among individuals with cancer increased from 6.81 per 100,000 in the pre-COVID period to 7.48 during COVID, and remained elevated to 7.75 post-COVID. (Table 1)
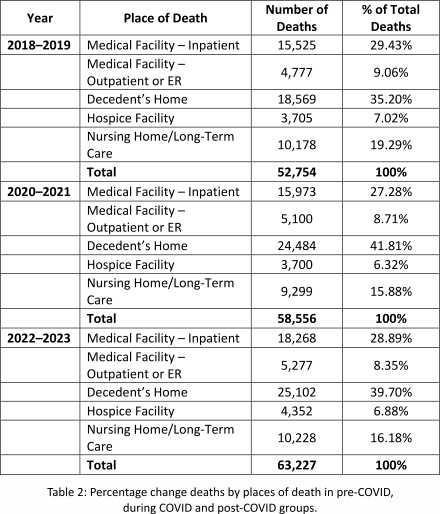
Home deaths increased from 35.2% (18,569 of 52,754) pre-COVID to 41.8% (24,484 of 58,556) during COVID, then to 39.7% post-COVID. In contrast, deaths in inpatient hospitals (-2.2%), outpatient/ER settings (-0.4%), and nursing homes (-3.4%) declined during the pandemic; however, hospice deaths remained relatively stable. (Table 2)
Age-stratified data showed that AAMR in ≥65 adults, increased by 9.9% during the pandemic (47.56 to 52.26) and by 14.0% post-COVID (54.24). Males consistently had higher mortality than females, with AAMRs increasing by 12.9% and 14.9% respectively. AAMR increased in non-Hispanic individuals by (+14.6%) vs (+13.2%) in Hispanic.
Asian individuals had the highest increase in AAMR +22.1% during COVID followed by multiple-race (+16.8%), White (+13.9%) and Black individuals (+12.75) In contrast AIAN individuals dropped to -5.2% post-COVID after an initial increase of +13.9%.
By region, AAMR in South increased to +13.6% during the pandemic which further increased to +22% post-COVID, followed by the Midwest (+6.60 to +11.1%), West (+9.9% to +10.9%), and Northeast (+6.93 to +6.8%).
Conclusion: Cardiovascular mortality among cancer patients rose during and after the pandemic, with disproportionate increases across demographic and regional groups. A sustained rise in home deaths suggests lasting changes in end-of-life care. These patterns underscore the need for strengthened chronic disease management and support systems for vulnerable populations during public health emergencies.
Research Question: What is the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cardiovascular mortality and the shifts in place of death in patients with cancer?
Methodology: We used CDC WONDER data (2018–2023) to identify cancer patients with mortality due to CVD. The study period was categorized into pre-COVID (2018–2019), during COVID (2020–2021), and post-COVID (2022–2023). We extracted age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 population, stratified by age, sex, race, ethnicity, and Census region. Deaths were categorized by location: inpatient, outpatient/emergency department, home, hospice, and nursing home/long-term care.
Results: Among 183,256 deaths, the AAMR for CVD among individuals with cancer increased from 6.81 per 100,000 in the pre-COVID period to 7.48 during COVID, and remained elevated to 7.75 post-COVID. (Table 1)
Home deaths increased from 35.2% (18,569 of 52,754) pre-COVID to 41.8% (24,484 of 58,556) during COVID, then to 39.7% post-COVID. In contrast, deaths in inpatient hospitals (-2.2%), outpatient/ER settings (-0.4%), and nursing homes (-3.4%) declined during the pandemic; however, hospice deaths remained relatively stable. (Table 2)
Age-stratified data showed that AAMR in ≥65 adults, increased by 9.9% during the pandemic (47.56 to 52.26) and by 14.0% post-COVID (54.24). Males consistently had higher mortality than females, with AAMRs increasing by 12.9% and 14.9% respectively. AAMR increased in non-Hispanic individuals by (+14.6%) vs (+13.2%) in Hispanic.
Asian individuals had the highest increase in AAMR +22.1% during COVID followed by multiple-race (+16.8%), White (+13.9%) and Black individuals (+12.75) In contrast AIAN individuals dropped to -5.2% post-COVID after an initial increase of +13.9%.
By region, AAMR in South increased to +13.6% during the pandemic which further increased to +22% post-COVID, followed by the Midwest (+6.60 to +11.1%), West (+9.9% to +10.9%), and Northeast (+6.93 to +6.8%).
Conclusion: Cardiovascular mortality among cancer patients rose during and after the pandemic, with disproportionate increases across demographic and regional groups. A sustained rise in home deaths suggests lasting changes in end-of-life care. These patterns underscore the need for strengthened chronic disease management and support systems for vulnerable populations during public health emergencies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Trial of Patients Receiving Remote Ischemic Conditioning in Early Stroke (PRICES) in a Tertiary Hospital in the Philippines: An Open Label Study
Ang Kevin Royce, Juangco Dan, Hernandez Maria Kim
A Retrospective Analysis of Chronic Kidney Disease and Arrhythmias-Related Mortality Among Adults in the United States (1999-2020): Insights into Disparities by Gender, Race/Ethnicity, and GeographyWaseem Neha, Nouman Zainab, Chaudhry Sohaib Aftab Ahmad, Tariq Waleed, Khan Iftikhar, Shah Mazhar, Farooqi Hanzala Ahmed, Faiz Muneeb