Final ID: Mo3062
The Prognostic Value of Modified Frailty Index in Complications and Survival Following Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: A Data-Driven Approach
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Frailty is a critical condition characterized by reduced physiological reserve. The modified Frailty Index (MFI-5) is a comorbidity-based tool that assesses five health variables to predict morbidity and mortality. While mFI-5 has been effective in various surgical contexts, its application in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has not been investigated.
Objectives:
This study evaluates the relationship between mFI-5 scores and PCI outcomes as predictors of complications.
Methods:
A retrospective analysis was conducted using the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network, focusing on adults aged 60 and older who underwent PCI either within one month or later, having an mFI-5 score of 4. Comparisons were made with those scoring 0, using ICD-10 codes for hypertension, obstructive respiratory disease, heart failure, and diabetes mellitus. Individuals with limitations in daily activities were excluded. Propensity score matching was employed to assess outcomes within 365 days post-PCI. Patients with prior outcome occurrences were excluded from analyses. Statistical comparisons were performed using Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank tests, with a significance level set at p < 0.05.
Results:
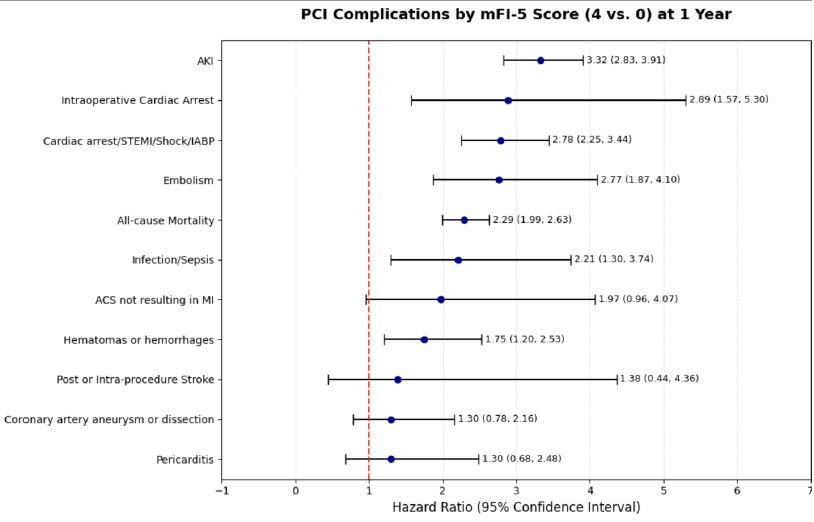
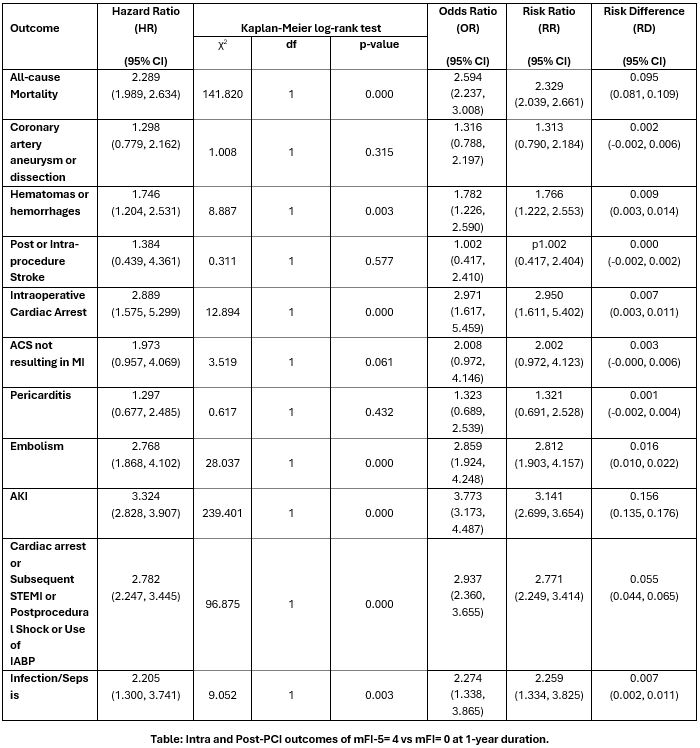
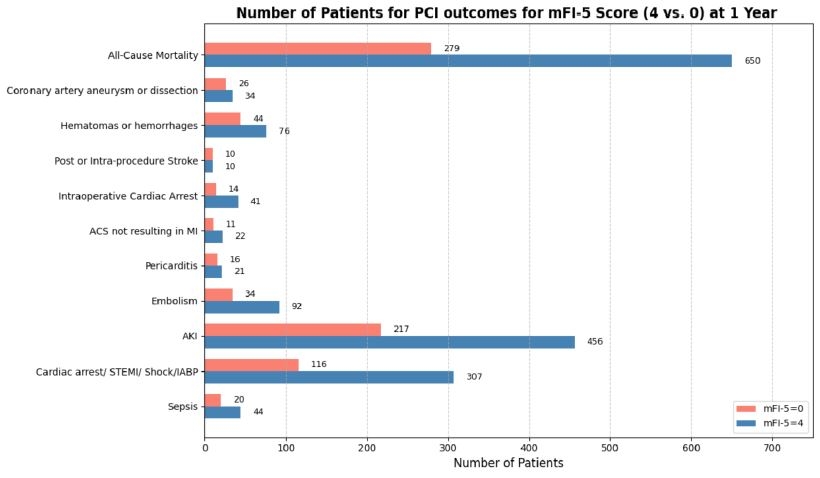
At the 1-year follow-up, patients with an MFI score of 4 experienced significantly higher risks of multiple adverse outcomes compared to those with an MFI score of 0. All-cause mortality was significantly elevated (HR 2.289; 95% CI: 1.989–2.634), as were hematomas or hemorrhages (HR 1.746; 95% CI: 1.204–2.531), intraoperative cardiac arrest (HR 2.889; 95% CI: 1.575–5.299), embolism (HR 2.768; 95% CI: 1.868–4.102), AKI (HR 3.324; 95% CI: 2.828–3.907), infection/sepsis (HR 2.205; 95% CI: 1.300–3.741), and composite outcomes including cardiac arrest, subsequent STEMI, IABP use, or shock (HR 2.782; 95% CI: 2.247–3.445). Risks for coronary artery aneurysm/dissection, stroke, ACS not resulting in MI, and pericarditis did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusions:
Higher frailty significantly increases the risk of adverse outcomes post-PCI, highlighting its prognostic value and the need for routine frailty assessments in pre-procedural risk stratification. Further studies are needed to validate these findings across broader populations and to develop targeted strategies aimed at reducing the elevated risks associated with frailty.
Frailty is a critical condition characterized by reduced physiological reserve. The modified Frailty Index (MFI-5) is a comorbidity-based tool that assesses five health variables to predict morbidity and mortality. While mFI-5 has been effective in various surgical contexts, its application in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has not been investigated.
Objectives:
This study evaluates the relationship between mFI-5 scores and PCI outcomes as predictors of complications.
Methods:
A retrospective analysis was conducted using the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network, focusing on adults aged 60 and older who underwent PCI either within one month or later, having an mFI-5 score of 4. Comparisons were made with those scoring 0, using ICD-10 codes for hypertension, obstructive respiratory disease, heart failure, and diabetes mellitus. Individuals with limitations in daily activities were excluded. Propensity score matching was employed to assess outcomes within 365 days post-PCI. Patients with prior outcome occurrences were excluded from analyses. Statistical comparisons were performed using Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank tests, with a significance level set at p < 0.05.
Results:
At the 1-year follow-up, patients with an MFI score of 4 experienced significantly higher risks of multiple adverse outcomes compared to those with an MFI score of 0. All-cause mortality was significantly elevated (HR 2.289; 95% CI: 1.989–2.634), as were hematomas or hemorrhages (HR 1.746; 95% CI: 1.204–2.531), intraoperative cardiac arrest (HR 2.889; 95% CI: 1.575–5.299), embolism (HR 2.768; 95% CI: 1.868–4.102), AKI (HR 3.324; 95% CI: 2.828–3.907), infection/sepsis (HR 2.205; 95% CI: 1.300–3.741), and composite outcomes including cardiac arrest, subsequent STEMI, IABP use, or shock (HR 2.782; 95% CI: 2.247–3.445). Risks for coronary artery aneurysm/dissection, stroke, ACS not resulting in MI, and pericarditis did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusions:
Higher frailty significantly increases the risk of adverse outcomes post-PCI, highlighting its prognostic value and the need for routine frailty assessments in pre-procedural risk stratification. Further studies are needed to validate these findings across broader populations and to develop targeted strategies aimed at reducing the elevated risks associated with frailty.
More abstracts on this topic:
Timing of Intracranial Stent Placement and One month Stroke and/or Death Rates in Patients with High Grade Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis: Pooled Analysis of SAMMPRIS and VISSIT Trials
Qureshi Adnan, Huang Yilun, Suri Fareed, Gomez Camilo
A Polypill Strategy for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: The POLY-HF TrialPandey Ambarish, Wang Thomas, Keshvani Neil, Rizvi Syed Kazim, Jain Anand, Coellar Juan David, Drazner Mark, Gupta Deepak, Chandra Alvin, Zaha Vlad