Final ID: MP2571
Dynamic PET Imaging Quantifies Absolute Measures of Calf Muscle Perfusion in a Porcine Model of Peripheral Endovascular Arterial Occlusion and PAD Patients with Claudication
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an atherosclerotic disorder of the lower extremities promoting muscle ischemia. Our lab previously validated the use of fluorine-18 sodium fluoride (18F-NaF) dynamic analog PET imaging for quantification of muscle perfusion in PAD. However, newer digital PET scanners with larger axial field-of-views could provide higher sensitivity detection of ischemia and broader perfusion assessment of the legs in PAD. This study sought to test the utility of a novel digital PET scanner for detecting muscle ischemia in a porcine model as well as PAD patients with claudication.
Methods: Female Yorkshire pigs (N=6, 16.1 ± 4.0 kg) underwent unilateral iliac arterial occlusion via endovascular deployment of a covered stent and Amplatzer plug. On the day of occlusion, a 2.5-minute dynamic PET scan of the legs was performed following administration of 18F-NaF (182.56 ± 9.55 MBq) using a large axial field-of-view digital PET scanner with bismuth germanate (BGO) crystals (GE Omni Legend). Co-registered CT images were acquired for attenuation correction and calf muscle segmentation. An image-derived arterial input was obtained from the abdominal aorta and time activity curves for the bilateral calves, to facilitate 1-tissue compartment modeling and calculation of skeletal muscle perfusion values (reported as ml/100g/min). The same dynamic PET approach was then translated to PAD patients (N = 21; 18F-NaF dose: 310.43 ± 22.2 MBq), using the popliteal artery as an arterial input, to assess calf muscle perfusion. T-tests were used to compare perfusion values between ischemic and non-ischemic limbs in pigs and patients.
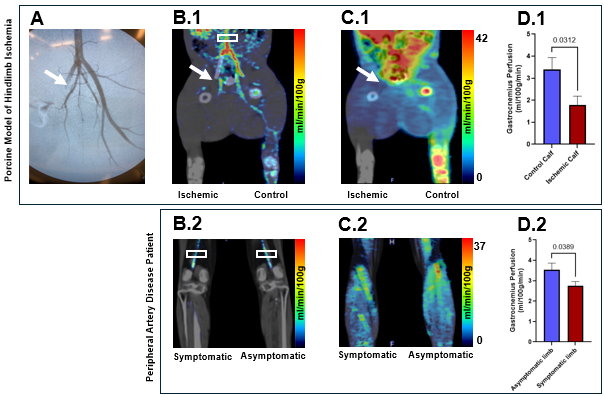
Results: Digital subtraction angiography confirmed successful stent/plug deployment and arterial occlusion in pigs immediately post-occlusion (Fig. 1A). Dynamic PET/CT imaging revealed excellent count detection for kinetic modeling (Fig. 1B.1-2) and significant reductions in calf muscle perfusion between occluded and non-occluded limbs in the porcine model (p=0.031; Fig. 1C.1). Translation to PAD patients demonstrated significant reductions in calf perfusion in symptomatic versus asymptomatic limbs (p=0.039; Fig. 1C.2).
Conclusions: Dynamic PET/CT imaging on emerging digital PET scanners allows for broader scan coverage, high-sensitivity detection of regional alterations in muscle ischemia in PAD, and provides unique opportunities for detection of disease and monitoring of treatment responses in PAD.
Methods: Female Yorkshire pigs (N=6, 16.1 ± 4.0 kg) underwent unilateral iliac arterial occlusion via endovascular deployment of a covered stent and Amplatzer plug. On the day of occlusion, a 2.5-minute dynamic PET scan of the legs was performed following administration of 18F-NaF (182.56 ± 9.55 MBq) using a large axial field-of-view digital PET scanner with bismuth germanate (BGO) crystals (GE Omni Legend). Co-registered CT images were acquired for attenuation correction and calf muscle segmentation. An image-derived arterial input was obtained from the abdominal aorta and time activity curves for the bilateral calves, to facilitate 1-tissue compartment modeling and calculation of skeletal muscle perfusion values (reported as ml/100g/min). The same dynamic PET approach was then translated to PAD patients (N = 21; 18F-NaF dose: 310.43 ± 22.2 MBq), using the popliteal artery as an arterial input, to assess calf muscle perfusion. T-tests were used to compare perfusion values between ischemic and non-ischemic limbs in pigs and patients.
Results: Digital subtraction angiography confirmed successful stent/plug deployment and arterial occlusion in pigs immediately post-occlusion (Fig. 1A). Dynamic PET/CT imaging revealed excellent count detection for kinetic modeling (Fig. 1B.1-2) and significant reductions in calf muscle perfusion between occluded and non-occluded limbs in the porcine model (p=0.031; Fig. 1C.1). Translation to PAD patients demonstrated significant reductions in calf perfusion in symptomatic versus asymptomatic limbs (p=0.039; Fig. 1C.2).
Conclusions: Dynamic PET/CT imaging on emerging digital PET scanners allows for broader scan coverage, high-sensitivity detection of regional alterations in muscle ischemia in PAD, and provides unique opportunities for detection of disease and monitoring of treatment responses in PAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A KLF2-BMPER-Smad1/5 checkpoint regulates high fluid shear stress-mediated artery remodeling
Deng Hanqiang, Zhang Jiasheng, Schwartz Martin
Aldosterone Promotes Aortic Dissection through Lactate/Lactylation-mediated Phenotypic Switching of Vascular Smooth Muscle CellLi Nanfang, Zhu Qing