Final ID: Su1147
Analysis of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Vascular Occlusion Test as a Complement to Ankle-Brachial Index and 6-Minute Walk Test in Patients Diagnosed with Peripheral Artery Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is caused by a lack of blood flow to the musculature relative to its metabolism which results in pain. PAD impacts up to 20% of patients around the world. PAD involves macrovascular and microvascular dysfunction. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) measures muscle oxygenation levels and assesses microvascular function. The standard of care for diagnosing PAD is the ankle-brachial index (ABI), which assesses macrovascular disease, and the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), which measures gait speed and claudication. NIRS has the potential to monitor progression of PAD.
Hypothesis
NIRS measurement of muscle oxygenation, during a standard test of vascular occlusion and post-occlusive hyperemia, the vascular occlusion test (VOT), is predictive of PAD severity as determined by ABI and 6MWT.
Methods
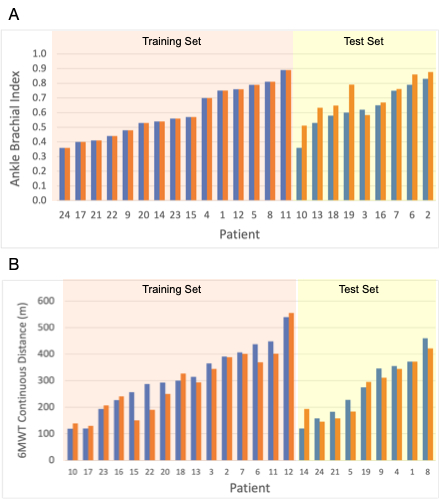
We studied 24 patients diagnosed with PAD. The mean age of the patients was 71.3 years, including 54% (n=13) males and 46% (n=11) females. The VOT consisted of rest, occlusion, and reperfusion phases each lasting 5 min (15 min total). Muscle oxygen saturation levels were recorded at 2 hertz. For every patient, 6 features were extracted from the VOT data using computational methods. The VOT features from 15 patients were used to train function-fitting neural network models to predict ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance. The models were then used to predict ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance from the VOT features of 9 test patients not used in the training,
Results
For patients in the test set, the ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance predicted by the models differed from the actual measurements by 14%±13% and 15%±17%, respectively (Figure 1). For patients in the training set, the ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance predicted by the models differed from the actual measurements by 0±0% and 12%±11%, respectively (Figure 1).
Conclusion
The VOT has the potential to predict the ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance of patients diagnosed with PAD, suggesting that the VOT can be automated and used to monitor the severity of PAD. With more data from both healthy patients and PAD patients, and improvement of the model, we anticipate that the VOT will complement ABI and 6MWT in the diagnosis and monitoring of PAD.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is caused by a lack of blood flow to the musculature relative to its metabolism which results in pain. PAD impacts up to 20% of patients around the world. PAD involves macrovascular and microvascular dysfunction. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) measures muscle oxygenation levels and assesses microvascular function. The standard of care for diagnosing PAD is the ankle-brachial index (ABI), which assesses macrovascular disease, and the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), which measures gait speed and claudication. NIRS has the potential to monitor progression of PAD.
Hypothesis
NIRS measurement of muscle oxygenation, during a standard test of vascular occlusion and post-occlusive hyperemia, the vascular occlusion test (VOT), is predictive of PAD severity as determined by ABI and 6MWT.
Methods
We studied 24 patients diagnosed with PAD. The mean age of the patients was 71.3 years, including 54% (n=13) males and 46% (n=11) females. The VOT consisted of rest, occlusion, and reperfusion phases each lasting 5 min (15 min total). Muscle oxygen saturation levels were recorded at 2 hertz. For every patient, 6 features were extracted from the VOT data using computational methods. The VOT features from 15 patients were used to train function-fitting neural network models to predict ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance. The models were then used to predict ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance from the VOT features of 9 test patients not used in the training,
Results
For patients in the test set, the ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance predicted by the models differed from the actual measurements by 14%±13% and 15%±17%, respectively (Figure 1). For patients in the training set, the ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance predicted by the models differed from the actual measurements by 0±0% and 12%±11%, respectively (Figure 1).
Conclusion
The VOT has the potential to predict the ABI and 6MWT Continuous Distance of patients diagnosed with PAD, suggesting that the VOT can be automated and used to monitor the severity of PAD. With more data from both healthy patients and PAD patients, and improvement of the model, we anticipate that the VOT will complement ABI and 6MWT in the diagnosis and monitoring of PAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
2-Deoxyuridine Associates with Recurrent Coronary Events
Pistritu Dan, Castano David, Liehn Elisa, Koh Cho Yeow, Gerszten Robert, Singaraja Roshni, Chan Mark, Shah Svati
Left Ventricular Septum Displacement Implications in the Limited Cardiac Reserve, RV to Pc Uncoupling and Oxygen Uptake During Exercise in Heart FailureSerrantoni Violetta, Crisci Giulia, Losito Maurizio, Zagarra Tania, Ginelli Daniele, Bursi Francesca, Guazzi Marco