Final ID: Th0077
Vessel-Specific CT Calcium Scoring in Peripheral Artery Disease Using Deep Learning
Abstract Body: Objective: CT calcium scoring is a tool for assessing disease severity and risk for adverse events in coronary artery disease; however, quantification of vessel-specific calcium burden from CT images in peripheral artery disease (PAD) has remained relatively understudied due to the time-consuming nature of segmenting the arterial network. Therefore, we sought to test the performance of a semi-automated deep learning approach to segment and quantify vessel-specific calcium burden from CT images in PAD patients to streamline eventual clinical implementation of calcium scoring in PAD.
Methods: Patients with PAD (N=80) were prospectively enrolled for non-contrast CT imaging. Images were manually segmented to quantify calcium mass for the femoral-popliteal, peroneal, anterior tibial, and posterior tibial arteries. Manually processed images were used as input data to train an nnU-Net deep learning model. Data augmentation techniques were applied to increase the dataset to 157 images (80 patients=157 legs) to achieve better generalization of results. The dataset was randomly split using an 90/10 ratio for model training and testing. Dice coefficient was calculated to assess the agreement between manual and deep learning image analysis results.
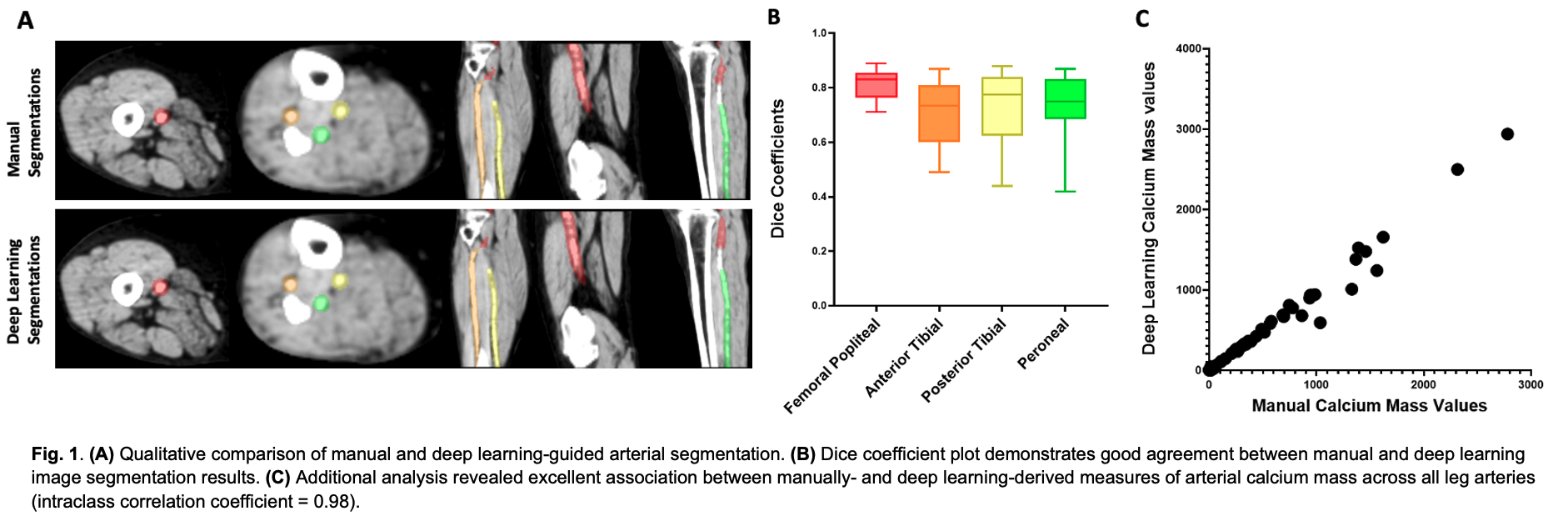
Results: Deep learning-guided image segmentation results qualitatively agreed with manual image analysis (Fig. 1A). Quantitatively, deep learning produced dice coefficients of 0.82 ± 0.05 for femoral-popliteal, 0.71 ± 0.12 for anterior tibial, 0.74 ± 0.12 for posterior tibial, and 0.73 ± 0.12 for the peroneal artery, thus representing good performance for multi-vessel segmentation (Fig. 1B). Calcium mass values derived from both manual and deep learning image analysis demonstrated excellent agreement, with an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.98 (Fig. 1C).
Conclusions: Deep learning allows for accurate quantification of vessel-specific CT calcium values for the lower extremities of PAD patients, which is a challenging task due to arteries comprising a small percentage (i.e., 0.07%) of the overall CT image. This AI-based approach significantly reduces CT image analysis time from hours to seconds and represents a promising approach for future risk stratification in PAD.
Methods: Patients with PAD (N=80) were prospectively enrolled for non-contrast CT imaging. Images were manually segmented to quantify calcium mass for the femoral-popliteal, peroneal, anterior tibial, and posterior tibial arteries. Manually processed images were used as input data to train an nnU-Net deep learning model. Data augmentation techniques were applied to increase the dataset to 157 images (80 patients=157 legs) to achieve better generalization of results. The dataset was randomly split using an 90/10 ratio for model training and testing. Dice coefficient was calculated to assess the agreement between manual and deep learning image analysis results.
Results: Deep learning-guided image segmentation results qualitatively agreed with manual image analysis (Fig. 1A). Quantitatively, deep learning produced dice coefficients of 0.82 ± 0.05 for femoral-popliteal, 0.71 ± 0.12 for anterior tibial, 0.74 ± 0.12 for posterior tibial, and 0.73 ± 0.12 for the peroneal artery, thus representing good performance for multi-vessel segmentation (Fig. 1B). Calcium mass values derived from both manual and deep learning image analysis demonstrated excellent agreement, with an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.98 (Fig. 1C).
Conclusions: Deep learning allows for accurate quantification of vessel-specific CT calcium values for the lower extremities of PAD patients, which is a challenging task due to arteries comprising a small percentage (i.e., 0.07%) of the overall CT image. This AI-based approach significantly reduces CT image analysis time from hours to seconds and represents a promising approach for future risk stratification in PAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
4D Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Identifies Differences in Regional Strain Patterns Among Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection or Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy
Henderson Christopher, Starnes Joseph, Samyn Margaret, Damon Bruce, Hernandez Lazaro, Goergen Craig, Soslow Jonathan, Prado Marco Aurélio, Earl Conner, Georgedurrett Kristen, Lee Simon, Nandi Deipanjan, Chan Kak-chen, Shugh Svetlana, Kikano Sandra
24-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase Plays a Significant Role in Inflammation During Peripheral Arterial DiseaseLassance-soares Roberta, Falero-diaz Gustavo, Montoya Christopher, Barboza Catarina