Final ID: Su4016
Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure in an Infant due to an Intronic Deletion Disrupting TAZ Splicing
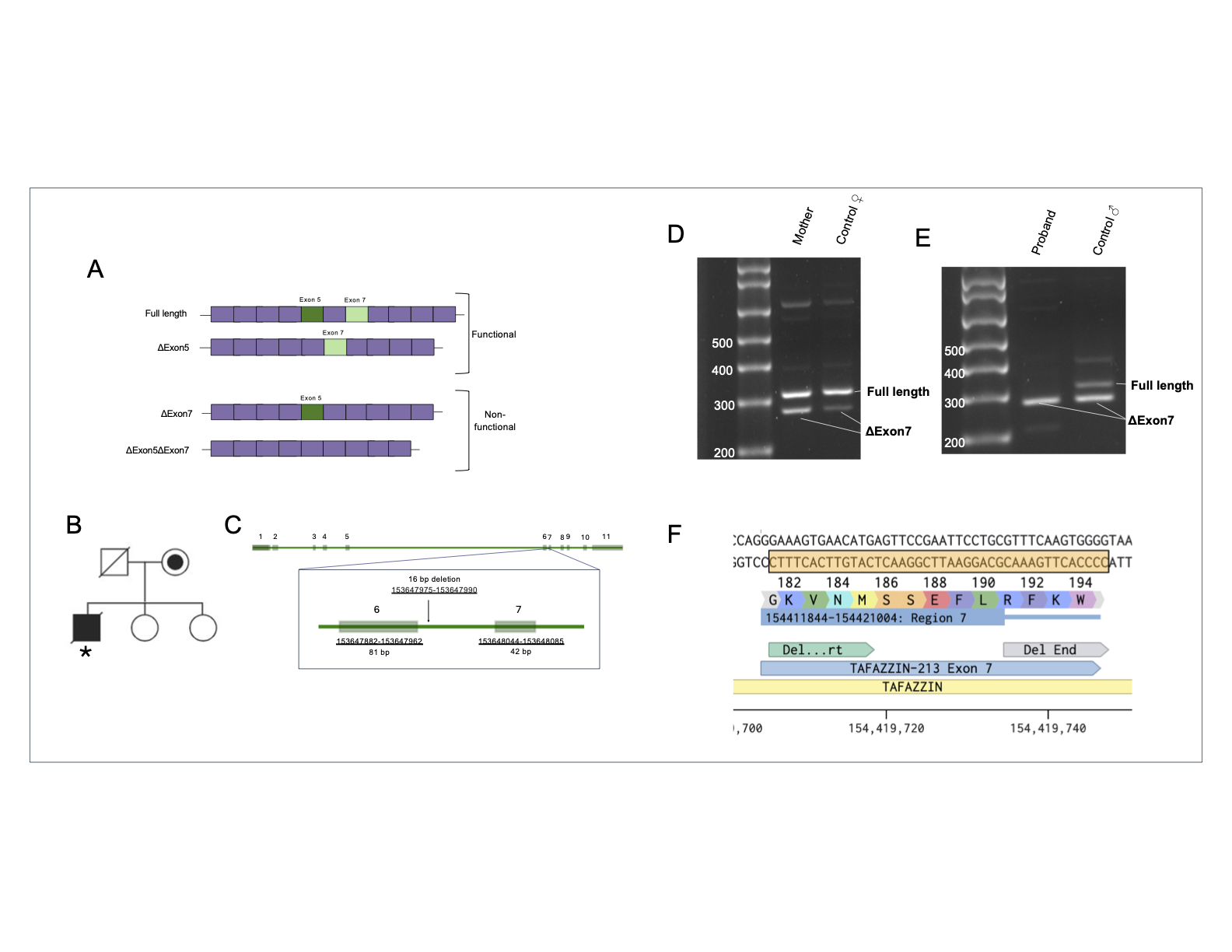
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Barth syndrome (BS) is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by loss of function mutations in the TAZ gene. BS is characterized by dilated cardiomyopathy, skeletal myopathy and neutropenia. TAZ encodes the Tafazzin protein, which catalyzes the transacylation of cardiolipin, a component of mitochondrial membranes. Several TAZ isoforms are observed in normal individuals, however, only a subset of these exhibit transacylase activity (Fig A). We identified a 16 base pair TAZ intronic deletion, initially classified as benign, in a 14-month-old male patient who presented with acute onset heart failure and subsequently passed away (Fig B,C).
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that the 16-base pair intronic deletion was not benign, and instead altered splicing of TAZ, leading to a nonfunctional TAZ isoform (ΔEx7) and heart failure.
Methods: To assess an effect on splicing, RNA was isolated from peripheral blood from the proband’s mother and a female control. RT-PCR was used to detect deletion of TAZ exon 7 (ΔEx7) in both samples and PCR products were sequenced. RNA was isolated from the hearts of the proband and a healthy control male infant and similarly analyzed for ΔEx7 TAZ.
Results: The blood sample from the proband’s mother exhibited more ΔEx7 TAZ compared to control (Fig D). The proband’s cardiac tissue expressed only ΔEx7 TAZ transcript, with undetectable levels of full-length TAZ transcript (Fig E), confirmed by sequencing to lack exon 7 (Fig F). Age, sex matched healthy control cardiac tissue expressed both isoforms.
Conclusion: The 16bp deletion in intron 6 of TAZ caused deletion of Exon 7, which is known to encode a nonfunctional Tafazzin protein. These results provide sufficient data to reclassify the genetic result to likely pathogenic and provide actionable results for management of the proband’s mother and her surviving children. These data underscore the importance of reanalysis and functional assessment of genetic variants associated with cardiomyopathy.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that the 16-base pair intronic deletion was not benign, and instead altered splicing of TAZ, leading to a nonfunctional TAZ isoform (ΔEx7) and heart failure.
Methods: To assess an effect on splicing, RNA was isolated from peripheral blood from the proband’s mother and a female control. RT-PCR was used to detect deletion of TAZ exon 7 (ΔEx7) in both samples and PCR products were sequenced. RNA was isolated from the hearts of the proband and a healthy control male infant and similarly analyzed for ΔEx7 TAZ.
Results: The blood sample from the proband’s mother exhibited more ΔEx7 TAZ compared to control (Fig D). The proband’s cardiac tissue expressed only ΔEx7 TAZ transcript, with undetectable levels of full-length TAZ transcript (Fig E), confirmed by sequencing to lack exon 7 (Fig F). Age, sex matched healthy control cardiac tissue expressed both isoforms.
Conclusion: The 16bp deletion in intron 6 of TAZ caused deletion of Exon 7, which is known to encode a nonfunctional Tafazzin protein. These results provide sufficient data to reclassify the genetic result to likely pathogenic and provide actionable results for management of the proband’s mother and her surviving children. These data underscore the importance of reanalysis and functional assessment of genetic variants associated with cardiomyopathy.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Phenylbutyric Acid Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Retention and Partially Restores Function of LDLR p.D622N Mutation In Vitro: A Potential Therapy for Hypercholesterolemia
Wang Yongxiang, Zhang Piyi, Bai Ming, Zhang Zheng
Base editing approach to limit the expression of Asgr1, Pcsk9 and Angptl3 for the control of hyperlipidemia in miceAgrahari Gaurav