Final ID: 4370149
Oxalate Exposure Alters Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Energetic Pathways in Cardiac Myocytes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Oxalate is a nonplanar anion that accumulates in the serum of patients with chronic kidney disease. In the urine, it can contribute to calcium oxalate kidney stone formation. Recent studies have suggested potential cardiovascular implications of oxalate, including detrimental effects of high serum oxalate on mitochondrial function as well as cardiac inflammation. However, the molecular mechanism of oxalate’s effects on cardiomyocytes remains unclear.
Methods: Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) were isolated from postnatal day 1 rats (n=20) using the Miltenyi isolation kit. Cells were plated on Primaria plates at a density of 0.8 million cells/well and treated for 24 hours with either 0 µM or 100 µM sodium oxalate (NaOx) in triplicate. RNA was extracted and prepared for Illumina Nova SeqX+ per the manufacturer’s protocol. Differential gene expression analysis was performed using DESeq2. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment was conducted using Enrichr with a false discovery rate threshold of <0.1.
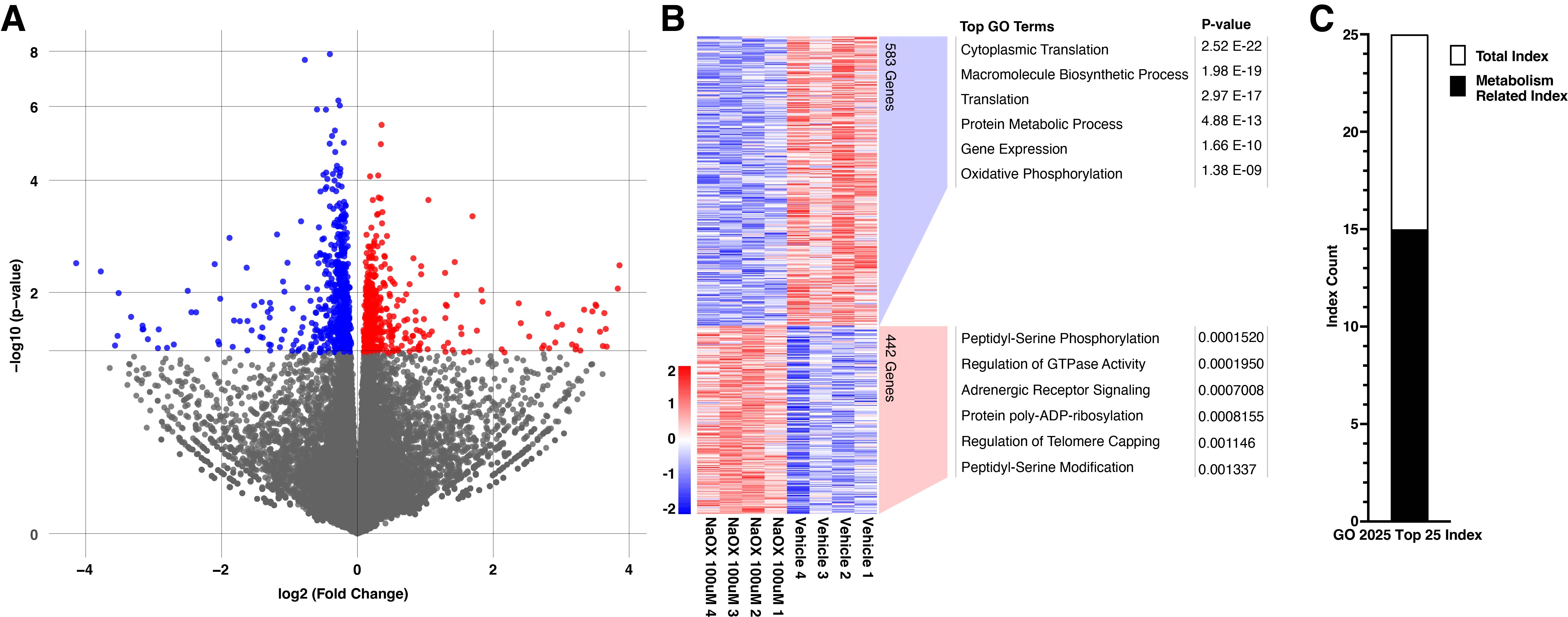
Results: A total of 1,025 differentially expressed genes (p < 0.05) were identified, including 583 significantly downregulated genes. These included key regulators of the electron transport chain, glucose transporters, and transcription factors involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. GO enrichment analysis revealed clustering of terms consistent with mitochondrial dysfunction and disrupted energetic pathways. Pathway analysis showed decreased expression of genes in the COX and NDUF families, implicating NRF-1 and its upstream coactivator PGC-1α as potential master regulators downregulated in response to oxalate exposure.
Conclusion: Transcriptomic and pathway analyses of oxalate-treated NRVMs indicate significant downregulation of genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial function. These findings suggest that mitochondrial biogenesis regulators, including NRF-1 and PGC-1α, may serve as mediators of oxalate-induced cardiomyocyte dysfunction. Additional studies are necessary to define the mechanisms leading to elevated serum oxalate levels with transcriptional dysregulation.
Methods: Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) were isolated from postnatal day 1 rats (n=20) using the Miltenyi isolation kit. Cells were plated on Primaria plates at a density of 0.8 million cells/well and treated for 24 hours with either 0 µM or 100 µM sodium oxalate (NaOx) in triplicate. RNA was extracted and prepared for Illumina Nova SeqX+ per the manufacturer’s protocol. Differential gene expression analysis was performed using DESeq2. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment was conducted using Enrichr with a false discovery rate threshold of <0.1.
Results: A total of 1,025 differentially expressed genes (p < 0.05) were identified, including 583 significantly downregulated genes. These included key regulators of the electron transport chain, glucose transporters, and transcription factors involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. GO enrichment analysis revealed clustering of terms consistent with mitochondrial dysfunction and disrupted energetic pathways. Pathway analysis showed decreased expression of genes in the COX and NDUF families, implicating NRF-1 and its upstream coactivator PGC-1α as potential master regulators downregulated in response to oxalate exposure.
Conclusion: Transcriptomic and pathway analyses of oxalate-treated NRVMs indicate significant downregulation of genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial function. These findings suggest that mitochondrial biogenesis regulators, including NRF-1 and PGC-1α, may serve as mediators of oxalate-induced cardiomyocyte dysfunction. Additional studies are necessary to define the mechanisms leading to elevated serum oxalate levels with transcriptional dysregulation.
More abstracts on this topic:
An ADPKD-Associated Pathway in Cardiac Homeostasis, Heart Failure, and Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic
Liu Chia-feng, Leon Steven, Wessely Oliver, Tang Wai Hong
A novel Urocortin-2 analog COR-1167 corrects cardiac and renal dysfunction on top of Empagliflozin in a rat model of acute decompensated heart failureStephan Yohan, Corruble Clement, Charrier Lucie, Nicol Lionel, Kowala Mark, Ozoux Marie-laure, Lawson Francesca, Janiak Philip, Mulder Paul