Final ID: Su2137
LPA-Targeted siRNAs Lower Lp(a) by Over 90%: A Meta-Analysis of Olpasiran, Lepodisiran, and Zerlasiran
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Elevated lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a genetically determined, independent risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Currently, no approved therapies specifically target Lp(a) reduction. Small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutics—such as olpasiran, lepodisiran, and zerlasiran—are promising investigational agents designed to address this therapeutic gap. These agents selectively target LPA mRNA in hepatocytes, suppressing apolipoprotein(a) synthesis and reducing circulating Lp(a) concentrations..
Research Question:
What is the pooled efficacy and safety profile of siRNA agents that target LPA mRNA?
Methods:
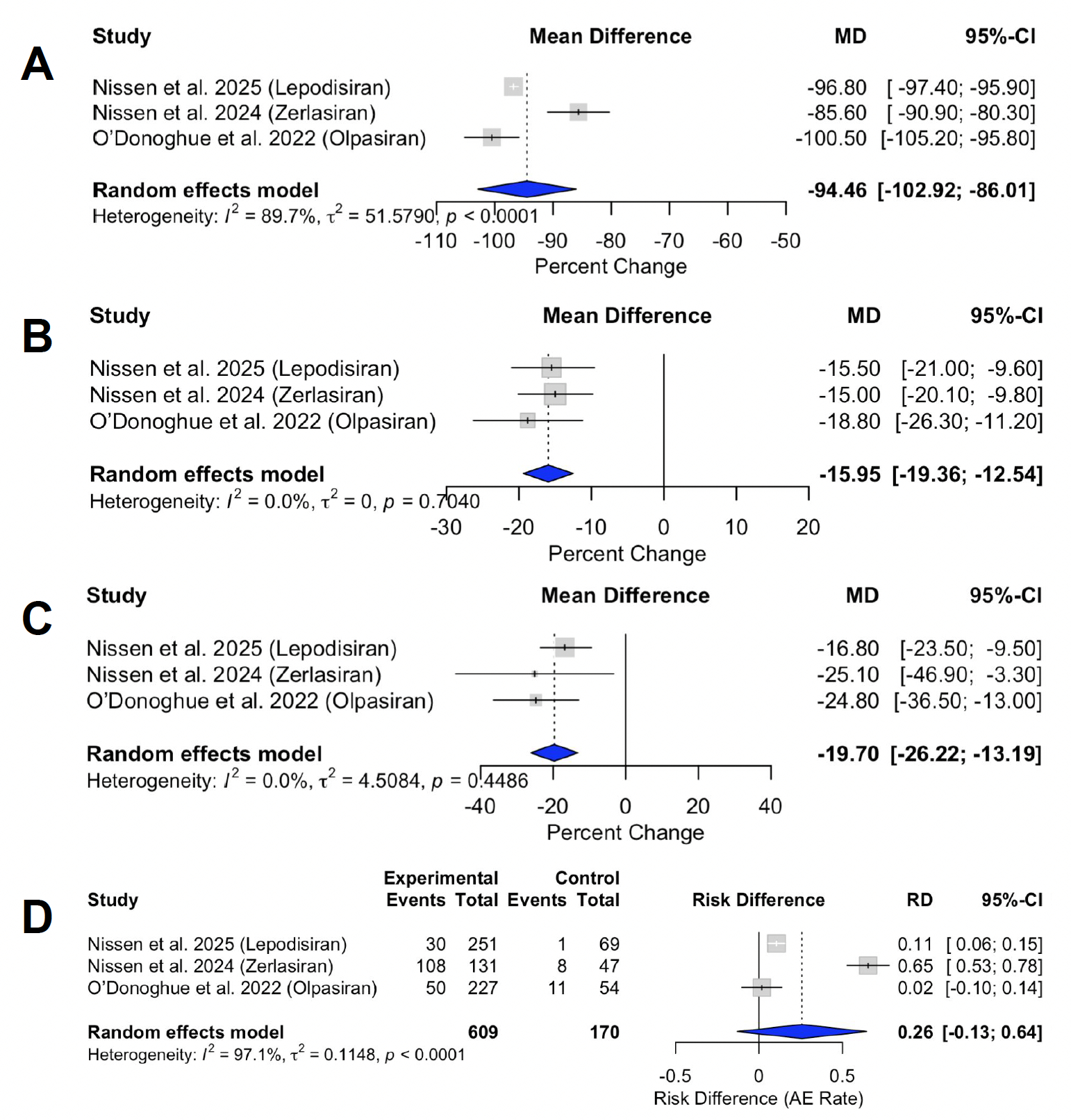
A systematic search of MEDLINE and EMBASE was conducted through June 2025 to identify trials evaluating siRNA therapies that directly silence LPA mRNA. Outcomes of interest included percent changes in Lp(a), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), along with adverse event rates compared to placebo. To ensure cross-trial consistency, efficacy endpoints were extracted from assessments conducted between weeks 34 and 36, using data from the highest siRNA dose per study. Forest plots display mean differences with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was quantified using the I2 statistic, and adverse events were summarized as absolute risk differences due to low event rates in control groups.
Results: Three phase 2 trials met the inclusion criteria. siRNA therapy achieved a significant pooled mean reduction in Lp(a) of −94.46% [95% CI −102.92 to −86.01], with substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 89.7%). siRNA therapies decreased ApoB by −15.95% [95% CI −19.36 to −12.54] and LDL-C by −19.70% [95% CI −26.22 to −13.19], both without significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). Adverse events occurred more frequently in the siRNA group, with a pooled absolute risk difference of 26.0% [95% CI −13.0 to 64.0] compared to placebo; however, this finding demonstrated high heterogeneity (I2 = 97.1%), and the confidence interval crossed the null.
Conclusions:
siRNA therapeutics targeting LPA mRNA demonstrate substantial efficacy, lowering Lp(a) levels by over 90% with concurrent reductions in ApoB and LDL-C. Ongoing phase 3 trials will be pivotal in further characterizing their safety profile and determining the extent to which these promising lipid changes translate into cardiovascular risk reduction.
Elevated lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a genetically determined, independent risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Currently, no approved therapies specifically target Lp(a) reduction. Small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutics—such as olpasiran, lepodisiran, and zerlasiran—are promising investigational agents designed to address this therapeutic gap. These agents selectively target LPA mRNA in hepatocytes, suppressing apolipoprotein(a) synthesis and reducing circulating Lp(a) concentrations..
Research Question:
What is the pooled efficacy and safety profile of siRNA agents that target LPA mRNA?
Methods:
A systematic search of MEDLINE and EMBASE was conducted through June 2025 to identify trials evaluating siRNA therapies that directly silence LPA mRNA. Outcomes of interest included percent changes in Lp(a), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), along with adverse event rates compared to placebo. To ensure cross-trial consistency, efficacy endpoints were extracted from assessments conducted between weeks 34 and 36, using data from the highest siRNA dose per study. Forest plots display mean differences with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was quantified using the I2 statistic, and adverse events were summarized as absolute risk differences due to low event rates in control groups.
Results: Three phase 2 trials met the inclusion criteria. siRNA therapy achieved a significant pooled mean reduction in Lp(a) of −94.46% [95% CI −102.92 to −86.01], with substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 89.7%). siRNA therapies decreased ApoB by −15.95% [95% CI −19.36 to −12.54] and LDL-C by −19.70% [95% CI −26.22 to −13.19], both without significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). Adverse events occurred more frequently in the siRNA group, with a pooled absolute risk difference of 26.0% [95% CI −13.0 to 64.0] compared to placebo; however, this finding demonstrated high heterogeneity (I2 = 97.1%), and the confidence interval crossed the null.
Conclusions:
siRNA therapeutics targeting LPA mRNA demonstrate substantial efficacy, lowering Lp(a) levels by over 90% with concurrent reductions in ApoB and LDL-C. Ongoing phase 3 trials will be pivotal in further characterizing their safety profile and determining the extent to which these promising lipid changes translate into cardiovascular risk reduction.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Tool for Evaluating Endothelial Function: Plethysmographic Flow-mediated Vasodilation (pFMD)
AAV-mediated Gene Delivery of PERM1 Prevents the Development of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in a Mouse Model of Pressure Overload
Kishimoto Shinji, Itarashiki Tomomasa, Higashi Yukihito, Maruhashi Tatsuya, Kajikawa Masato, Mizobuchi Aya, Harada Takahiro, Yamaji Takayuki, Nakano Yukiko, Mohamad Yusoff Farina, Yada Tomohiko
AAV-mediated Gene Delivery of PERM1 Prevents the Development of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in a Mouse Model of Pressure Overload
Sreedevi Karthi, Doku Abigail Oforiwaa, Thomas Rebekah, Salama Sarah, Zaitsev Alexey, Warren Junco