Final ID: MP683
Unscrewing Sign: A Visual Indicator For Atrial Leadless Pacemaker Dislodgment
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
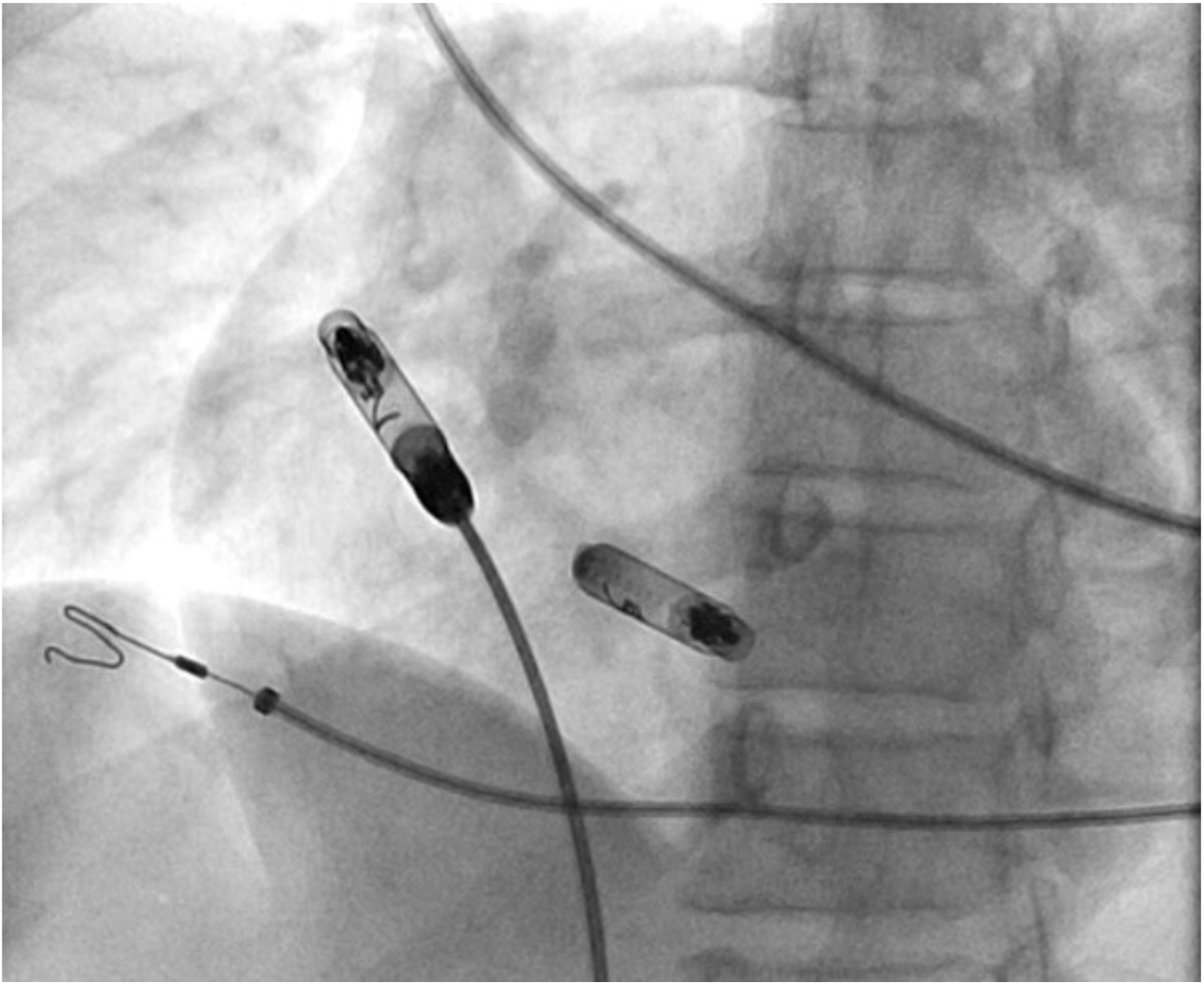
The AVEIR DR i2i Study demonstrated safety of atrial leadless pacemakers with a dislodgment rate of only 1.7%. Data on factors influencing dislodgments however remains limited. Known contributors include suboptimal electrical mapping parameters, absence of current of injury during implantation, and excessive device manipulation during positioning. We present two cases of atrial leadless pacemaker dislodgment occurring in the absence of these established risk factors, each exhibiting a distinctive post-implantation imaging finding consistent with progressive 'unscrewing' of the pacemaker, visually characterized by anticlockwise movement of the Chevron. This radiographic pattern may serve as an early indicator for impending device dislodgment.
Case Presentation
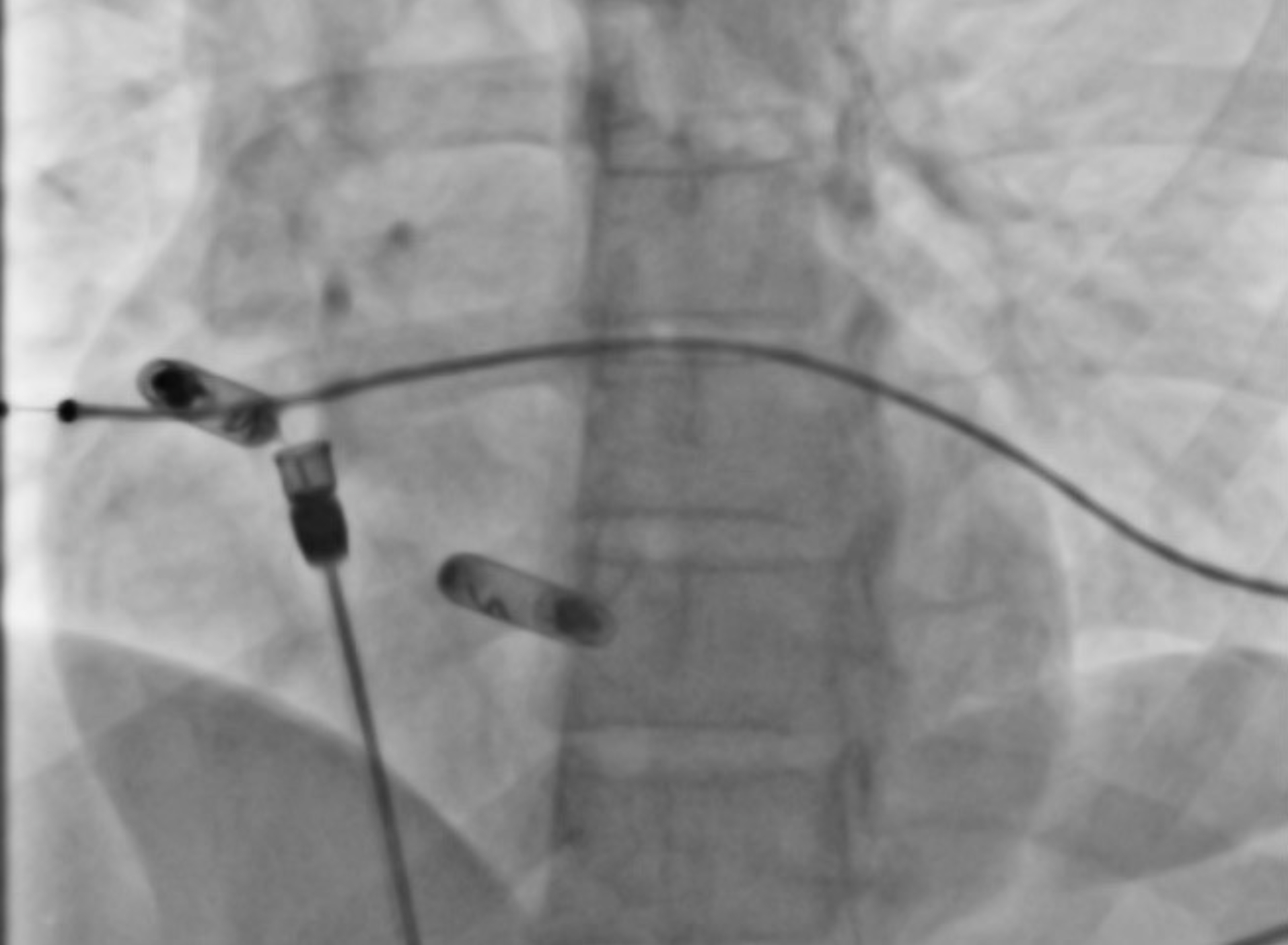
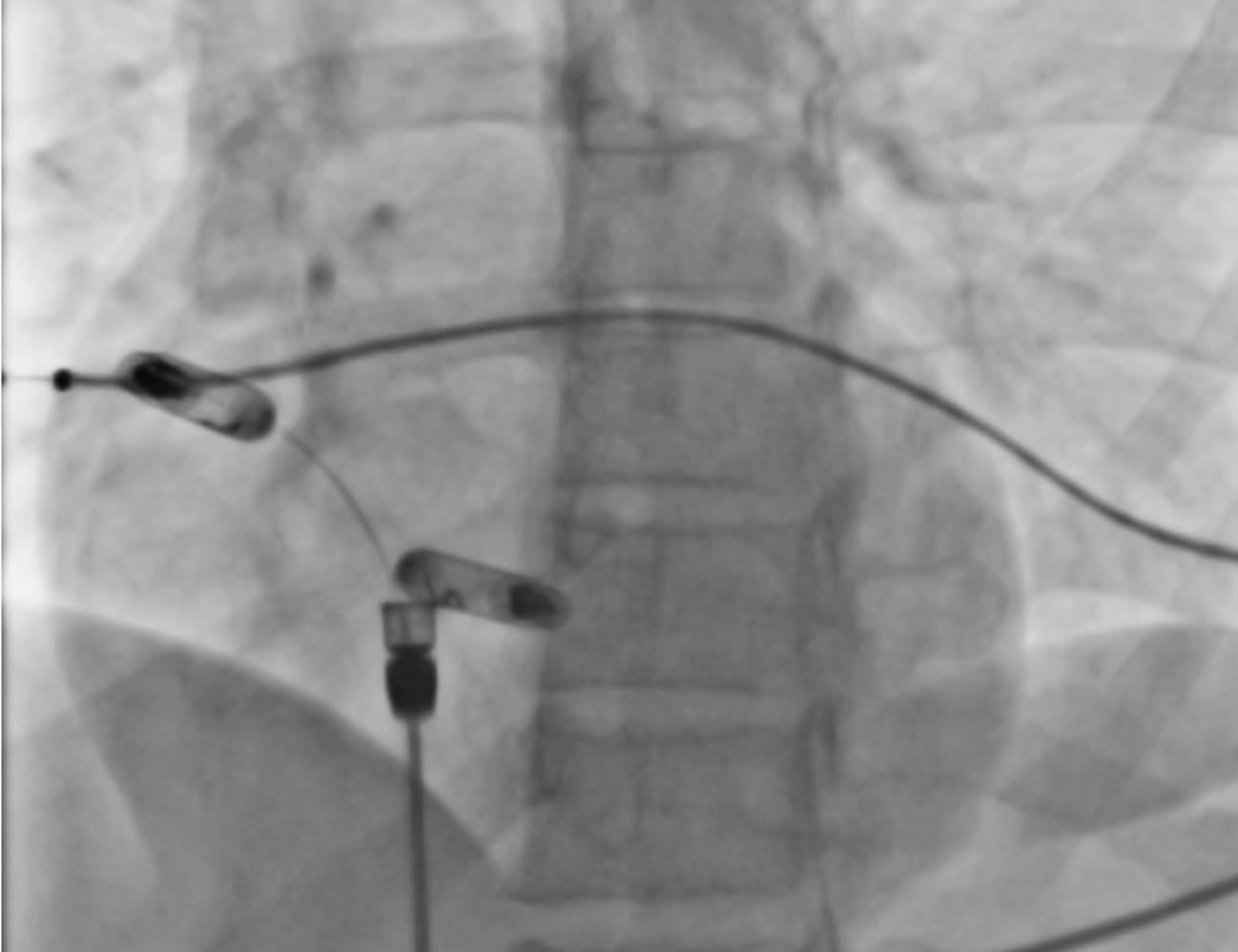
Case 1: 41-year-old female with symptomatic bradycardia, syncope and complete heart block underwent a dual chamber leadless pacemaker implantation. Electrical Mapping and current of injury was excellent. The device was implanted per protocol with one and half clockwise rotation. On postoperative day one, atrial loss of capture was noted. Chest X ray showed exaggerated device motion and revision was recommended. The pacemaker was removed using snaring and a new atrial leadless pacemaker was implanted. Upon reviewing the images from the first procedure, it was noticed that the chevron marker had rotated back (anticlockwise) around its axis leading to 'unscrewing' of the device.
Case 2: 84-year-old male with a history of atrial flutter ablation, type 2 Diabetes, and hypothyroidism presented with symptomatic bradycardia and sinus pauses. Patient underwent atrial leadless pacemaker implantation. Electrical Mapping and current of injury was excellent. Next morning, atrial loss of capture was noted. An abdominal x-ray revealed that the device had dislodged into the pelvis. Interventional radiology was consulted who retrieved the device via snare. Upon reviewing the images, we noted that post-implantation, the chevron sign had rotated anticlockwise half a rotation.
Discussion/Conclusion
Our cases did not have any of the known risk factors for dislodgment. The anticlockwise movement of the chevron sign may serve as an early indicator of dislodgment. Particular attention should be paid to the movement of the chevron post-procedure. Other associations such as hypertrophic myocardium, genetics, and valvular and rhythm abnormalities could play a role in unscrewing the pacemaker and need to be closely studied.
The AVEIR DR i2i Study demonstrated safety of atrial leadless pacemakers with a dislodgment rate of only 1.7%. Data on factors influencing dislodgments however remains limited. Known contributors include suboptimal electrical mapping parameters, absence of current of injury during implantation, and excessive device manipulation during positioning. We present two cases of atrial leadless pacemaker dislodgment occurring in the absence of these established risk factors, each exhibiting a distinctive post-implantation imaging finding consistent with progressive 'unscrewing' of the pacemaker, visually characterized by anticlockwise movement of the Chevron. This radiographic pattern may serve as an early indicator for impending device dislodgment.
Case Presentation
Case 1: 41-year-old female with symptomatic bradycardia, syncope and complete heart block underwent a dual chamber leadless pacemaker implantation. Electrical Mapping and current of injury was excellent. The device was implanted per protocol with one and half clockwise rotation. On postoperative day one, atrial loss of capture was noted. Chest X ray showed exaggerated device motion and revision was recommended. The pacemaker was removed using snaring and a new atrial leadless pacemaker was implanted. Upon reviewing the images from the first procedure, it was noticed that the chevron marker had rotated back (anticlockwise) around its axis leading to 'unscrewing' of the device.
Case 2: 84-year-old male with a history of atrial flutter ablation, type 2 Diabetes, and hypothyroidism presented with symptomatic bradycardia and sinus pauses. Patient underwent atrial leadless pacemaker implantation. Electrical Mapping and current of injury was excellent. Next morning, atrial loss of capture was noted. An abdominal x-ray revealed that the device had dislodged into the pelvis. Interventional radiology was consulted who retrieved the device via snare. Upon reviewing the images, we noted that post-implantation, the chevron sign had rotated anticlockwise half a rotation.
Discussion/Conclusion
Our cases did not have any of the known risk factors for dislodgment. The anticlockwise movement of the chevron sign may serve as an early indicator of dislodgment. Particular attention should be paid to the movement of the chevron post-procedure. Other associations such as hypertrophic myocardium, genetics, and valvular and rhythm abnormalities could play a role in unscrewing the pacemaker and need to be closely studied.
More abstracts on this topic:
Clonal Fate Mapping of Sinoatrial Node Progenitors
Kethana Khushi, Black Brian, Galang Giselle, Chouhan Gagandeep, Mandla Ravi, Sinha Tanvi, Devine Walter, Mohan Rajiv, Soe Amanda, Vedantham Vasanth
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patientsHaimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron