Final ID: MP938
Single-Cell Resolution Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Cellular and Molecular Dysregulation in Human Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Lung tissue exhibits intricate spatial organization and dynamic cellular interactions. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) remain poorly understood in the spatial context of human lung tissue. This study aims to delineate single-cell resolution spatial transcriptomic profiles of human PAH lungs to uncover dysregulated cellular and molecular pathways.
Hypothesis: Single-cell resolution spatial transcriptomics can reveal key cellular and molecular alterations associated with PAH pathogenesis.
Approach: Lung tissues from 10 healthy donors and 13 idiopathic PAH (IPAH) patients were obtained through the Pulmonary Hypertension Breakthrough Initiative (PHBI). Samples were profiled using the 10X Genomics Xenium platform (5K gene panel). Cell types were annotated by integrating single-cell RNA-seq data from same patients samples using Seurat V5. Gene modules were identified using non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), and spatial localization and expression differences were assessed between PAH and control tissues.
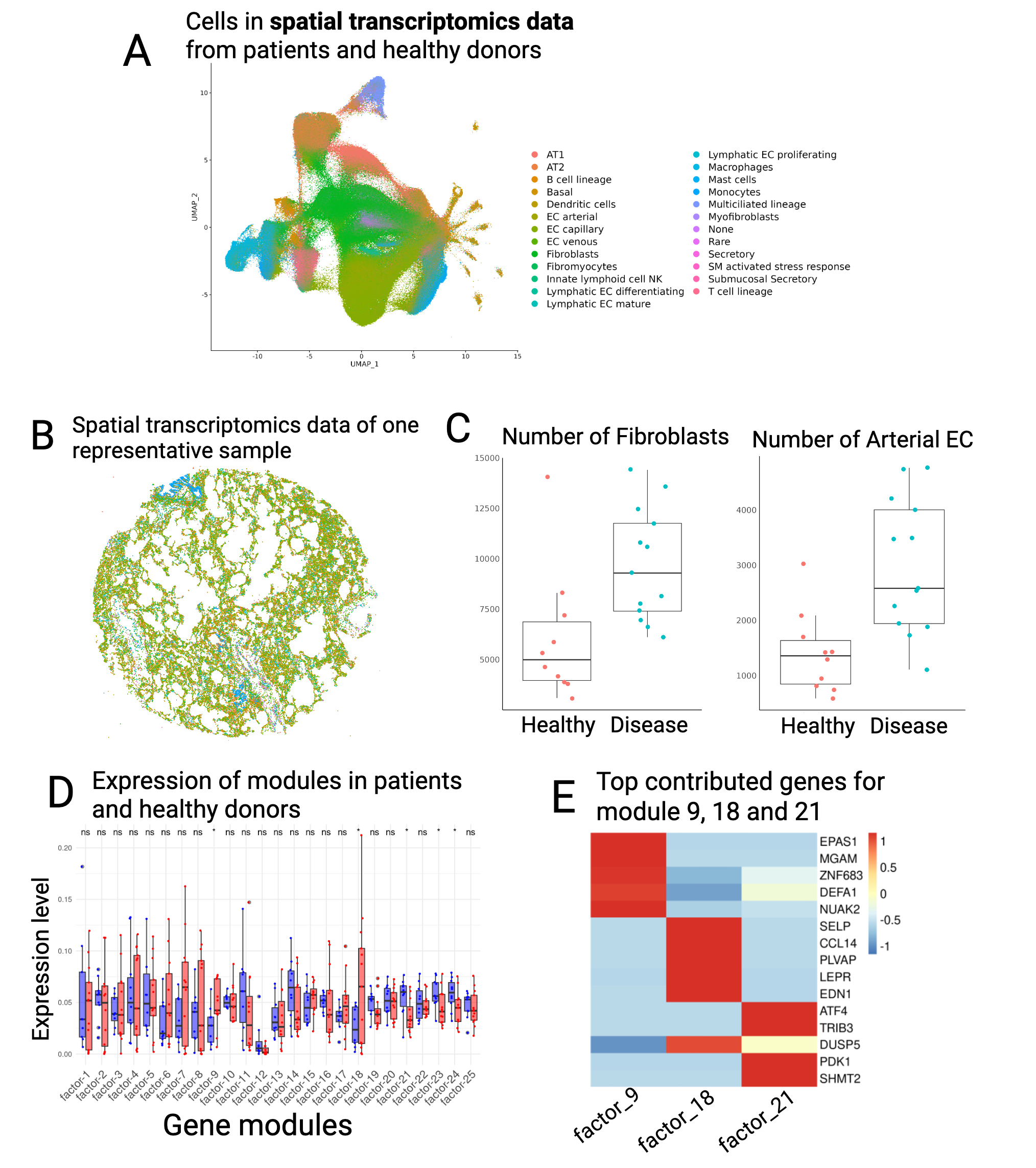
Results: A total of 702,159 cells were identified across 23 samples (10 controls, 13 IPAH patients). Twenty-five distinct cell types were annotated (Figure A), with spatial localization consistent with H&E-stained histological images (Figure B). Arterial endothelial cells and fibroblasts were significantly increased in IPAH lungs (Figure C). NMF analysis identified three gene modules (9, 18, and 21) enriched in arterial endothelial cells. Modules 9 (e.g., EPAS1, MGAM) and 18 (SELP, CCL14) were upregulated in PAH, while module 21 (ATF4, TRIB3, PDK1, SHMT2) was downregulated (Figures D–E). Additionally, ENPP2, ESM1, and POSTN were elevated in arterial ECs from IPAH lungs.
Conclusion: This study presents the first spatial transcriptomic atlas of human PAH lungs at single-cell resolution. Increased abundance and altered gene expression in arterial endothelial cells and fibroblasts highlight their roles in vascular remodeling. Our findings support the use of high-resolution spatial transcriptomics to uncover novel pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets in PAH.
Keywords: Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, Spatial transcriptomics, Single-cell resolution, Arterial endothelial cells
Hypothesis: Single-cell resolution spatial transcriptomics can reveal key cellular and molecular alterations associated with PAH pathogenesis.
Approach: Lung tissues from 10 healthy donors and 13 idiopathic PAH (IPAH) patients were obtained through the Pulmonary Hypertension Breakthrough Initiative (PHBI). Samples were profiled using the 10X Genomics Xenium platform (5K gene panel). Cell types were annotated by integrating single-cell RNA-seq data from same patients samples using Seurat V5. Gene modules were identified using non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), and spatial localization and expression differences were assessed between PAH and control tissues.
Results: A total of 702,159 cells were identified across 23 samples (10 controls, 13 IPAH patients). Twenty-five distinct cell types were annotated (Figure A), with spatial localization consistent with H&E-stained histological images (Figure B). Arterial endothelial cells and fibroblasts were significantly increased in IPAH lungs (Figure C). NMF analysis identified three gene modules (9, 18, and 21) enriched in arterial endothelial cells. Modules 9 (e.g., EPAS1, MGAM) and 18 (SELP, CCL14) were upregulated in PAH, while module 21 (ATF4, TRIB3, PDK1, SHMT2) was downregulated (Figures D–E). Additionally, ENPP2, ESM1, and POSTN were elevated in arterial ECs from IPAH lungs.
Conclusion: This study presents the first spatial transcriptomic atlas of human PAH lungs at single-cell resolution. Increased abundance and altered gene expression in arterial endothelial cells and fibroblasts highlight their roles in vascular remodeling. Our findings support the use of high-resolution spatial transcriptomics to uncover novel pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets in PAH.
Keywords: Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, Spatial transcriptomics, Single-cell resolution, Arterial endothelial cells
More abstracts on this topic:
Admission Cell-free DNA Predicts Cardiogenic Shock Progression and In-Hospital Mortality
Park Ashley, Kong Hyesik, Andargie Temesgen, Jang Moon, Solomon Michael, Brusca Samuel, Barnett Christopher, Obrien Connor, Agbor-enoh Sean
Contemporary Demographics, Management, and Outcomes in Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Pre- and Post-AI Era ComparisonHebbo Elsa, Elhage Hassan Malika, Jaber Wissam