Final ID: MP970
Monoamine Oxidase-A Promotes Cardiomyocyte Senescence and Aggravates Diastolic Dysfunction in HFpEF via cGAS-STING Signaling
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) involves myocardial aging, inflammation, and diastolic dysfunction. Monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A), a mitochondrial enzyme generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), may contribute to cardiac injury, but its role in HFpEF-associated cardiomyocyte senescence is unclear.
Hypothesis:
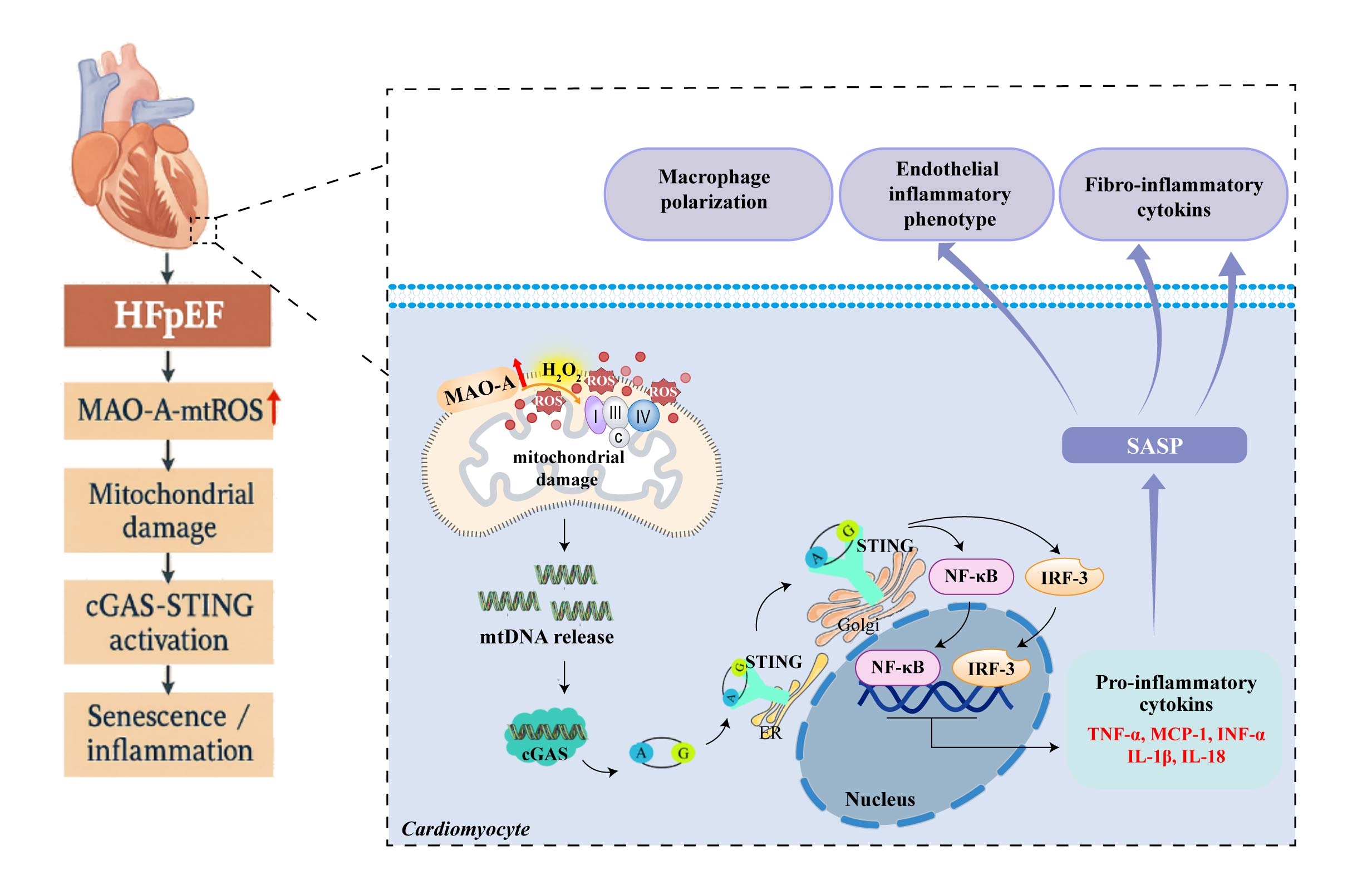
Cardiac MAO-A promotes cardiomyocyte senescence via ROS-induced mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) release and cGAS-STING signaling, exacerbating HFpEF.
Methods:
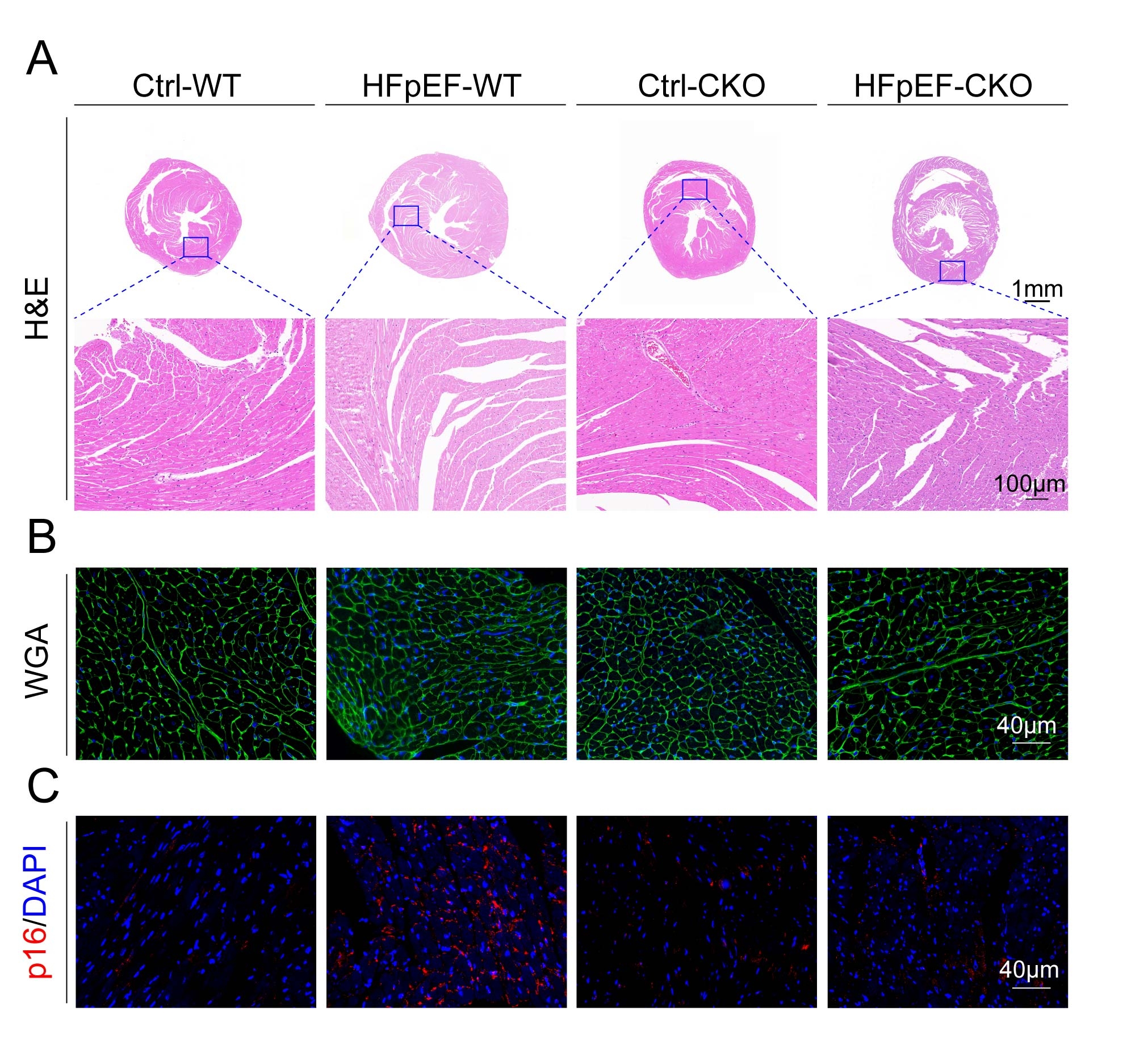
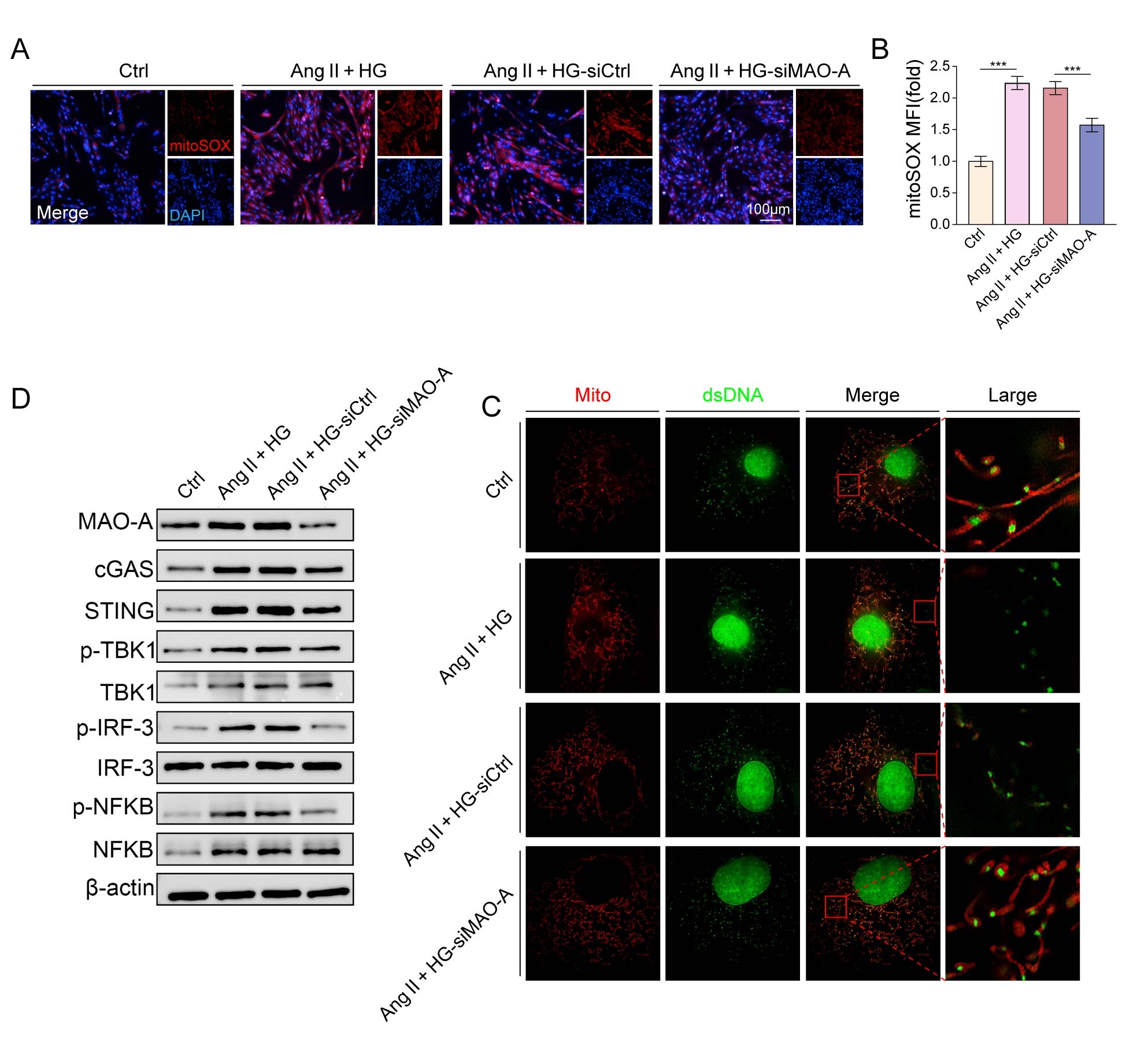
Plasma MAO-A activity, circulating mtDNA, and inflammatory cytokines were measured in HFpEF patients and controls. In mice, HFpEF was induced (high-fat diet+l-NAME, 15 wk) in cardiac-specific MAO-A knockout (Maoa^fl/fl; αMHC-Cre) and control littermates, with additional groups receiving MAO-A inhibitor (clorgyline) or STING inhibitor (H-151). Cardiac function, histology, ROS, mtDNA leakage, cGAS-STING activation, and senescence markers were evaluated. In vitro, H9c2 cardiomyoblasts were treated with angiotensin II+high glucose ± MAO-A siRNA. Mitochondrial ROS, cGAS-STING, senescence markers (SA-β-gal, Cdkn2a/Cdkn1a), and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) secretion were assessed. Conditioned media were used to evaluate fibroblast activation, macrophage polarization, and endothelial inflammation.
Results:
HFpEF patients had increased MAO-A activity and circulating mtDNA correlating with worse diastolic dysfunction. In mice, cardiomyocyte-specific MAO-A deletion or MAO-A/STING inhibition reduced ROS, mtDNA leakage, cGAS-STING activation, senescence markers, and improved diastolic function . In vitro, dual stimulation activated cGAS-STING, induced senescence and SASP secretion, effects attenuated by MAO-A silencing. Conditioned media from senescent H9c2 cells significantly induced cardiac fibroblast activation, as evidenced by increased α-smooth muscle actin; promoted macrophage M1 polarization, indicated by elevated inducible nitric oxide synthase; and triggered an endothelial inflammatory phenotype, characterized by higher vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression together with enhanced monocyte adhesion. These effects were partially reversed when MAO-A was silenced in the donor H9c2 cells.
Conclusions:
MAO-A promotes ROS-dependent cardiomyocyte senescence and diastolic dysfunction in HFpEF via cGAS-STING signaling. Targeting this axis may offer therapeutic benefit in HFpEF.
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) involves myocardial aging, inflammation, and diastolic dysfunction. Monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A), a mitochondrial enzyme generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), may contribute to cardiac injury, but its role in HFpEF-associated cardiomyocyte senescence is unclear.
Hypothesis:
Cardiac MAO-A promotes cardiomyocyte senescence via ROS-induced mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) release and cGAS-STING signaling, exacerbating HFpEF.
Methods:
Plasma MAO-A activity, circulating mtDNA, and inflammatory cytokines were measured in HFpEF patients and controls. In mice, HFpEF was induced (high-fat diet+l-NAME, 15 wk) in cardiac-specific MAO-A knockout (Maoa^fl/fl; αMHC-Cre) and control littermates, with additional groups receiving MAO-A inhibitor (clorgyline) or STING inhibitor (H-151). Cardiac function, histology, ROS, mtDNA leakage, cGAS-STING activation, and senescence markers were evaluated. In vitro, H9c2 cardiomyoblasts were treated with angiotensin II+high glucose ± MAO-A siRNA. Mitochondrial ROS, cGAS-STING, senescence markers (SA-β-gal, Cdkn2a/Cdkn1a), and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) secretion were assessed. Conditioned media were used to evaluate fibroblast activation, macrophage polarization, and endothelial inflammation.
Results:
HFpEF patients had increased MAO-A activity and circulating mtDNA correlating with worse diastolic dysfunction. In mice, cardiomyocyte-specific MAO-A deletion or MAO-A/STING inhibition reduced ROS, mtDNA leakage, cGAS-STING activation, senescence markers, and improved diastolic function . In vitro, dual stimulation activated cGAS-STING, induced senescence and SASP secretion, effects attenuated by MAO-A silencing. Conditioned media from senescent H9c2 cells significantly induced cardiac fibroblast activation, as evidenced by increased α-smooth muscle actin; promoted macrophage M1 polarization, indicated by elevated inducible nitric oxide synthase; and triggered an endothelial inflammatory phenotype, characterized by higher vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression together with enhanced monocyte adhesion. These effects were partially reversed when MAO-A was silenced in the donor H9c2 cells.
Conclusions:
MAO-A promotes ROS-dependent cardiomyocyte senescence and diastolic dysfunction in HFpEF via cGAS-STING signaling. Targeting this axis may offer therapeutic benefit in HFpEF.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal Alters Alternative Polyadenylation to Regulate mRNA Isoform Diversity in the Transition from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts to Myofibroblasts
Natarajan Kartiga, Neupane Rahul, Yalamanchili Hari Krishna, Palaniyandi Suresh, Wagner Eric, Guha Ashrith, Amirthalingam Thandavarayan Rajarajan
Aberrant Trans- and De- Nitrosylation Underpins Nitrosative Stress in Cardiometabolic HFpEFLi Zhen, Borch Jensen Martin, Vondriska Thomas, Lefer David, Gehred Natalie, Gromova Tatiana, Lapenna Kyle, Sharp Thomas, Chen Jingshu, Shambhu Smitha, Yu Xiaoman, Goodchild Traci