Final ID: MP399
WAVE-AI: Wearable and Portable Vision-enabled ECG interpretation using AI
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Clinical 12-lead ECGs are used to diagnose a range of conditions, but the diagnostic utility of wearable and portable devices is limited to a limited number of rhythm disorders. These devices capture lead I ECG, which are displayed as a PDF. We present a vision-text transformer – WAVE-AI - capable of generating accurate and comprehensive interpretations from images (e.g., PDFs) of single-lead ECGs recorded on wearable and portable devices.
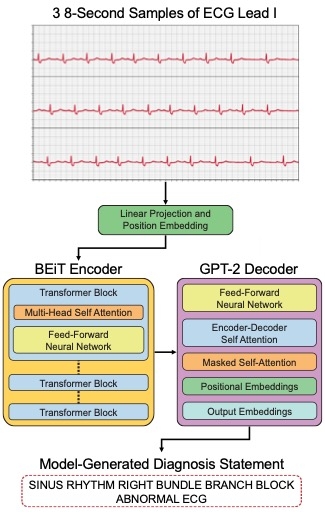
Methods: We fine-tuned an ECG image-text foundation model, ECG-GPT, using 389,482 ECGs and accompanying corresponding diagnosis statements from a large tertiary health system to develop a model that could infer a full ECG report from a printed lead I image. For this, we plotted lead I in multiple image formats to enable the model to generate reports from PDF outputs from various consumer devices (Figure 1). We evaluated model performance in a held-out test set across structured clinical assessment, semantic similarity, and conventional natural language generation metrics.
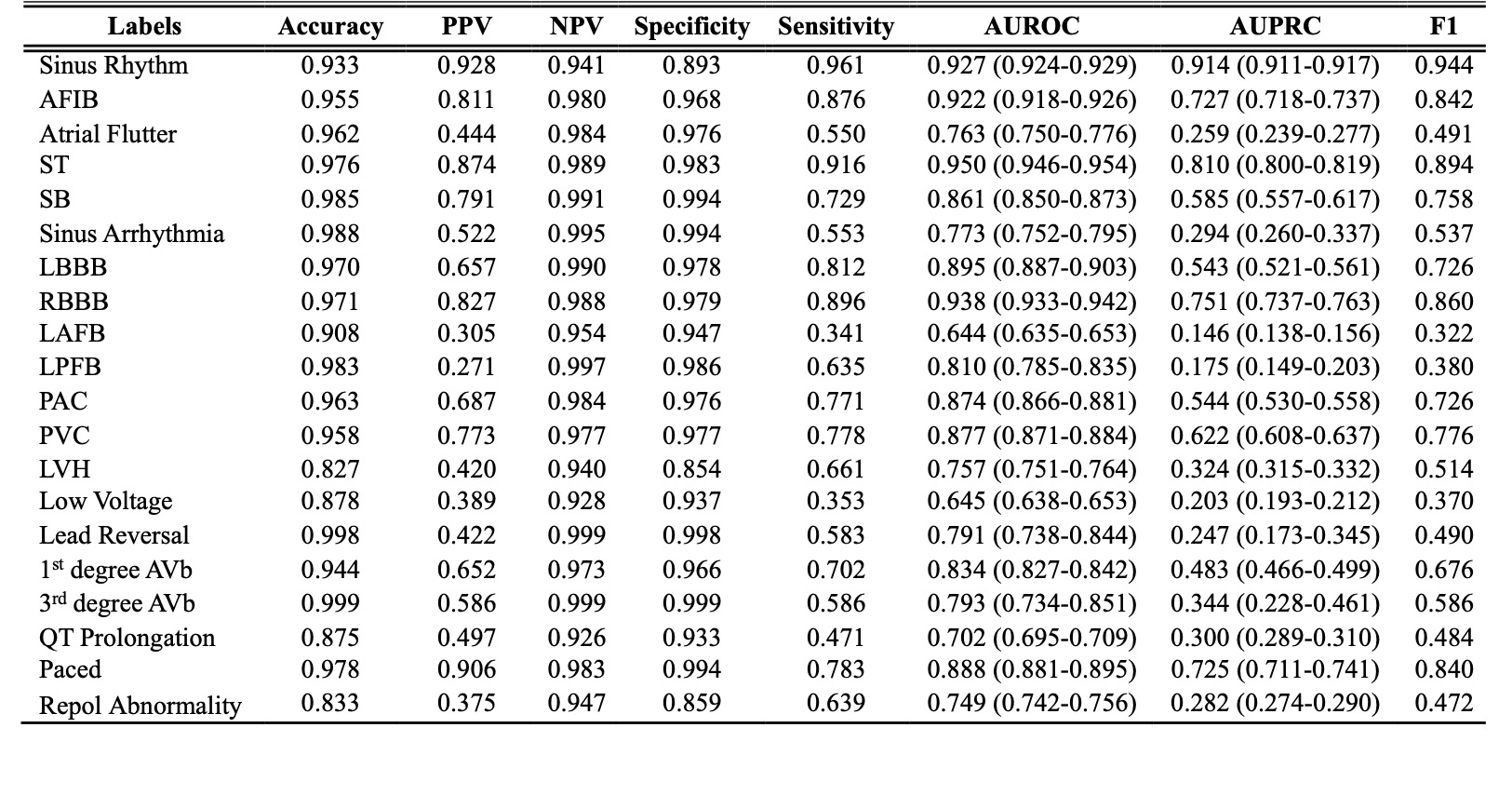
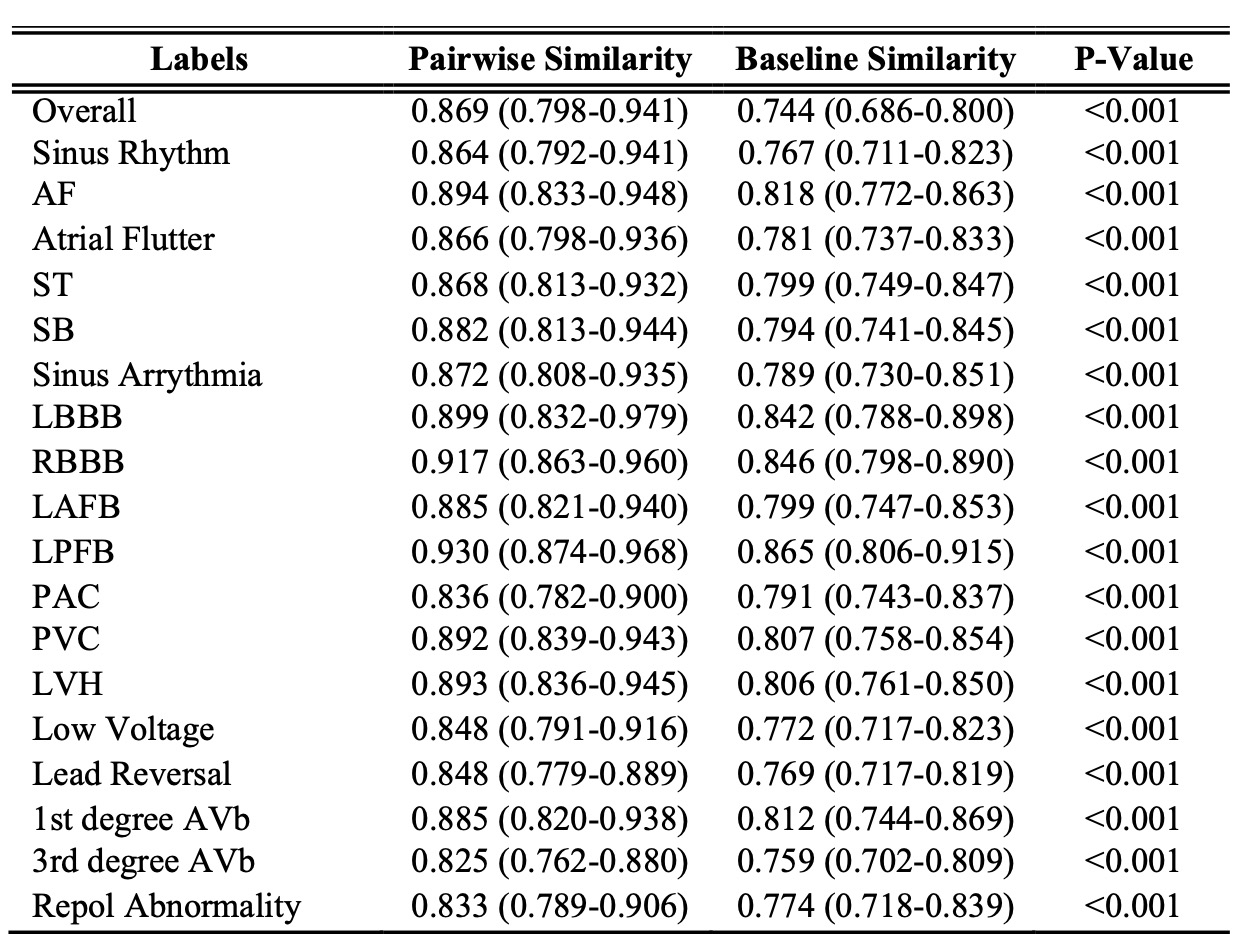
Results: In 43,108 ECGs distinct from development, the model performed well across 20 rhythm and conduction abnormalities extracted from diagnosis statements, with high AUROCs, sensitivities, and specificities (Table 1). The AUROCs for detecting atrial fibrillation, right bundle branch block, and sinus tachycardia were 0.92, 0.94, and 0.95, respectively. The model identified the full context of diagnosis statements, including all associated modifiers and conditions, with a median pairwise similarity of 0.87 (IQR 0.80-0.94), significantly greater than the similarity of 0.74 (IQR 0.69-0.80, p < 0.001) between two randomly selected statements (Table 2). The model also performed well across conventional metrics, with ROUGE-L and BLEU-1 scores of 0.576 and 0.472, respectively.
Conclusions: WAVE-AI is a vision encoder-decoder model capable of generating ECG reports from single-lead ECG images. This approach represents an automated and accessible strategy for generating expert-level complete ECG reporting on lead I ECGs that can be acquired from wearable and portable devices.
Methods: We fine-tuned an ECG image-text foundation model, ECG-GPT, using 389,482 ECGs and accompanying corresponding diagnosis statements from a large tertiary health system to develop a model that could infer a full ECG report from a printed lead I image. For this, we plotted lead I in multiple image formats to enable the model to generate reports from PDF outputs from various consumer devices (Figure 1). We evaluated model performance in a held-out test set across structured clinical assessment, semantic similarity, and conventional natural language generation metrics.
Results: In 43,108 ECGs distinct from development, the model performed well across 20 rhythm and conduction abnormalities extracted from diagnosis statements, with high AUROCs, sensitivities, and specificities (Table 1). The AUROCs for detecting atrial fibrillation, right bundle branch block, and sinus tachycardia were 0.92, 0.94, and 0.95, respectively. The model identified the full context of diagnosis statements, including all associated modifiers and conditions, with a median pairwise similarity of 0.87 (IQR 0.80-0.94), significantly greater than the similarity of 0.74 (IQR 0.69-0.80, p < 0.001) between two randomly selected statements (Table 2). The model also performed well across conventional metrics, with ROUGE-L and BLEU-1 scores of 0.576 and 0.472, respectively.
Conclusions: WAVE-AI is a vision encoder-decoder model capable of generating ECG reports from single-lead ECG images. This approach represents an automated and accessible strategy for generating expert-level complete ECG reporting on lead I ECGs that can be acquired from wearable and portable devices.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial Light at Night and Asleep Blood Pressure in Black Adults
Gloston Gabrielle, Thomas Stephen
A ChatGLM-based stroke diagnosis and prediction toolSong Xiaowei, Wang Jiayi, Ma Weizhi, Wu Jian, Wang Yueming, Gao Ceshu, Wei Chenming, Pi Jingtao