Final ID: MDP1445
Cardiac Arginination Activates RIP3/CAMKII/MLKL Signaling RALBP1 Signal for ICIs-associated Myocarditis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: ICIs-induced cardiotoxicity, particularly myocarditis, poses a significant risk. This study aims to elucidate evidence of direct damage to cardiomyocytes by ICIs and explore potential molecular mechanisms for preventing ICIAM.
Methods: Non-targeted metabolomics examined differential metabolites changes in ICIAM patients and mice. Mass spectrometry identified substrates and modification sites of the enzyme acting on aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARSs). Specific acylation modification site antibody for RALBP1 were customized. The levels of endogenous and exogenous arginine acylation-modified RALBP1 were validated in cells. Immunofluorescence staining was performed to verify the degree of acylation modification. RALBP1 knockout were generated to investigate the impact of RALBP1 on cardiac function and related signaling pathways. RALBP1 deacylation modification was verified by SIRT3 knock out. RALBP1 inhibitor RBC8 validated the therapeutic effects of arginylation modification on ICIAM mice. Finally, the effect of acylation modification on RALBP1 399th lysine spot mutation (K399R) and demodification (K399A).
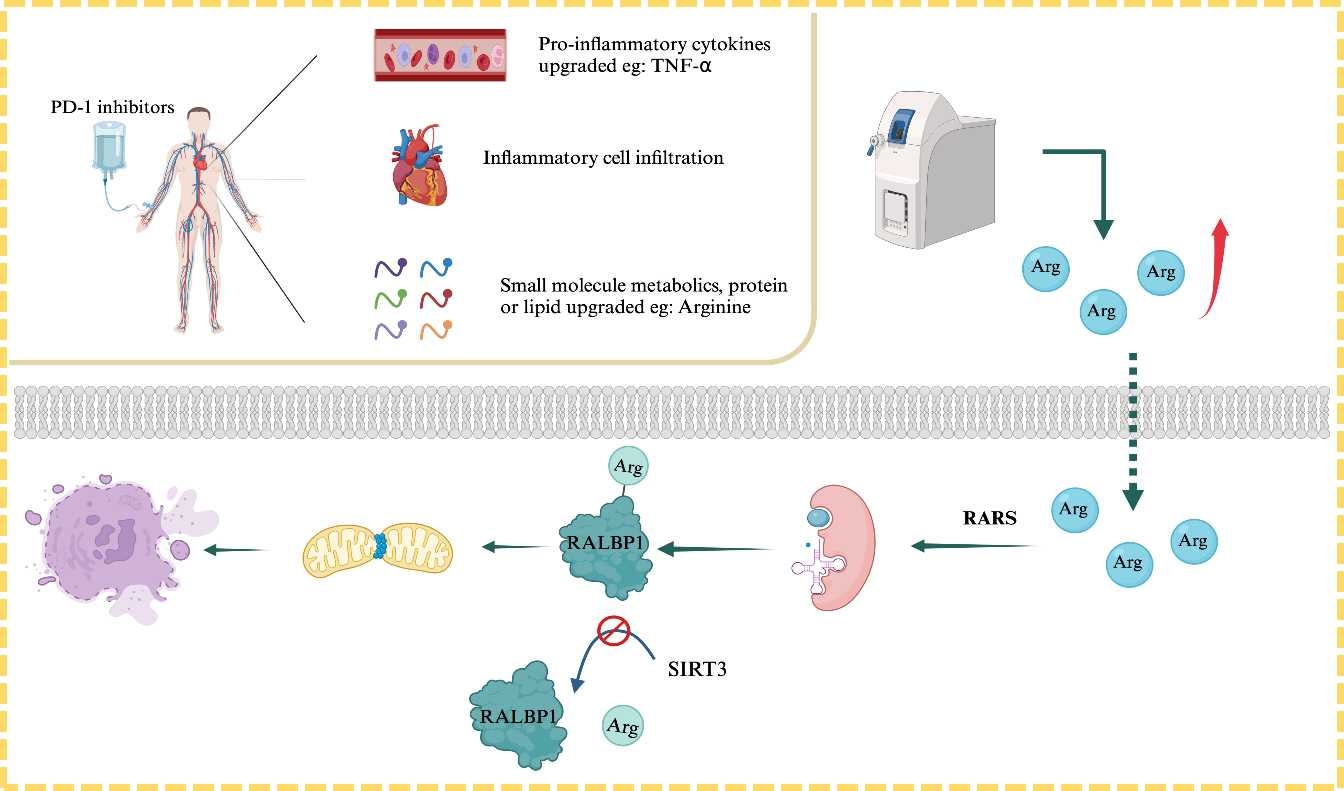
Results: ICIs could induce necroptosis in cadiomyocytes through MAMs-CAMKIIδ pathways. Non-targeted metabolomics indicated arginine-related metabolism might be significant in mice and human. Meanwhile, ARSs for arginine could bind to downstream substrate RALBP1 and catalyze arginylation, which was significantly increased in ICIAM. RALBP1 knockout significantly improved cardiac function, reduced arginylation reaction, inhibition of MAM-CAMKIIδ pathway activation in ICIAM mice. SIRT3 could bind to RALBP1 to inhibit acylation reaction. Necroptosis was inhibited after arginine deacetylation modification occured. RBC8 could significantly improve mouse cardiac function and suppress necroptosis occurrence. K399A-RALBP1 exhibited a increased cardiac function after deacetylation modification and inhibited necroptosis. Conversely, K399A-RALBP1 exhibited a decreased cardiac function after increased arginylation reaction and activated necroptosis.
Conclusion: Increased serum arginine levels increases the risk of developing myocarditis in cancer patients receiving ICIs therapy by promoting RALBP1 signaling. Inhibiting RALBP1 acylation reaction or RARS activity, suppressing MAMs-CaMKIIδ pathway activation, prevents ICIAM occurrence, highlighting the potential role of nutritional and drug interventions as a novel strategy for prevention and treatment of ICIAM.
Methods: Non-targeted metabolomics examined differential metabolites changes in ICIAM patients and mice. Mass spectrometry identified substrates and modification sites of the enzyme acting on aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARSs). Specific acylation modification site antibody for RALBP1 were customized. The levels of endogenous and exogenous arginine acylation-modified RALBP1 were validated in cells. Immunofluorescence staining was performed to verify the degree of acylation modification. RALBP1 knockout were generated to investigate the impact of RALBP1 on cardiac function and related signaling pathways. RALBP1 deacylation modification was verified by SIRT3 knock out. RALBP1 inhibitor RBC8 validated the therapeutic effects of arginylation modification on ICIAM mice. Finally, the effect of acylation modification on RALBP1 399th lysine spot mutation (K399R) and demodification (K399A).
Results: ICIs could induce necroptosis in cadiomyocytes through MAMs-CAMKIIδ pathways. Non-targeted metabolomics indicated arginine-related metabolism might be significant in mice and human. Meanwhile, ARSs for arginine could bind to downstream substrate RALBP1 and catalyze arginylation, which was significantly increased in ICIAM. RALBP1 knockout significantly improved cardiac function, reduced arginylation reaction, inhibition of MAM-CAMKIIδ pathway activation in ICIAM mice. SIRT3 could bind to RALBP1 to inhibit acylation reaction. Necroptosis was inhibited after arginine deacetylation modification occured. RBC8 could significantly improve mouse cardiac function and suppress necroptosis occurrence. K399A-RALBP1 exhibited a increased cardiac function after deacetylation modification and inhibited necroptosis. Conversely, K399A-RALBP1 exhibited a decreased cardiac function after increased arginylation reaction and activated necroptosis.
Conclusion: Increased serum arginine levels increases the risk of developing myocarditis in cancer patients receiving ICIs therapy by promoting RALBP1 signaling. Inhibiting RALBP1 acylation reaction or RARS activity, suppressing MAMs-CaMKIIδ pathway activation, prevents ICIAM occurrence, highlighting the potential role of nutritional and drug interventions as a novel strategy for prevention and treatment of ICIAM.
More abstracts on this topic:
Loss of TRAF2 Signaling Mediates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Doxorubicin-Cardiomyopathy
Kirshenbaum Lorrie, Dhingra Rimpy, Rabinovich-nikitin Inna, Gang Hongying, Margulets Victoria, Diwan Abhinav, Javaheri Ali
90 days readmission rates, predictors, and causes of readmission in heart failure patients with history of irradiation: nationwide retrospective analysisTeaima Taha, Quevedo Ramirez Andres, Jha Vivek, Ibarra Joshua, Soon-shiong Raquel, Gomez Valencia Javier