Final ID: Sa3081
Spatial Multi-omics Profiling of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is characterized by left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction. Coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMVD) occurs in most HCM patients without epicardial stenosis, potentially causing ischemia, fibrosis, and adverse outcomes. While imaging shows reduced perfusion reserve and arteriolar remodeling, the cellular mechanisms remain unclear. We applied spatial multi-omics in an HCM mouse model to identify key cellular subpopulations and regulatory networks underlying CMVD.
Methods: Coronary microvascular function was evaluated in Myh6R404Q/WT mice. Coronary flow reserve (CFR) was measured via Doppler blood flow. Myocardial microvascular density was quantitatively assessed using heart tissue clearing. Myocardial samples were analyzed by single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) and Stereo-seq spatial transcriptomics.
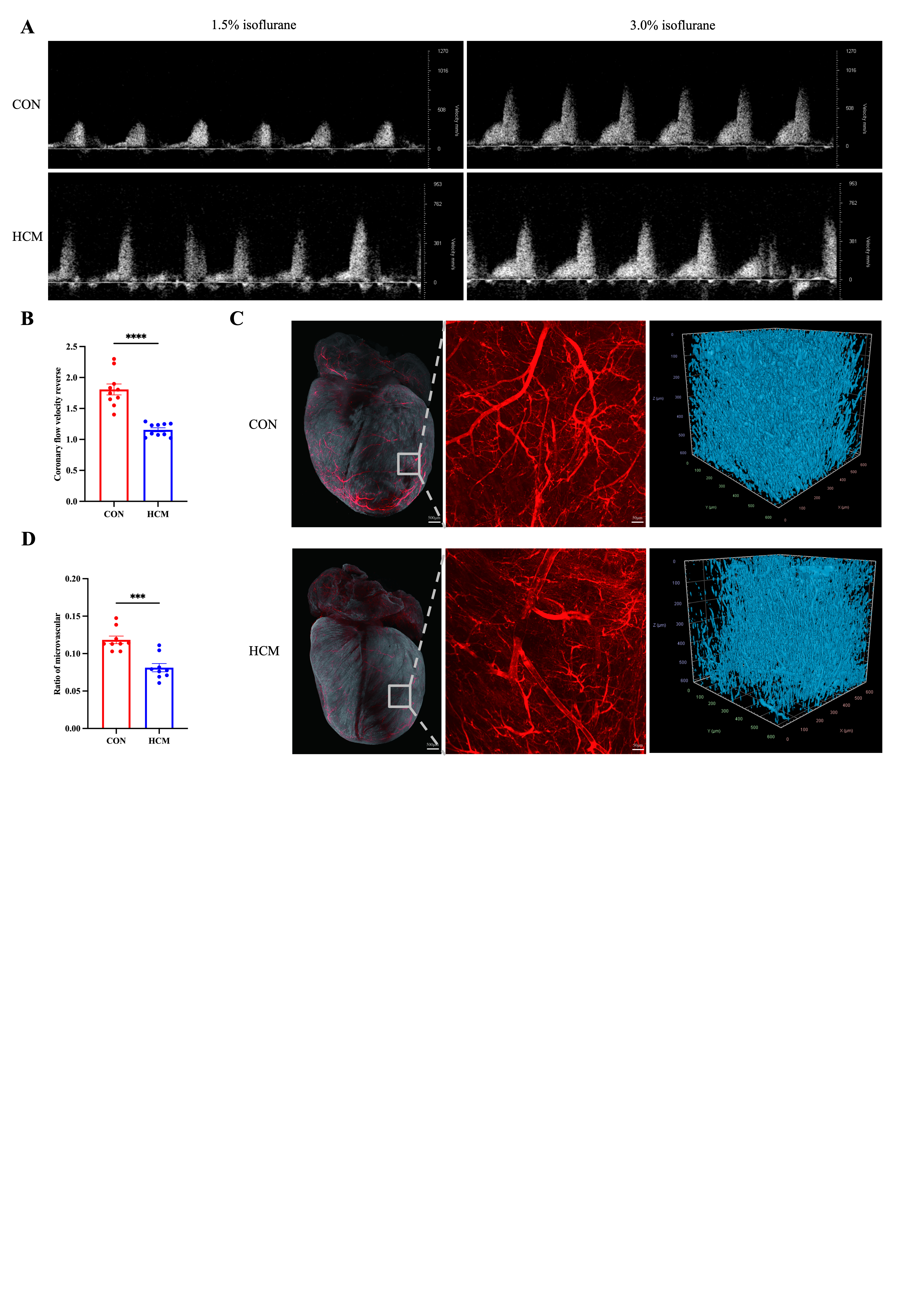
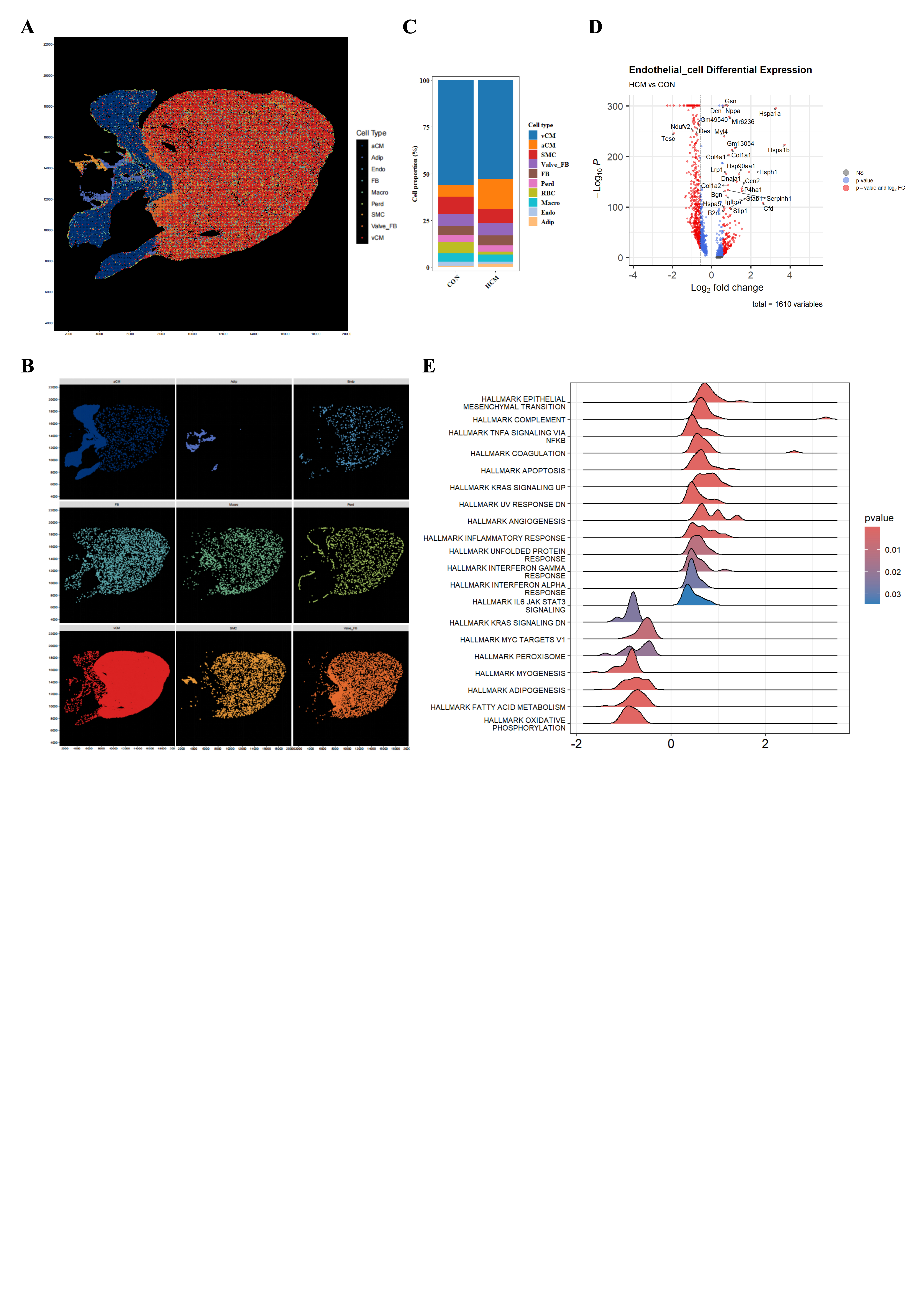
Results: Echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance results showed that Myh6R404Q/WT mice had significant myocardial hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction. Meanwhile, we measured the coronary blood flow velocity under resting and drug-loaded conditions based on Doppler blood flow and calculated the CFR. It was found that the CFR in Myh6R404Q/WT mice was significantly decreased compared with that in the control group (Figure 1A-B). In addition, we quantitatively evaluated the myocardial microvascular density by combining heart tissue clearing and machine learning. The results showed that the microvascular density in Myh6R404Q/WT mice was significantly lower than that in the control group (Figure 1C-D). Stereo-seq analysis (50x50 DNB bins/cell bins) revealed significantly reduced endothelial cell proportion, confirming severe CMVD. Atrial myocyte proportion increased, likely due to compensatory atrial dilation from ventricular dysfunction (Figure 2A-C). snRNA-seq showed 1610 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in endothelial cells (HCM vs. CON; Figure 2D). GSEA indicated DEG enrichment in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, NF-κB signaling, apoptosis, and angiogenesis (Figure 2E), suggesting pathway involvement in HCM-related CMVD.
Conclusions: In summary, our experimental results verified the presence of severe CMVD in Myh6R404Q/WT mice. snRNA-seq and Stereo-seq preliminarily revealed potential regulatory mechanisms of HCM-related CMVD. Future work will deeply analyze multi-omics data to screen molecular targets and perform causal verification in HCM heart organoids.
Methods: Coronary microvascular function was evaluated in Myh6R404Q/WT mice. Coronary flow reserve (CFR) was measured via Doppler blood flow. Myocardial microvascular density was quantitatively assessed using heart tissue clearing. Myocardial samples were analyzed by single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) and Stereo-seq spatial transcriptomics.
Results: Echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance results showed that Myh6R404Q/WT mice had significant myocardial hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction. Meanwhile, we measured the coronary blood flow velocity under resting and drug-loaded conditions based on Doppler blood flow and calculated the CFR. It was found that the CFR in Myh6R404Q/WT mice was significantly decreased compared with that in the control group (Figure 1A-B). In addition, we quantitatively evaluated the myocardial microvascular density by combining heart tissue clearing and machine learning. The results showed that the microvascular density in Myh6R404Q/WT mice was significantly lower than that in the control group (Figure 1C-D). Stereo-seq analysis (50x50 DNB bins/cell bins) revealed significantly reduced endothelial cell proportion, confirming severe CMVD. Atrial myocyte proportion increased, likely due to compensatory atrial dilation from ventricular dysfunction (Figure 2A-C). snRNA-seq showed 1610 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in endothelial cells (HCM vs. CON; Figure 2D). GSEA indicated DEG enrichment in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, NF-κB signaling, apoptosis, and angiogenesis (Figure 2E), suggesting pathway involvement in HCM-related CMVD.
Conclusions: In summary, our experimental results verified the presence of severe CMVD in Myh6R404Q/WT mice. snRNA-seq and Stereo-seq preliminarily revealed potential regulatory mechanisms of HCM-related CMVD. Future work will deeply analyze multi-omics data to screen molecular targets and perform causal verification in HCM heart organoids.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anti-CD47 therapy induces early macrophage-specific transcriptomic changes associated with the resolution of inflammation in a murine model of atherosclerosis
Klarin Derek, Cheruvu Pavan, Basson Craig, Kaplan Charles, Gao Hua, Signore Pierre, Jeyaseelan Jey, Paavola Kevin, Cheung Eric, Yun Rui, Zhang Meng, Leeper Nicholas
Age Associated T cells (TAA cells) expressing Granzyme k are novel cell types in Atherosclerotic plaques.Patil Mallikarjun, Tyrrell Daniel, Ali Md Akkas, Siam Md Hasanul Banna, Brazell James